Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Primitive gut formation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
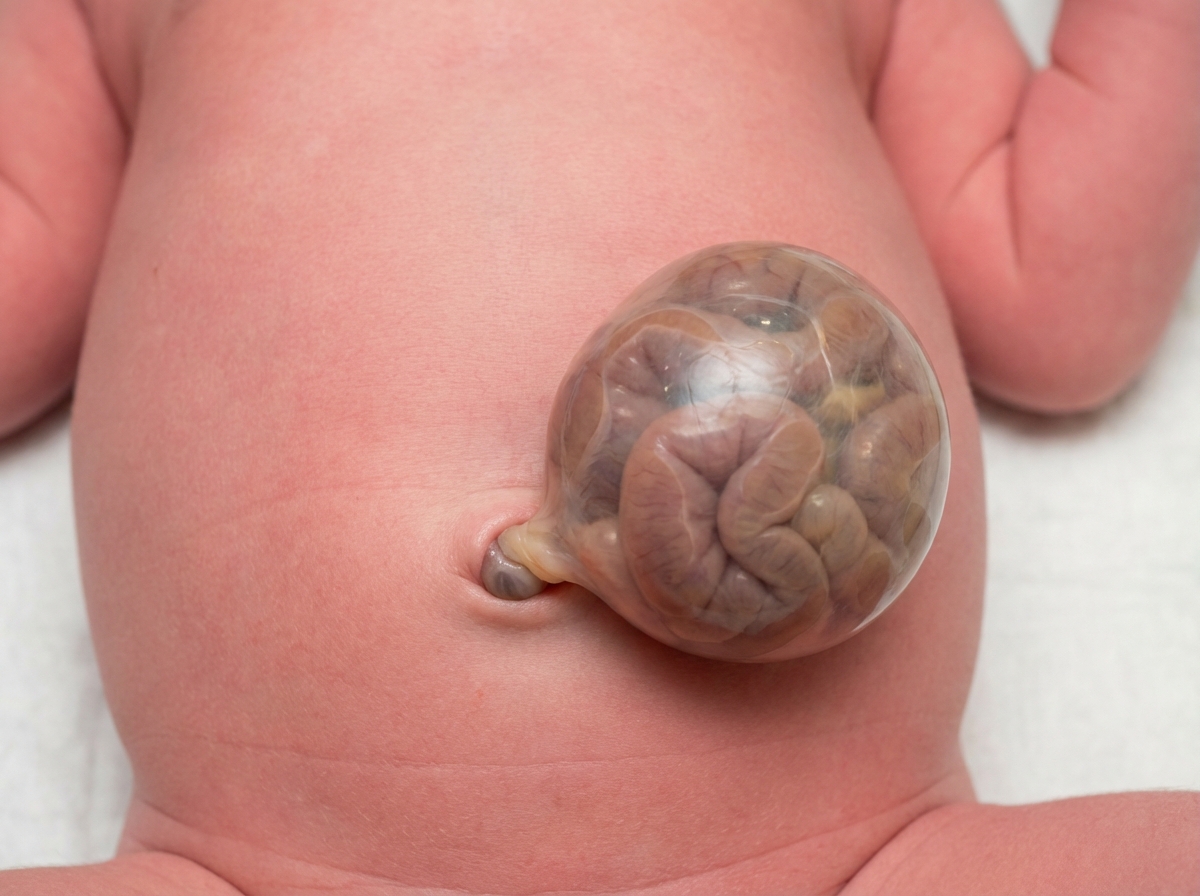
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department in active labor. She has had no prenatal care and is unsure of the gestational age. Labor progresses rapidly and spontaneous vaginal delivery of a baby boy occurs 3 hours after presentation. On initial exam, the child is 1.9 kg (4.2 lb) with a small head and jaw. A sac-like structure containing intestine, as can be seen in the picture, protrudes from the abdominal wall. What complication is closely associated with this presentation?
- A. Lack of abdominal wall muscles
- B. Dehydration and necrosis of bowel
- C. Duodenal atresia
- D. Twisting of the bowel around itself
- E. Cardiac defect (Correct Answer)
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Cardiac defect***
- The presentation of a **sac-like structure containing intestine protruding from the abdominal wall** (suggesting an **omphalocele**) along with **microcephaly** (small head), **micrognathia** (small jaw), and **low birth weight** are classic features of **Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)** or **Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)**.
- These chromosomal abnormalities are strongly associated with various significant anomalies, including severe **cardiac defects** (e.g., ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defects), which occur in **>80% of cases**.
- **Omphalocele** itself is associated with cardiac anomalies in approximately **30-50% of cases**, making cardiac defects the most closely associated complication.
*Lack of abdominal wall muscles*
- This description is more indicative of **prune belly syndrome (Eagle-Barrett syndrome)**, characterized by absence or deficiency of abdominal wall musculature.
- With **gastroschisis**, there is also an abdominal wall defect, but the defect is typically lateral to the umbilicus and there is no protective sac covering the bowel.
*Dehydration and necrosis of bowel*
- This complication is more characteristic of **gastroschisis** due to the direct exposure of the unprotected bowel to amniotic fluid, leading to inflammation, thickening, and potential vascular compromise.
- In an **omphalocele**, the bowel is protected by a sac (containing peritoneum and amnion), significantly reducing the immediate risk of dehydration and necrosis unless the sac ruptures.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**, characterized by a "double bubble" sign on imaging.
- While omphalocele can occasionally occur with Trisomy 21, the constellation of findings in this case (microcephaly, micrognathia, low birth weight) is more consistent with Trisomy 13 or 18 rather than Trisomy 21.
*Twisting of the bowel around itself*
- **Volvulus** refers to the twisting of a loop of intestine around its mesentery, which can lead to bowel obstruction and ischemia.
- While volvulus can occur with intestinal malrotation (which may be present with omphalocele), it is not the most closely associated **congenital** complication of the chromosomal syndrome suggested by this clinical presentation.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 2: A 34-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 2-hour history of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting that began an hour after she finished lunch. Examination shows abdominal guarding and rigidity; bowel sounds are reduced. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows the dorsal pancreatic duct draining into the minor papilla and a separate smaller duct draining into the major papilla. The spleen is located anterior to the left kidney. A disruption of which of the following embryological processes is the most likely cause of this patient's imaging findings?
- A. Proliferation of mesenchyme in the dorsal mesentery
- B. Differentiation of the proximal hepatic diverticulum
- C. Fusion of the pancreatic buds (Correct Answer)
- D. Rotation of the midgut
- E. Rotation of the dorsal mesogastrium
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Fusion of the pancreatic buds***
- The imaging findings describe **pancreas divisum**, a congenital anomaly where the **dorsal and ventral pancreatic buds fail to fuse** completely.
- This leads to the dorsal pancreatic duct (containing most of the gland volume) draining through the **minor papilla**, which is functionally insufficient and can cause recurrent pancreatitis as seen in this patient with signs of peritonitis.
*Proliferation of mesenchyme in the dorsal mesentery*
- This process is primarily associated with the development of the **spleen**, which is derived from mesenchymal cells in the dorsal mesogastrium.
- While the spleen's position is mentioned, its development or abnormal position is not the cause of the pancreatic ductal anomaly described.
*Differentiation of the proximal hepatic diverticulum*
- The **hepatic diverticulum** gives rise to the liver, gallbladder, and biliary tree.
- Abnormalities in this process would lead to issues with these organs, not with the pancreatic ductal system.
*Rotation of the dorsal mesogastrium*
- The **dorsal mesogastrium** rotates during embryological development and gives rise to structures including the spleen and the greater omentum.
- While abnormal rotation could explain splenic malposition, it does not directly explain the pancreatic ductal anomaly (pancreas divisum) described in the imaging.
*Rotation of the midgut*
- The **midgut rotation** is a complex embryological process involving the looping and rotation of the intestines around the superior mesenteric artery.
- Errors in this process can lead to malrotation, volvulus, or intestinal atresia, but not pancreatic ductal anomalies.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 3: A 75-year-old man presents to the clinic for chronic fatigue of 3 months duration. Past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, both of which are controlled with medications, as well as constipation. He denies any fever, weight loss, pain, or focal neurologic deficits. A complete blood count reveals microcytic anemia, and a stool guaiac test is positive for blood. He is subsequently evaluated with a colonoscopy. The physician notes some “small pouches” in the colon despite poor visualization due to inadequate bowel prep. What is the blood vessel that supplies the area with the above findings?
- A. Ileocolic artery
- B. Superior mesenteric artery
- C. Inferior mesenteric artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Middle colic artery
- E. Right colic artery
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Inferior mesenteric artery***
- The patient's **microcytic anemia** and **positive stool guaiac test** indicate chronic gastrointestinal blood loss, highly suggestive of **diverticulosis** presenting as "small pouches" in the colon.
- Diverticulosis commonly affects the **descending colon** and **sigmoid colon**, which are primarily supplied by branches of the **inferior mesenteric artery**.
*Ileocolic artery*
- The ileocolic artery is a branch of the **superior mesenteric artery** and supplies the **ileum**, **cecum**, and **ascending colon**.
- Diverticula are less commonly found in these regions compared to the left colon.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The superior mesenteric artery supplies the **midgut derivatives**, including the **small intestine** and the **right half of the large intestine** (up to the distal transverse colon).
- While it supplies a large portion of the GI tract, the typical location of diverticulosis (descending and sigmoid colon) is outside its primary distribution.
*Middle colic artery*
- The middle colic artery is a branch of the **superior mesenteric artery** and supplies the **transverse colon**.
- While diverticula can occur in the transverse colon, it is not the most common location, and the inferior mesenteric artery supplies the areas most frequently affected.
*Right colic artery*
- The right colic artery is a branch of the **superior mesenteric artery** and supplies the **ascending colon**.
- Diverticula are less frequently found in the ascending colon compared to the descending and sigmoid colon.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old gentleman passes away after a car accident. On routine autopsy it is incidentally noted that he has both a ventral and dorsal pancreatic duct. This incidental finding observed by the pathologist is generated due to failure of which of the following embryological processes?
- A. Apoptosis
- B. Stem cell differentiation
- C. Notochord signaling
- D. Neural crest cell migration
- E. Fusion (Correct Answer)
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Fusion***
- The pancreas develops from a **ventral and a dorsal bud** that typically **fuse** during development.
- Failure of these two pancreatic buds (and their associated ducts) to completely fuse can result in **pancreas divisum**, where two separate ductal systems persist, corresponding to the dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts.
*Apoptosis*
- **Apoptosis** (programmed cell death) is crucial for the removal of unwanted cells and sculpting tissues during embryogenesis, such as the formation of digits or the regression of certain structures.
- It does not directly explain the persistence of two separate pancreatic ducts due to non-fusion of developmental buds.
*Stem cell differentiation*
- **Stem cell differentiation** is the process by which less specialized stem cells become more specialized cell types, which is fundamental to organ development and tissue formation.
- While essential for pancreatic development, it doesn't specifically account for the anatomical anomaly of two persistent ducts.
*Notochord signaling*
- **Notochord signaling** is vital for inducing the formation of the neural tube and defining the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo, as well as influencing the development of other nearby structures.
- This process is not directly related to the fusion of pancreatic buds, which occurs later and is influenced by interactions between mesenchymal and endodermal tissues.
*Neural crest cell migration*
- **Neural crest cells** are multipotent cells that migrate extensively throughout the embryo to form a wide variety of tissues, including parts of the peripheral nervous system, melanocytes, and bone/cartilage of the face and skull.
- Their migratory pathways and derivatives are not directly involved in the development and fusion of the pancreatic ductal system.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 5: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother for evaluation of severe abdominal pain that began one hour ago. On examination, the patient is afebrile and has diffuse rebound tenderness with acute epigastric pain. A stool guaiac test is positive. A small bowel perforation is suspected. What is the embryologic structure that is the underlying cause of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Fibrous cord remnant
- B. Anal membrane
- C. Vermiform appendix
- D. Cloaca
- E. Vitelline duct (Correct Answer)
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Vitelline duct***
- The symptoms of **severe abdominal pain**, rebound tenderness, epigastric pain, and **positive stool guaiac** (indicating bleeding) in a 2-year-old suggest a bleeding **Meckel's diverticulum**, which is a remnant of the **vitelline duct**.
- **Meckel's diverticulum** is the most common congenital anomaly of the GI tract, often containing **ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue** that can lead to ulceration, bleeding, or perforation.
*Fibrous cord remnant*
- While a fibrous cord remnant can be associated with the **vitelline duct**, it typically presents with **intestinal obstruction (volvulus or intussusception)** rather than perforation and bleeding from ectopic mucosa.
- A fibrous cord is a potential complication of a persistent **vitelline duct**, but it is not the underlying embryologic structure responsible for ectopic tissue or bleeding.
*Anal membrane*
- The **anal membrane** is involved in the development of the **anus and rectum**.
- Persistence of the **anal membrane** would lead to **anal atresia** or stenosis, causing symptoms of difficult defecation or obstruction, not abdominal pain and perforation like in this case.
*Vermiform appendix*
- The **vermiform appendix** is a lymphoid organ arising from the **cecum**.
- While **appendicitis** can cause severe abdominal pain and perforation, a positive stool guaiac and presentation with ectopic gastric tissue leading to ulceration are not characteristic features.
*Cloaca*
- The **cloaca** is a common embryologic structure that divides into the **urogenital sinus** and the **anorectal canal**.
- Abnormalities of the **cloaca** typically result in complex **anomalies of the urogenital and GI tracts**, such as persistent cloaca with a single perineal opening, not an isolated perforation with bleeding.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 6: A new imaging modality is being tested to study vitelline duct morphology. A fetus at 20 weeks' gestation is found to have partial obliteration of this duct. Which of the following is the most likely sequela of this condition?
- A. Discharge of urine from the umbilicus
- B. Dilation of the descending colon
- C. Swelling in the genital region
- D. Protrusion of abdominal viscera into the umbilical cord
- E. Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (Correct Answer)
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract***
- Partial obliteration of the vitelline duct can lead to a **Meckel's diverticulum**, which is a remnant of the **yolk sac**.
- Meckel's diverticulum may contain **ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue**, leading to acid secretion, ulceration, and subsequent **gastrointestinal bleeding**.
*Discharge of urine from the umbilicus*
- This symptom is characteristic of a **patent urachus**, which is an abnormal connection between the **bladder and the umbilicus**, not related to the vitelline duct.
- The urachus is a remnant of the **allantois**, a different embryonic structure.
*Dilation of the descending colon*
- **Dilation of the colon** is more commonly associated with conditions like **Hirschsprung's disease** or other causes of intestinal obstruction, which are not directly linked to vitelline duct anomalies.
- Vitelline duct issues primarily affect the **small intestine** (ileum).
*Swelling in the genital region*
- Swelling in the genital region could indicate conditions such as a **hydrocele**, **hernia**, or **ambiguous genitalia**, which are unrelated to vitelline duct pathology.
- Vitelline duct remnants typically present around the **umbilical region or within the small bowel**.
*Protrusion of abdominal viscera into the umbilical cord*
- This description is characteristic of an **omphalocele**, a congenital defect where abdominal contents herniate through the **umbilical ring**, covered by a sac.
- While related to umbilical development, an omphalocele is a distinct condition from vitelline duct anomalies, which involve the vestigial connection between the **midgut and the yolk sac**.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 7: A 10-month-old infant is brought in by his parents because he is vomiting and not passing stool. His parents say he has vomited multiple times over the past couple of hours, but the most recent vomit was green. The patient has no significant past medical history. On physical examination, the patient is irritable and crying. On palpation in the periumbilical region, an abdominal mass is present. Emergency laparotomy is performed, which shows a part of the patient’s intestine folded into the section adjacent to it. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Pyloric stenosis
- B. Hirschsprung’s disease
- C. Duodenal atresia
- D. Intussusception (Correct Answer)
- E. Meckel’s diverticulum
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Intussusception***
- This diagnosis is highly suggested by the classic presentation of a 10-month-old infant with **bilious vomiting**, **abdominal pain** (irritability), and an **abdominal mass** in the periumbilical region, coupled with the surgical finding of one part of the intestine telescoping into an adjacent section.
- The sudden onset of symptoms in an otherwise healthy infant, along with **green vomit** (indicating bile) and an acute abdomen, are hallmark signs of this condition.
*Pyloric stenosis*
- This condition typically presents with **non-bilious projectile vomiting** in infants usually between 3 weeks and 6 months of age, with an **olive-shaped mass** in the epigastrium.
- The patient's **bilious vomiting** and the specific finding of intestinal telescoping rule out pyloric stenosis.
*Hirschsprung’s disease*
- This condition usually presents with **failure to pass meconium** in the neonatal period or chronic constipation and abdominal distension in older infants.
- While it involves the intestine, it is a **motility disorder** due to the absence of ganglion cells, not an anatomical telescoping of bowel.
*Duodenal atresia*
- This is a congenital obstruction of the duodenum, typically diagnosed shortly after birth with **bilious vomiting** and a characteristic "**double bubble**" sign on X-ray.
- It would not involve an abdominal mass or the intussusception described.
*Meckel’s diverticulum*
- This condition is a remnant of the vitelline duct and can present with painless rectal bleeding or, less commonly, intestinal obstruction, **volvulus**, or **intussusception** if it acts as a lead point.
- While it can be a rare cause of intussusception, the question directly describes the pathophysiology of intussusception itself rather than a diverticulum causing it.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 9: A 4-week-old infant presents with progressively worsening jaundice. Laboratory studies show direct hyperbilirubinemia, elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase, and pale stools. Liver biopsy shows bile duct proliferation and portal fibrosis. Intraoperative cholangiogram reveals absence of extrahepatic bile ducts with normal intrahepatic ducts proximally. The gallbladder is present but atretic. Synthesize the embryological timing and pathophysiological mechanism of this postnatal progressive condition.
- A. Failure of recanalization of solid bile duct stage at week 6-7 with progressive inflammation
- B. Defective hepatic diverticulum formation from foregut at week 4 causing ductal absence
- C. Perinatal inflammatory obliterative cholangiopathy affecting extrahepatic ducts after normal formation (Correct Answer)
- D. Abnormal neural crest cell migration affecting bile duct innervation and motility
- E. Congenital cytomegalovirus causing intrauterine ductal destruction at week 12
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Perinatal inflammatory obliterative cholangiopathy affecting extrahepatic ducts after normal formation***
- **Biliary atresia** is currently understood as a progressive, **acquired inflammatory** process that obliterates ducts that were initially formed correctly during embryogenesis.
- The clinical presentation of **progressive jaundice**, **pale (acholic) stools**, and **direct hyperbilirubinemia** appearing after birth supports a perinatal insult rather than an embryonic malformation.
*Failure of recanalization of solid bile duct stage at week 6-7 with progressive inflammation*
- This describes the **"tandem" theory** or failure of the solid stage, which typically results in more severe embryonic-type atresia often associated with other **congenital anomalies** (situs inversus).
- Most cases of biliary atresia do not show a failure of recanalization, as clinical evidence suggests the ducts were functional for a period in utero.
*Defective hepatic diverticulum formation from foregut at week 4 causing ductal absence*
- A defect in the **hepatic diverticulum** would result in total **agenesis** of the biliary system and potentially the liver parenchyma, not a localized postnatal obstruction.
- In this case, the **intrahepatic ducts** are normal and the gallbladder is present, which contradicts a primary defect in early foregut budding.
*Abnormal neural crest cell migration affecting bile duct innervation and motility*
- **Neural crest cell** migration defects are classically associated with **Hirschsprung disease** (affecting the enteric nervous system), not the structural obliteration of bile ducts.
- Biliary atresia involves mechanical **fibrosis and obstruction** of the lumen, rather than a primary disorder of biliary tree motility or innervation.
*Congenital cytomegalovirus causing intrauterine ductal destruction at week 12*
- While some viral triggers (like **Reovirus** or Rotavirus) are suspected in the inflammatory process, **Cytomegalovirus (CMV)** typically causes a neonatal hepatitis rather than isolated extrahepatic ductal obliteration.
- Intrauterine destruction at week 12 would likely present with symptoms immediately at birth, whereas this infant showed **progressive worsening** over 4 weeks.
Primitive gut formation US Medical PG Question 10: A newborn presents with respiratory distress immediately after birth. Chest radiograph shows bowel loops in the left hemithorax with mediastinal shift to the right and hypoplastic left lung. The infant has scaphoid abdomen. During fetal ultrasound at 9 weeks, normal diaphragm development was noted, but at 20 weeks, abdominal contents were seen in the chest. Evaluate the critical developmental period and mechanism of lung hypoplasia.
- A. Failure of pleuroperitoneal membrane closure at week 6 with subsequent lung compression during canalicular phase
- B. Premature return of midgut at week 8 causing diaphragmatic rupture and lung compression
- C. Late diaphragmatic defect at week 20 preventing normal pseudoglandular phase lung development
- D. Defective muscularization of diaphragm after week 12 with gradual herniation and lung hypoplasia (Correct Answer)
- E. Failure of septum transversum formation at week 4 preventing lung bud elongation
Primitive gut formation Explanation: ***Defective muscularization of diaphragm after week 12 with gradual herniation and lung hypoplasia***
- In this specific case, a normal diaphragm at 9 weeks followed by herniation at 20 weeks indicates a **secondary defect** in **muscularization** rather than a primary failure of pleuroperitoneal membrane closure.
- The resulting **herniation of abdominal contents** into the thorax compresses the developing lung, leading to **pulmonary hypoplasia** and the classic **scaphoid abdomen** presentation.
*Failure of pleuroperitoneal membrane closure at week 6 with subsequent lung compression during canalicular phase*
- This describes the **Bochdalek hernia**, but the timeline provided (normal at 9 weeks) contradicts a primary closure failure occurring at **week 6**.
- While it causes lung compression, the most critical damage to **bronchial branching** occurs during the **pseudoglandular phase** (weeks 5-17), not just the canalicular phase.
*Premature return of midgut at week 8 causing diaphragmatic rupture and lung compression*
- The **midgut hernia** normally returns to the abdomen around **week 10**, so a return at week 8 would be premature and does not cause **diaphragmatic rupture**.
- Diaphragmatic defects are developmental failures of specific components (septum transversum, membranes, or muscle), not a result of **mechanical rupture** from gut movement.
*Late diaphragmatic defect at week 20 preventing normal pseudoglandular phase lung development*
- The **pseudoglandular phase** occurs between **weeks 5 and 17**; a defect appearing at week 20 would be too late to disrupt this critical stage of **branching morphogenesis**.
- Most cases of **congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH)** that result in severe hypoplasia involve a defect present prior to the completion of the pseudoglandular stage.
*Failure of septum transversum formation at week 4 preventing lung bud elongation*
- The **septum transversum** primarily forms the **central tendon** of the diaphragm and its failure would present as a much earlier, more catastrophic defect.
- **Lung bud elongation** begins at week 4, but the scenario describes a fetus with normal early development confirmed by **ultrasound at 9 weeks**.
More Primitive gut formation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.