Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Foregut development and derivatives. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
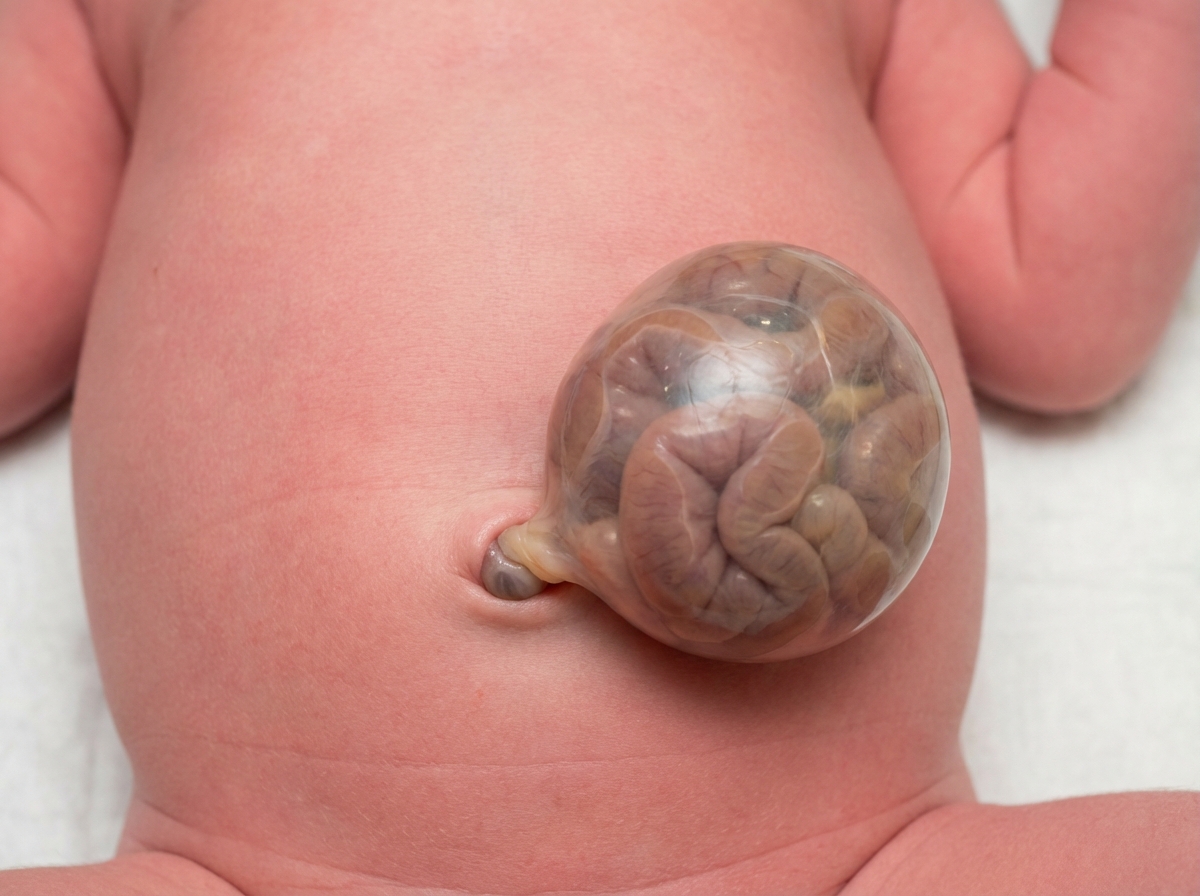
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department in active labor. She has had no prenatal care and is unsure of the gestational age. Labor progresses rapidly and spontaneous vaginal delivery of a baby boy occurs 3 hours after presentation. On initial exam, the child is 1.9 kg (4.2 lb) with a small head and jaw. A sac-like structure containing intestine, as can be seen in the picture, protrudes from the abdominal wall. What complication is closely associated with this presentation?
- A. Lack of abdominal wall muscles
- B. Dehydration and necrosis of bowel
- C. Duodenal atresia
- D. Twisting of the bowel around itself
- E. Cardiac defect (Correct Answer)
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Cardiac defect***
- The presentation of a **sac-like structure containing intestine protruding from the abdominal wall** (suggesting an **omphalocele**) along with **microcephaly** (small head), **micrognathia** (small jaw), and **low birth weight** are classic features of **Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)** or **Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)**.
- These chromosomal abnormalities are strongly associated with various significant anomalies, including severe **cardiac defects** (e.g., ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defects), which occur in **>80% of cases**.
- **Omphalocele** itself is associated with cardiac anomalies in approximately **30-50% of cases**, making cardiac defects the most closely associated complication.
*Lack of abdominal wall muscles*
- This description is more indicative of **prune belly syndrome (Eagle-Barrett syndrome)**, characterized by absence or deficiency of abdominal wall musculature.
- With **gastroschisis**, there is also an abdominal wall defect, but the defect is typically lateral to the umbilicus and there is no protective sac covering the bowel.
*Dehydration and necrosis of bowel*
- This complication is more characteristic of **gastroschisis** due to the direct exposure of the unprotected bowel to amniotic fluid, leading to inflammation, thickening, and potential vascular compromise.
- In an **omphalocele**, the bowel is protected by a sac (containing peritoneum and amnion), significantly reducing the immediate risk of dehydration and necrosis unless the sac ruptures.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**, characterized by a "double bubble" sign on imaging.
- While omphalocele can occasionally occur with Trisomy 21, the constellation of findings in this case (microcephaly, micrognathia, low birth weight) is more consistent with Trisomy 13 or 18 rather than Trisomy 21.
*Twisting of the bowel around itself*
- **Volvulus** refers to the twisting of a loop of intestine around its mesentery, which can lead to bowel obstruction and ischemia.
- While volvulus can occur with intestinal malrotation (which may be present with omphalocele), it is not the most closely associated **congenital** complication of the chromosomal syndrome suggested by this clinical presentation.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 2: During a surgical procedure to repair an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the surgeon must be careful to avoid injury to which of the following arterial structures that originates near the level of the renal vessels?
- A. Left renal artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Celiac trunk
- C. Right renal artery
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Left renal artery***
- The **left renal artery** arises from the aorta usually just below the superior mesenteric artery, making it susceptible to injury during an **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair** if the aneurysm extends proximally.
- Its proximity to the typical location of AAA, often near or involving the **infrarenal aorta**, necessitates careful identification and protection during clamping or graft placement.
*Celiac trunk*
- The **celiac trunk** originates higher up from the aorta, typically at the level of **T12-L1 vertebrae**, well above the common infrarenal AAA repair site.
- While important, it is generally less directly threatened during a typical infrarenal AAA repair compared to arteries immediately adjacent to or within the aneurysm sac.
*Right renal artery*
- The **right renal artery** also originates from the aorta near the level of the renal veins, but it is typically located more posteriorly and usually passes behind the inferior vena cava.
- Although it can be at risk, the left renal artery's course is often more anterior and directly in the field of dissection for the **aortic neck** during AAA repair.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery (SMA)** originates from the aorta proximal to the renal arteries, typically around the L1 vertebral level.
- While crucial, its origin is usually cephalad to the infrarenal aneurysm neck, making it generally less prone to direct injury during infrarenal AAA repair, though flow must be monitored.
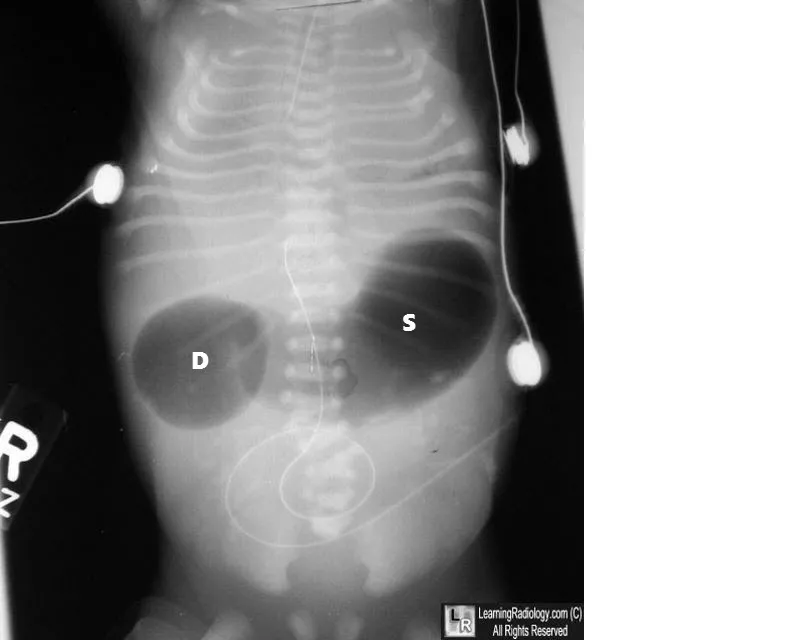
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 3: A 4-week-old infant is brought to the emergency department by his parents with violent vomiting. It started about 3 days ago and has slowly gotten worse. He vomits after most feedings but seems to keep some formula down. His mother notes that he is eager to feed between episodes and seems to be putting on weight. Other than an uncomplicated course of chlamydia conjunctivitis, the infant has been healthy. He was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. The physical exam is significant for a palpable mass in the right upper quadrant. What is the first-line confirmatory diagnostic test and associated finding?
- A. Abdominal ultrasound; elongated pyloric channel and muscle hypertrophy (Correct Answer)
- B. Barium upper GI series; GE junction and portion of the stomach in thorax
- C. Air enema; filling defect and coil spring sign
- D. Barium upper GI series; bird beak sign and corkscrewing
- E. Abdominal X-ray; ‘double bubble’ sign
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Abdominal ultrasound; elongated pyloric channel and muscle hypertrophy***
- The clinical picture of **projectile vomiting** in a 4-week-old infant, **eagerness to feed** ("hungry vomiter"), and **palpable olive-shaped mass** in the right upper quadrant is classic for **pyloric stenosis**.
- **Abdominal ultrasonography** is the gold standard for diagnosis, revealing an **elongated pyloric channel** (>16mm) and thickened pyloric muscle (>3-4mm).
- Pyloric stenosis typically presents between 3-6 weeks of age with progressive non-bilious vomiting.
*Barium upper GI series; GE junction and portion of the stomach in thorax*
- A **barium upper GI series** showing the **GE junction and stomach in the thorax** would indicate a **hiatal hernia**, which is not consistent with the palpable mass or "hungry vomiter" presentation.
- While hiatal hernias can cause vomiting and reflux, they typically don't present with this specific type of projectile vomiting or a palpable abdominal mass.
*Air enema; filling defect and coil spring sign*
- An **air enema** showing a **filling defect** and **coil spring sign** is characteristic of **intussusception**, which usually presents with sudden onset of **crampy abdominal pain**, **currant jelly stools**, and a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant.
- The clinical presentation does not fit intussusception, which typically occurs in older infants (6-36 months) and has a more acute presentation.
*Barium upper GI series; bird beak sign and corkscrewing*
- A **barium upper GI series** showing a **bird beak sign** and **corkscrewing** is pathognomonic for **midgut volvulus**, a surgical emergency.
- While volvulus can cause bilious vomiting and abdominal distension, the presentation of non-bilious vomiting with a palpable pyloric mass is more typical of pyloric stenosis.
*Abdominal X-ray; 'double bubble' sign*
- An **abdominal X-ray** revealing a **'double bubble' sign** is indicative of **duodenal atresia** or **annular pancreas**, leading to complete duodenal obstruction.
- This condition typically presents with **bilious vomiting** shortly after birth (within first day of life) and does not involve a palpable hypertrophied pylorus.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-year-old male is brought to his pediatrician by his mother because of abdominal pain and blood in the stool. Scintigraphy reveals uptake in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen. Persistence of which of the following structures is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Ureteric bud
- B. Urachus
- C. Paramesonephric duct
- D. Omphalomesenteric duct (Correct Answer)
- E. Allantois
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Omphalomesenteric duct***
- Persistence of the **omphalomesenteric duct** (vitelline duct) can lead to a **Meckel's diverticulum**, which often contains **ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue**.
- This ectopic tissue can cause **ulceration and bleeding**, leading to abdominal pain and **melena** (blood in stool), and will show uptake on a Technetium-99m pertechnetate scan (scintigraphy) for ectopic gastric mucosa.
*Ureteric bud*
- The ureteric bud forms the **ureter, renal pelvis, calyces**, and **collecting ducts** of the kidney.
- Anomalies of the ureteric bud typically present with **urinary tract issues**, such as hydronephrosis or renal agenesis, not abdominal pain and bloody stools from GI bleeding.
*Urachus*
- The urachus is a remnant of the **allantois** connecting the fetal bladder to the umbilicus.
- Persistent urachal remnants can cause urine leakage from the umbilicus, cysts, or infections, but generally not abdominal pain and bloody stools.
*Paramesonephric duct*
- The paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts form the **female reproductive organs** (fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, upper vagina).
- Persistence or anomalies of these ducts are relevant to **gynecological issues** and infertility in females, not the GI symptoms described in a male child.
*Allantois*
- The allantois contributes to the formation of the **urachus** and is involved in early blood formation and bladder development.
- While related to the urachus, its direct persistence or anomalies typically don't cause the specific presentation of abdominal pain and bloody stools due to ectopic gastric mucosa.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 5: A research team is studying certain congenital anomalies of the respiratory tract. The method consists of marking a certain germinal layer with an isotope, following its development stages in chicken embryos, and finally analyzing the specimen. A given specimen of tissue is presented in the exhibit. Which of the following germinal structures most likely gave rise to the epithelial lining of this specimen?
- A. Ectoderm
- B. Neural crest
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Surface ectoderm
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **epithelial lining** of the entire respiratory tract, including the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, is derived from the **endoderm**.
- The **laryngotracheal groove** develops from the ventral wall of the primitive foregut, which is endodermal in origin, further differentiating into the respiratory tree.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** primarily forms the epidermis, hair, nails, and the nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial lining of the respiratory tract.
*Neural crest*
- **Neural crest cells** contribute to a wide variety of structures, including components of the peripheral nervous system, head mesenchyme, and melanocytes.
- They are not involved in forming the epithelial lining of the respiratory system.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** forms the connective tissue, cartilage, and muscle components of the respiratory tract, such as the smooth muscle and cartilage rings of the trachea and bronchi, and the visceral pleura.
- However, it does not form the epithelial lining itself.
*Surface ectoderm*
- **Surface ectoderm** specifically gives rise to the epidermis, hair, nails, and glands of the skin, as well as the oral cavity epithelium.
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial structures of the respiratory tract.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 6: A 3-week-old firstborn baby girl is brought to the pediatric emergency room with projectile vomiting. She started vomiting while feeding 12 hours ago and has been unable to keep anything down since then. After vomiting, she appears well and hungry, attempting to feed again. The vomitus has been non-bloody and non-bilious. The last wet diaper was 10 hours ago. The child was born at 40 weeks gestation to a healthy mother. On examination, the child appears sleepy but has a healthy cry during the exam. The child has dry mucous membranes and delayed capillary refill. There is a palpable olive-shaped epigastric mass on palpation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Failure of neural crest cell migration into the rectum
- B. Telescoping of the small bowel into the large bowel
- C. Hypertrophic muscularis externa (Correct Answer)
- D. Patent tract between the trachea and esophagus
- E. Failure of duodenal lumen recanalization
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Hypertrophic muscularis externa***
- The presented symptoms, including **projectile vomiting** in a 3-week-old, **non-bilious** emesis, post-vomiting **hunger**, and a **palpable olive-shaped mass** in the epigastrium, are classic signs of **pyloric stenosis**. This condition is caused by the **hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter's muscularis externa**.
- Pyloric stenosis commonly presents between **2-8 weeks of age** and leads to an obstruction of gastric outflow, causing the characteristic vomiting and signs of dehydration like **dry mucous membranes** and **delayed capillary refill**.
*Failure of neural crest cell migration into the rectum*
- This describes **Hirschsprung disease**, which typically presents with **constipation**, **abdominal distension**, and a **failure to pass meconium** in the neonatal period.
- While it involves GI obstruction, its symptoms and location of obstruction are distinctly different from the projectile vomiting seen in this case.
*Telescoping of the small bowel into the large bowel*
- This is known as **intussusception**, which usually presents with **intermittent, colicky abdominal pain**, **"currant jelly" stools** (due to blood and mucus), and a sausage-shaped abdominal mass, typically in older infants (3 months to 3 years).
- The type of vomiting (often bilious) and stool characteristics are different from the patient's presentation.
*Patent tract between the trachea and esophagus*
- This describes a **tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF)**, often associated with esophageal atresia. Infants with TEF typically present with **choking, coughing, and cyanosis** during feeds, as well as aspiration, due to misdirection of fluid into the lungs.
- The symptoms are immediate and severe with initial feeds and do not typically involve progressive projectile vomiting after several weeks of life.
*Failure of duodenal lumen recanalization*
- This leads to **duodenal atresia**, which typically presents with **bilious vomiting** within the first 24-48 hours of life, and the classic "double bubble" sign on X-ray.
- The vomiting in this case is **non-bilious** and started later, which rules out duodenal atresia.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 7: A 10-month-old infant is brought in by his parents because he is vomiting and not passing stool. His parents say he has vomited multiple times over the past couple of hours, but the most recent vomit was green. The patient has no significant past medical history. On physical examination, the patient is irritable and crying. On palpation in the periumbilical region, an abdominal mass is present. Emergency laparotomy is performed, which shows a part of the patient’s intestine folded into the section adjacent to it. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Pyloric stenosis
- B. Hirschsprung’s disease
- C. Duodenal atresia
- D. Intussusception (Correct Answer)
- E. Meckel’s diverticulum
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Intussusception***
- This diagnosis is highly suggested by the classic presentation of a 10-month-old infant with **bilious vomiting**, **abdominal pain** (irritability), and an **abdominal mass** in the periumbilical region, coupled with the surgical finding of one part of the intestine telescoping into an adjacent section.
- The sudden onset of symptoms in an otherwise healthy infant, along with **green vomit** (indicating bile) and an acute abdomen, are hallmark signs of this condition.
*Pyloric stenosis*
- This condition typically presents with **non-bilious projectile vomiting** in infants usually between 3 weeks and 6 months of age, with an **olive-shaped mass** in the epigastrium.
- The patient's **bilious vomiting** and the specific finding of intestinal telescoping rule out pyloric stenosis.
*Hirschsprung’s disease*
- This condition usually presents with **failure to pass meconium** in the neonatal period or chronic constipation and abdominal distension in older infants.
- While it involves the intestine, it is a **motility disorder** due to the absence of ganglion cells, not an anatomical telescoping of bowel.
*Duodenal atresia*
- This is a congenital obstruction of the duodenum, typically diagnosed shortly after birth with **bilious vomiting** and a characteristic "**double bubble**" sign on X-ray.
- It would not involve an abdominal mass or the intussusception described.
*Meckel’s diverticulum*
- This condition is a remnant of the vitelline duct and can present with painless rectal bleeding or, less commonly, intestinal obstruction, **volvulus**, or **intussusception** if it acts as a lead point.
- While it can be a rare cause of intussusception, the question directly describes the pathophysiology of intussusception itself rather than a diverticulum causing it.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 9: A newborn boy born vaginally to a healthy 37-year-old G3P1 from a pregnancy complicated by hydramnios fails to pass meconium after 24 hours of life. The vital signs are within normal limits for his age. The abdomen is distended, the anus is patent, and the rectal examination reveals pale mucous with non-pigmented meconium. Based on a barium enema, the boy is diagnosed with sigmoid colonic atresia. Disruption of which structure during fetal development could lead to this anomaly?
- A. Inferior mesenteric artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Superior mesenteric artery
- C. Vitelline duct
- D. Cloaca
- E. Celiac artery
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Inferior mesenteric artery***
- **Sigmoid colonic atresia**, as observed in this case, results from an ischemic event affecting the segment of the bowel supplied by the **inferior mesenteric artery** during fetal development.
- Interruption of blood flow to this region can lead to subsequent **atresia** as the affected part of the intestine necroses and is reabsorbed.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies the midgut structures, including the small intestine and parts of the large intestine up to the transverse colon.
- Disruption of the superior mesenteric artery would typically lead to atresias higher up in the **gastrointestinal tract**, such as jejunal or ileal atresias, not sigmoid colonic atresia.
*Vitelline duct*
- The **vitelline duct** (also known as the omphalomesenteric duct) connects the midgut to the yolk sac during early fetal development.
- Persistent patency or partial obliteration of the vitelline duct can lead to anomalies like **Meckel's diverticulum** or vitelline cysts, which are distinct from colonic atresia.
*Cloaca*
- The **cloaca** is a common cavity for the digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts during early embryonic development.
- Defects in cloacal development lead to complex malformations involving these systems, such as **imperforate anus** or persistent cloaca, rather than isolated colonic atresia with a patent anus.
*Celiac artery*
- The **celiac artery** supplies the foregut structures, including the stomach, duodenum, liver, and spleen.
- Disruption of the celiac artery during fetal development would result in malformations of these upper gastrointestinal organs, not the sigmoid colon.
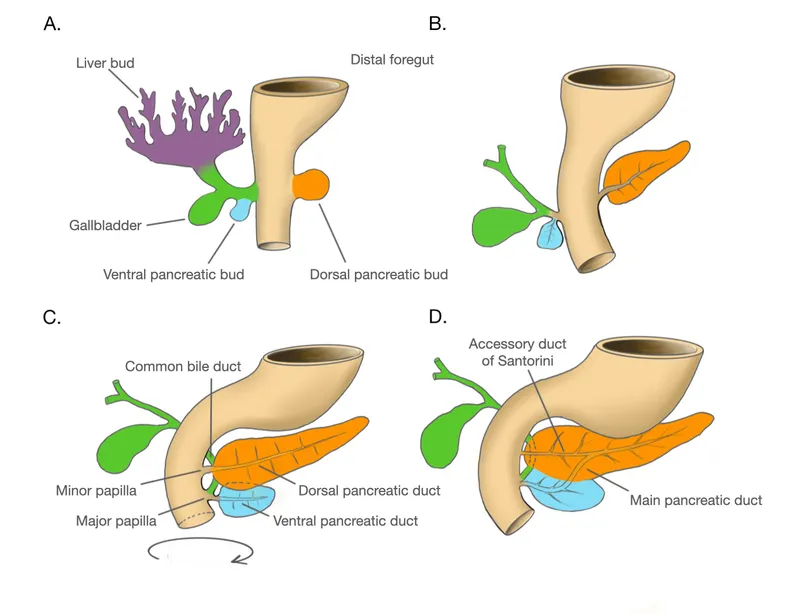
Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG Question 10: A 60-year-old gentleman passes away after a car accident. On routine autopsy it is incidentally noted that he has both a ventral and dorsal pancreatic duct. This incidental finding observed by the pathologist is generated due to failure of which of the following embryological processes?
- A. Apoptosis
- B. Stem cell differentiation
- C. Notochord signaling
- D. Neural crest cell migration
- E. Fusion (Correct Answer)
Foregut development and derivatives Explanation: ***Fusion***
- The pancreas develops from a **ventral and a dorsal bud** that typically **fuse** during development.
- Failure of these two pancreatic buds (and their associated ducts) to completely fuse can result in **pancreas divisum**, where two separate ductal systems persist, corresponding to the dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts.
*Apoptosis*
- **Apoptosis** (programmed cell death) is crucial for the removal of unwanted cells and sculpting tissues during embryogenesis, such as the formation of digits or the regression of certain structures.
- It does not directly explain the persistence of two separate pancreatic ducts due to non-fusion of developmental buds.
*Stem cell differentiation*
- **Stem cell differentiation** is the process by which less specialized stem cells become more specialized cell types, which is fundamental to organ development and tissue formation.
- While essential for pancreatic development, it doesn't specifically account for the anatomical anomaly of two persistent ducts.
*Notochord signaling*
- **Notochord signaling** is vital for inducing the formation of the neural tube and defining the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo, as well as influencing the development of other nearby structures.
- This process is not directly related to the fusion of pancreatic buds, which occurs later and is influenced by interactions between mesenchymal and endodermal tissues.
*Neural crest cell migration*
- **Neural crest cells** are multipotent cells that migrate extensively throughout the embryo to form a wide variety of tissues, including parts of the peripheral nervous system, melanocytes, and bone/cartilage of the face and skull.
- Their migratory pathways and derivatives are not directly involved in the development and fusion of the pancreatic ductal system.
More Foregut development and derivatives US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.