Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Spread of infection through fascial planes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 1: The surgical equipment used during a craniectomy is sterilized using pressurized steam at 121°C for 15 minutes. Reuse of these instruments can cause transmission of which of the following pathogens?
- A. Non-enveloped viruses
- B. Sporulating bacteria
- C. Prions (Correct Answer)
- D. Enveloped viruses
- E. Yeasts
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Prions***
- Prions are **abnormally folded proteins** that are highly resistant to standard sterilization methods like steam autoclaving at 121°C, making them a risk for transmission through reused surgical instruments.
- They cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) like **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease**, where even trace amounts can be highly infectious.
*Non-enveloped viruses*
- Non-enveloped viruses are generally **more resistant to heat and disinfectants** than enveloped viruses but are typically inactivated by recommended steam sterilization protocols.
- Standard autoclaving conditions are effective in destroying most non-enveloped viruses.
*Sporulating bacteria*
- **Bacterial spores**, such as those from *Clostridium* or *Bacillus*, are known for their high resistance to heat and chemicals, but are usually **inactivated by steam sterilization at 121°C** for 15 minutes.
- This method is specifically designed to kill bacterial spores effectively.
*Enveloped viruses*
- Enveloped viruses are the **least resistant to heat and chemical disinfectants** due to their lipid envelope.
- They are readily **inactivated by standard steam sterilization** at 121°C.
*Yeasts*
- **Yeasts** are eukaryotic microorganisms that are typically **susceptible to heat sterilization**.
- They are effectively killed by typical steam autoclaving conditions used for surgical instruments.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 2: A 20-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of severe muscle soreness, nausea, and darkened urine for 2 days. The patient is on the college track team and has been training intensively for an upcoming event. One month ago, she had a urinary tract infection and was treated with nitrofurantoin. She appears healthy. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 64/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. There is diffuse muscle tenderness over the arms, legs, and back. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.8 g/dL
Leukocyte count 7,000/mm3
Platelet count 265,000/mm3
Serum
Creatine kinase 22,000 U/L
Lactate dehydrogenase 380 U/L
Urine
Blood 3+
Protein 1+
RBC negative
WBC 1–2/hpf
This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Myocarditis
- B. Metabolic alkalosis
- C. Compartment syndrome
- D. Acute kidney injury (Correct Answer)
- E. Hemolytic anemia
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Acute kidney injury***
- The patient's elevated **creatine kinase (CK)** of 22,000 U/L, muscle soreness, and dark urine (positive for blood but negative for red blood cells) are all indicative of **rhabdomyolysis**.
- **Rhabdomyolysis** releases large amounts of myoglobin, which is nephrotoxic and can precipitate in the renal tubules, leading to **acute tubular necrosis** and subsequent acute kidney injury.
*Myocarditis*
- While CK elevations can be seen in myocarditis, this patient's presentation is dominated by **skeletal muscle symptoms** and a history of intense exercise.
- There are no specific cardiac symptoms or signs (e.g., chest pain, arrhythmias) to suggest myocardial involvement.
*Metabolic alkalosis*
- Rhabdomyolysis typically causes **metabolic acidosis** due to the release of cellular contents, including phosphate and sulfate.
- There is no clinical or lab evidence (e.g., vomiting, diuretic use) to suggest metabolic alkalosis.
*Compartment syndrome*
- **Compartment syndrome** involves increased pressure within a muscle compartment, leading to pain, pallor, paresthesia, pulselessness, and paralysis.
- While rhabdomyolysis can occasionally lead to severe swelling that causes compartment syndrome, the diffuse muscle tenderness and absence of focal limb findings make it less likely as the primary direct complication.
*Hemolytic anemia*
- Though the urine is positive for blood and negative for RBCs, this is characteristic of **myoglobinuria**, not hemoglobinuria, which would indicate hemolytic anemia.
- The patient's **hemoglobin** is normal (12.8 g/dL), and there are no other signs of hemolysis (e.g., jaundice, reticulocytosis).
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 3: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of acute left-sided chest pain and dyspnea following a motor vehicle accident. His pulse is 122/min and blood pressure is 85/45 mm Hg. Physical examination shows distended neck veins and tracheal displacement to the right side. The left chest is hyperresonant to percussion and there are decreased breath sounds. This patient would most benefit from needle insertion at which of the following anatomical sites?
- A. 5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line
- B. 8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line
- C. 2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line (Correct Answer)
- D. Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin
- E. 5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line***
- The patient's symptoms (chest pain, dyspnea, hypotension, distended neck veins, tracheal deviation, hyperresonance, and decreased breath sounds on the left) are classic signs of a **tension pneumothorax**.
- Immediate treatment for **tension pneumothorax** involves needle decompression at the **2nd intercostal space** in the midclavicular line to relieve pressure and restore hemodynamic stability.
*5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line*
- This location is typically used for **chest tube insertion** in a more controlled setting, not for emergent needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it's a safe location for pleural access, it is not the **first-line site** for immediate life-saving decompression.
*8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line*
- This site is too low and posterior for effective needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax, which requires rapid access to the **apex of the lung**.
- It is more commonly used for **thoracentesis** to drain fluid from the pleural cavity.
*Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin*
- This location is primarily used for **pericardiocentesis** to drain fluid from the pericardial sac in cases of cardiac tamponade.
- It is not appropriate for addressing a **pneumothorax**, which involves air in the pleural space.
*5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line*
- This site is a common alternative for **chest tube insertion** but is not the preferred or most immediate site for needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it offers pleural access, the **2nd intercostal space** anteriorly is chosen for expediency and safety in an emergency.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 4: A 38-year-old woman undergoes hemithyroidectomy for treatment of localized, well-differentiated papillary thyroid carcinoma. The lesion is removed with clear margins. However, during the surgery, a structure lying directly adjacent to the superior thyroid artery at the upper pole of the thyroid lobe is damaged. This patient is most likely to experience which of the following symptoms?
- A. Shortness of breath
- B. Weakness of shoulder shrug
- C. Voice pitch limitation (Correct Answer)
- D. Difficulty swallowing
- E. Ineffective cough
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Voice pitch limitation***
- Damage to the structure directly adjacent to the **superior thyroid artery** at the upper pole of the thyroid likely involves the **external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN)**.
- This nerve innervates the **cricothyroid muscle**, which is responsible for **tensing the vocal cords** and controlling **voice pitch**.
- Injury results in inability to change pitch, voice fatigue during prolonged speaking, and reduced vocal range.
*Shortness of breath*
- While damage to other nerves like the **recurrent laryngeal nerve** could cause vocal cord paralysis and potentially lead to airway compromise, this is less directly associated with the superior thyroid artery.
- Shortness of breath is not the specific consequence of EBSLN injury near the superior thyroid artery.
*Weakness of shoulder shrug*
- Weakness of shoulder shrug is associated with damage to the **spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)**, which innervates the **trapezius muscle**.
- This nerve is anatomically distinct from structures near the superior thyroid artery at the upper pole of the thyroid.
*Difficulty swallowing*
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can result from damage to the **vagus nerve (cranial nerve X)** or its pharyngeal branches, but it is not the direct consequence of injury near the superior thyroid artery.
- Damage to the EBSLN primarily affects voice pitch and quality, not swallowing.
*Ineffective cough*
- An ineffective cough results from paralysis of the vocal cords (preventing glottic closure) or weakness of respiratory muscles, typically from **recurrent laryngeal nerve** damage or phrenic nerve injury.
- EBSLN damage primarily affects voice pitch and does not significantly impair cough effectiveness.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old female recovering from a total shoulder arthroplasty completed 6 days ago presents complaining of joint pain in her repaired shoulder. Temperature is 39 degrees Celsius. Physical examination demonstrates erythema and significant tenderness around the incision site. Wound cultures reveal Gram-positive cocci that are resistant to nafcillin. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Streptococcus pyogenes
- B. Escherichia coli
- C. Streptococcus viridans
- D. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- E. Staphylococcus aureus (Correct Answer)
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Staphylococcus aureus***
- The combination of **post-surgical infection**, **erythema**, and fever with **Gram-positive cocci** that are **nafcillin-resistant** is highly indicative of **Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)**.
- *S. aureus* is a common cause of **surgical site infections**, and its resistance to nafcillin implies it is MRSA, a significant clinical concern for its difficulty in treatment.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- While *S. pyogenes* is a Gram-positive coccus that can cause skin and soft tissue infections, it is typically **susceptible to penicillin** and related antibiotics like nafcillin, unlike the organism described.
- It is more commonly associated with **streptococcal pharyngitis** or **cellulitis**, and while it can cause severe disease, its resistance profile doesn't match the clinical picture.
*Escherichia coli*
- *E. coli* is a **Gram-negative rod**, not a Gram-positive coccus.
- It is a common cause of **urinary tract infections** and **gastrointestinal infections**, making it an unlikely pathogen for a post-surgical joint infection unless contaminated from a visceral source.
*Streptococcus viridans*
- **Viridans streptococci** are Gram-positive cocci but are typically associated with **endocarditis** or dental infections, especially after poor dental hygiene or procedures.
- They are usually **susceptible to penicillin** and do not typically exhibit nafcillin resistance as the primary feature in a post-arthroplasty infection.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- *S. epidermidis* is a **coagulase-negative Staphylococcus** known for forming **biofilms on prosthetic devices**, leading to chronic, low-grade infections.
- While it can be nafcillin-resistant, the **acute presentation** with fever and significant inflammation suggests a more virulent pathogen like *S. aureus*, as *S. epidermidis* infections are typically indolent.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 6: A 31-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with severe left leg pain and paresthesias 4 hours after his leg got trapped by the closing door of a bus. Initially, he had a mild pain which gradually increased to unbearable levels. Past medical history is noncontributory. In the Emergency Department, his blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, heart rate is 87/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, and temperature is 36.8℃ (98.2℉). On physical exam, his left calf is firm and severely tender on palpation. The patient cannot actively dorsiflex his left foot, and passive dorsiflexion is limited. Posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses are 2+ in the right leg and 1+ in the left leg. Axial load does not increase the pain. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Lower limb CT scan
- B. Lower limb ultrasound
- C. Splinting and limb rest
- D. Fasciotomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Lower limb X-ray in two projections
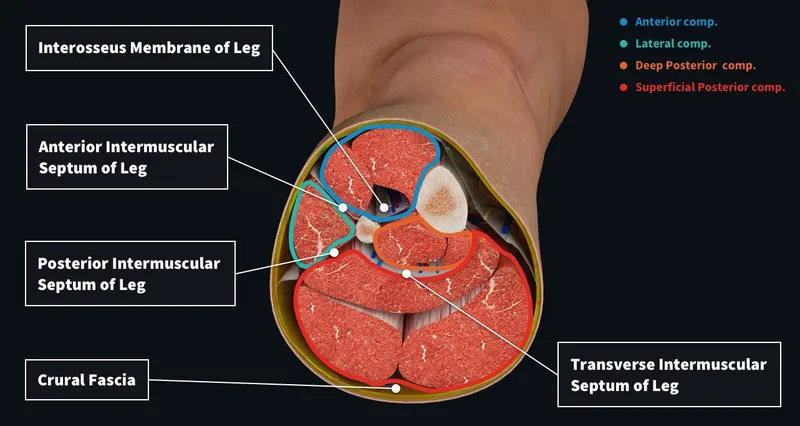
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Fasciotomy***
- The patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **acute compartment syndrome**, including unrelieved pain by analgesics, paresthesias, pain with passive stretching, and a tense compartment due to the bus door trauma.
- **Fasciotomy** is the definitive and urgent treatment to relieve pressure within the muscle compartments, prevent muscle ischemia, and avoid permanent nerve damage or limb loss.
*Lower limb CT scan*
- A **CT scan** is primarily used to evaluate bony structures and soft tissue injuries but is not the most immediate or definitive diagnostic tool for acute compartment syndrome.
- Delaying **fasciotomy** for imaging in a clear case of compartment syndrome can lead to irreversible damage.
*Lower limb ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** can assess vascular flow and some soft tissue aspects but is not accurate or rapid enough for diagnosing compartment syndrome.
- It would not provide the necessary information to guide urgent surgical intervention.
*Splinting and limb rest*
- This approach is appropriate for fractures or soft tissue injuries without compartment syndrome; however, in acute compartment syndrome, **splinting or limb rest** will worsen the condition.
- **Immobilization** and elevation are contraindicated as they can further decrease blood flow and increase compartment pressure.
*Lower limb X-ray in two projections*
- An **X-ray** is useful for ruling out fractures but will not provide information about compartment pressure or muscle viability.
- While a fracture can sometimes cause compartment syndrome, the immediate concern here is the compartment syndrome itself, for which **X-rays** are not diagnostic.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 7: A 40-year-old male is brought into the emergency department as the unrestrained passenger in a motor vehicle collision. On presentation he is obtunded with multiple ecchymoses on his chest and abdomen. There is marked distortion of his left lower extremity. His blood pressure is 90/64 mmHg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 24/min. Physical exam is limited by the patient’s mental state. The patient appears to be in pain while breathing and has tenderness to palpation of the abdomen. Neck veins are distended. Auscultation of the lungs reveals absent breath sounds on the left and hyperresonance to percussion. An emergent procedure is done and the patient improves. Had a chest radiograph of the patient been obtained on presentation to the ED, which of the following findings would most likely have been seen?
- A. Collection of fluid in the left lung base
- B. Consolidation of the left lower lobe
- C. Tracheal deviation to the right (Correct Answer)
- D. Bilateral fluffy infiltrates at the lung bases
- E. Fractured rib on the left
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Tracheal deviation to the right***
- The patient's presentation with **absent breath sounds** on the left, **hyperresonance** to percussion, **distended neck veins**, and **hypotension** after trauma is highly suggestive of a **tension pneumothorax**.
- In a tension pneumothorax, air accumulates under high pressure in the pleural space, pushing the **mediastinum** (including the trachea) to the **contralateral side**.
*Collection of fluid in the left lung base*
- A collection of fluid, such as in a **hemothorax** or **pleural effusion**, would typically cause **dullness to percussion**, not hyperresonance.
- While possible with trauma, effusions do not typically cause the acute, severe hemodynamic compromise or tracheal deviation seen here.
*Consolidation of the left lower lobe*
- **Consolidation**, typically seen in pneumonia or atelectasis, would present with **dullness to percussion** and potentially **bronchial breath sounds** or crackles, which contrasts with the absent breath sounds and hyperresonance described.
- It would also not explain the distended neck veins or mediastinal shift.
*Bilateral fluffy infiltrates at the lung bases*
- **Bilateral fluffy infiltrates** are characteristic of conditions like **pulmonary edema** or **Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)**.
- These conditions do not fit with the unilateral findings (absent breath sounds, hyperresonance on the left) or the acute traumatic etiology and signs of mediastinal shift.
*Fractured rib on the left*
- While a **fractured rib** is common in motor vehicle collisions, it is a cause rather than a direct radiographic finding that explains all the given symptoms.
- A rib fracture itself would not cause absent breath sounds, hyperresonance, distended neck veins, or tracheal deviation unless it led to a more severe complication like a **pneumothorax**.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 8: A 35-year-old woman presents with progressive vision loss and severe headache. MRI shows cavernous sinus thrombosis with extension into the superior ophthalmic vein. Blood cultures grow Staphylococcus aureus. History reveals she had squeezed a facial pustule near her upper lip 5 days prior. Evaluate the anatomical explanation and risk stratification for this complication.
- A. Direct lymphatic spread from facial infection due to rich subcutaneous lymphatic network
- B. Valveless facial venous system allowing retrograde flow from danger triangle to cavernous sinus (Correct Answer)
- C. Contiguous spread through cribriform plate from nasal cavity involvement
- D. Hematogenous seeding via internal jugular vein and sigmoid sinus
- E. Extension through pterygoid venous plexus communicating with middle meningeal vein
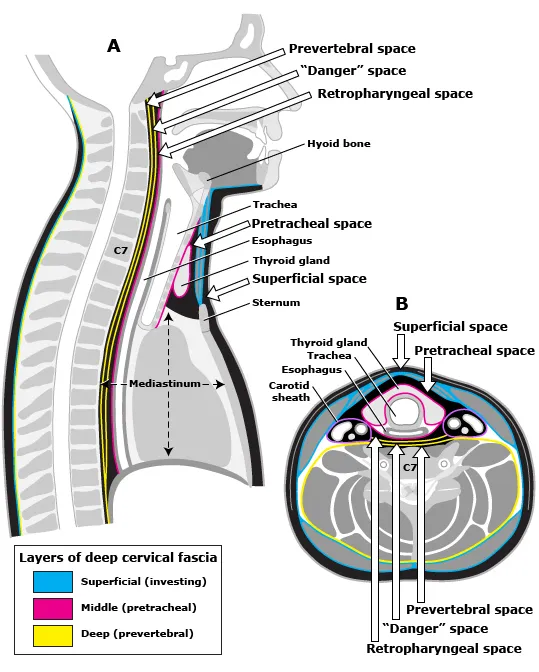
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Valveless facial venous system allowing retrograde flow from danger triangle to cavernous sinus***
- The **danger triangle of the face** (perioral and nasal areas) contains **valveless veins**, which allows blood to flow in a **retrograde** direction toward the intracranial space.
- Infections in this region can spread via the **angular vein** into the **superior ophthalmic vein**, directly reaching the **cavernous sinus** and causing septic thrombosis.
*Direct lymphatic spread from facial infection due to rich subcutaneous lymphatic network*
- While the face has a rich **lymphatic network**, lymphatic drainage typically leads to **submandibular or cervical lymph nodes**, not the cavernous sinus.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a **vascular complication** specifically involving the **venous system**, not the lymphatic system.
*Contiguous spread through cribriform plate from nasal cavity involvement*
- The **cribriform plate** is a route for infections to enter the **subarachnoid space**, primarily leading to **meningitis** or brain abscesses.
- It does not serve as the primary anatomical conduit for superficial facial infections to localize within the **cavernous sinus**.
*Hematogenous seeding via internal jugular vein and sigmoid sinus*
- The **internal jugular vein** and **sigmoid sinus** represent the **outflow tract** away from the brain; flow to the cavernous sinus through this route would be highly atypical.
- Bacterial seeding via this route would usually imply **systemic bacteremia** or infection in the **mastoid air cells**, rather than a localized facial pustule.
*Extension through pterygoid venous plexus communicating with middle meningeal vein*
- The **pterygoid venous plexus** can communicate with the cavernous sinus, but it primarily drains the **infratemporal fossa** and deep face, not the superficial upper lip.
- The **middle meningeal vein** drains into the pterygoid plexus or sphenoparietal sinus and is not the classic path for **danger triangle** infections.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old diabetic man undergoes emergent fasciotomy for compartment syndrome of the right leg following a tibia-fibula fracture. Intraoperatively, the anterior compartment muscles appear dusky and do not contract with stimulation. The lateral compartment muscles appear viable. Deep posterior compartment shows borderline viability with weak contraction. Superficial posterior compartment is clearly viable. Synthesize a management plan that optimizes limb salvage while minimizing morbidity.
- A. Debride anterior compartment only, leave wounds open, second look in 48 hours for other compartments
- B. Debride all nonviable muscle, preserve borderline tissue, second look in 24 hours (Correct Answer)
- C. Complete debridement of anterior and deep posterior compartments with immediate wound closure
- D. Below-knee amputation given extent of muscle necrosis and diabetes
- E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for 48 hours before deciding on debridement versus amputation
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Debride all nonviable muscle, preserve borderline tissue, second look in 24 hours***
- Immediate **debridement** of non-contractile, dusky muscle is crucial to prevent **myoglobinuria**, metabolic acidosis, and **acute kidney injury**.
- Marginal tissue should be preserved during the initial surgery to maximize potential **limb salvage**, necessitating a **mandatory second-look** procedure within 24-48 hours.
*Debride anterior compartment only, leave wounds open, second look in 48 hours for other compartments*
- Leaving known nonviable muscle in the anterior compartment for 48 hours increases the risk of **secondary infection** and systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- Re-exploration should be performed sooner (24 hours) when multiple compartments show **borderline viability** to ensure timely intervention.
*Complete debridement of anterior and deep posterior compartments with immediate wound closure*
- **Immediate wound closure** is strictly contraindicated in compartment syndrome as it can cause a recurrence of increased pressure and facilitates **anaerobic infection**.
- Over-debridement of the **deep posterior compartment** before its viability is definitively determined could result in unnecessary loss of **plantarflexion** and sensation.
*Below-knee amputation given extent of muscle necrosis and diabetes*
- **Amputation** is premature as the lateral and superficial posterior compartments are viable, providing a foundation for a **functional limb**.
- While **diabetes** may complicate healing, it is not an absolute indication for primary amputation in the setting of salvageable muscle groups.
*Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for 48 hours before deciding on debridement versus amputation*
- Delaying surgical **debridement** of necrotic tissue to pursue **HBO therapy** is dangerous and allows for the progression of sepsis and muscle breakdown.
- HBO therapy is an **adjunct**, not a replacement for mechanical decompression and removal of dead tissue in **acute compartment syndrome**.
Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old man sustains a gunshot wound to the medial upper arm. He presents with inability to flex his elbow and loss of sensation over the lateral forearm. Angiography shows intact brachial artery, but compartment pressures in the anterior arm compartment are 55 mmHg. His blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg after resuscitation. Evaluate the optimal surgical approach considering all clinical factors.
- A. Immediate fasciotomy of anterior compartment with nerve exploration and vascular repair
- B. Fasciotomy of both anterior and posterior compartments with primary nerve repair
- C. Further resuscitation to MAP >65, then fasciotomy with delayed nerve repair
- D. Emergent fasciotomy, debridement, and temporary vascular shunt placement
- E. Complete neurovascular exploration with definitive repair and compartment release (Correct Answer)
Spread of infection through fascial planes Explanation: ***Complete neurovascular exploration with definitive repair and compartment release***
- The patient exhibits clinical and objective signs of **acute compartment syndrome** (pressure 55 mmHg) and **musculocutaneous nerve** injury, requiring emergency surgical intervention.
- A total assessment is necessary because the **gunshot wound** trajectory near the medial arm risks occult damage to the **neurovascular bundle** despite initial angiographic findings.
*Immediate fasciotomy of anterior compartment with nerve exploration and vascular repair*
- While an anterior fasciotomy is vital, focusing solely on the anterior compartment may be insufficient if the high-energy trauma caused **posterior compartment** injury.
- **Vascular repair** is not indicated at this stage as angiography has already confirmed the **brachial artery** is intact.
*Fasciotomy of both anterior and posterior compartments with primary nerve repair*
- Primary nerve repair is often contraindicated in **high-velocity gunshot wounds** due to the "zone of injury" and potential for further tissue debridement needs.
- While dual-compartment release is thorough, the emphasis on **primary repair** in an unstable, potentially contaminated trauma setting is surgically premature.
*Further resuscitation to MAP >65, then fasciotomy with delayed nerve repair*
- While hemodynamic stability is important, the **Delta pressure** (60 - 55 = 5 mmHg) is critically low, meaning any delay in fasciotomy will lead to **muscle necrosis**.
- Resuscitation should occur **concurrently** with surgical preparation rather than as a prerequisite that delays limb-saving decompression.
*Emergent fasciotomy, debridement, and temporary vascular shunt placement*
- The use of a **temporary vascular shunt** is reserved for patients with confirmed arterial transection to maintain distal perfusion during damage control.
- Since the **brachial artery** is intact per angiography, shunting is unnecessary and adds pointless risk and operative time.
More Spread of infection through fascial planes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.