Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Specialized connective tissues. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
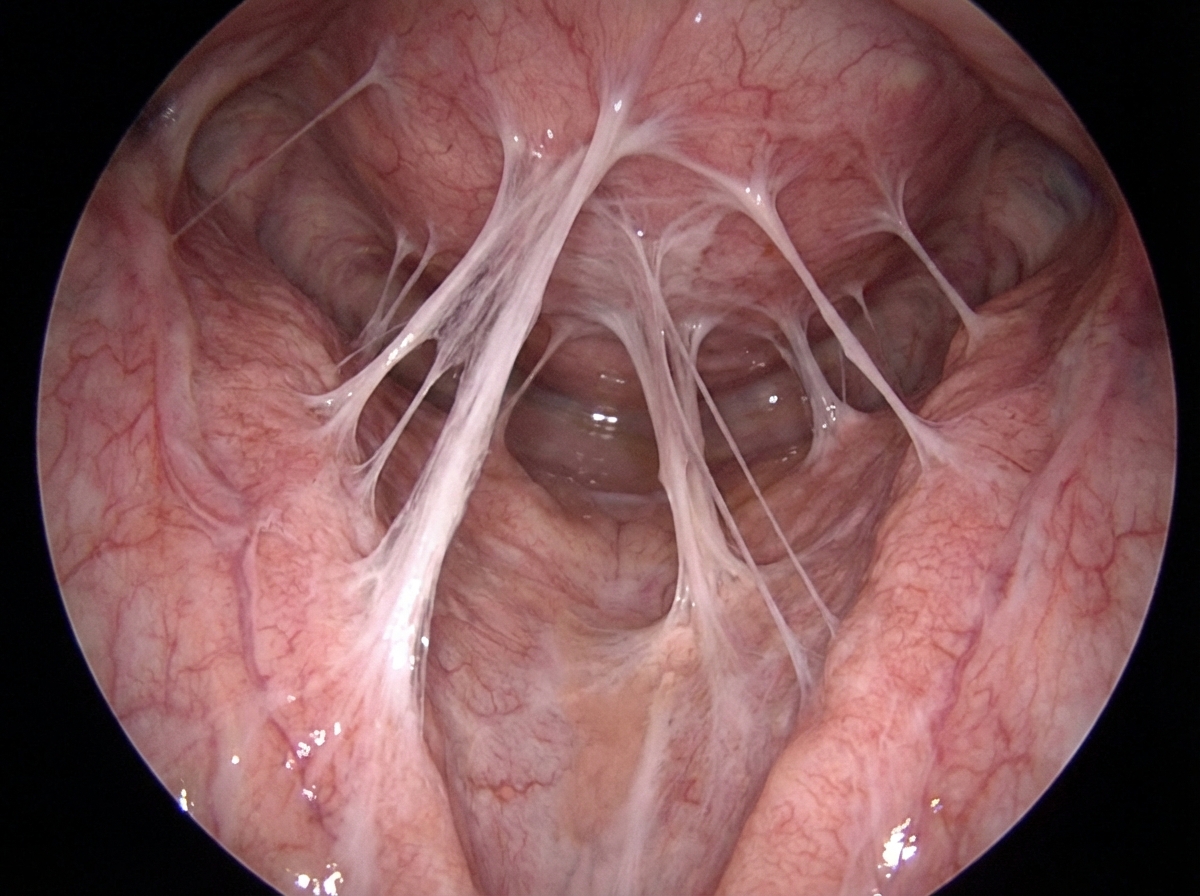
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 1: A 28-year-old woman and her husband are admitted to the office due to difficulties conceiving a child for the past year. Her menarche was at the age of 15 years, and her periods have been regular since then. Her medical history is positive for an abortion with curettage 5 years ago. A spermogram on the partner is performed, and it shows motile sperm cells. An ultrasound is performed on the patient and it is unremarkable. The laboratory results show that the FSH, LH, TSH, and prolactin levels are within normal ranges. A hysteroscopy is additionally performed and multiple adhesions are found in the uterus (refer to the image). Which of the following is the most likely composition of the scar tissue present in the uterus?
- A. Type 3 collagen
- B. Type 4 collagen
- C. Type 2 collagen
- D. Type 1 collagen (Correct Answer)
- E. Elastin
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Type 1 collagen***
- This patient presents with **Asherman's syndrome**, characterized by intrauterine adhesions, often following uterine surgery like **curettage**. These adhesions are primarily composed of **Type 1 collagen**, which is the most abundant type of collagen in the human body and a major component of scar tissue.
- **Type 1 collagen** provides tensile strength and is crucial for wound healing and forming scar tissue in most connective tissues, including the uterus.
*Type 3 collagen*
- **Type 3 collagen** is found in distensible tissues like blood vessels, the uterus, and skin, and is important during the **early stages of wound healing**.
- While present in the uterus and initially involved in wound repair, **mature scar tissue** predominantly consists of **Type 1 collagen**.
*Type 4 collagen*
- **Type 4 collagen** is a major component of the **basal lamina**, a specialized extracellular matrix that underlies epithelial and endothelial cells.
- It does not form fibrillar structures and is not the primary component of robust scar tissue found in Asherman's syndrome.
*Type 2 collagen*
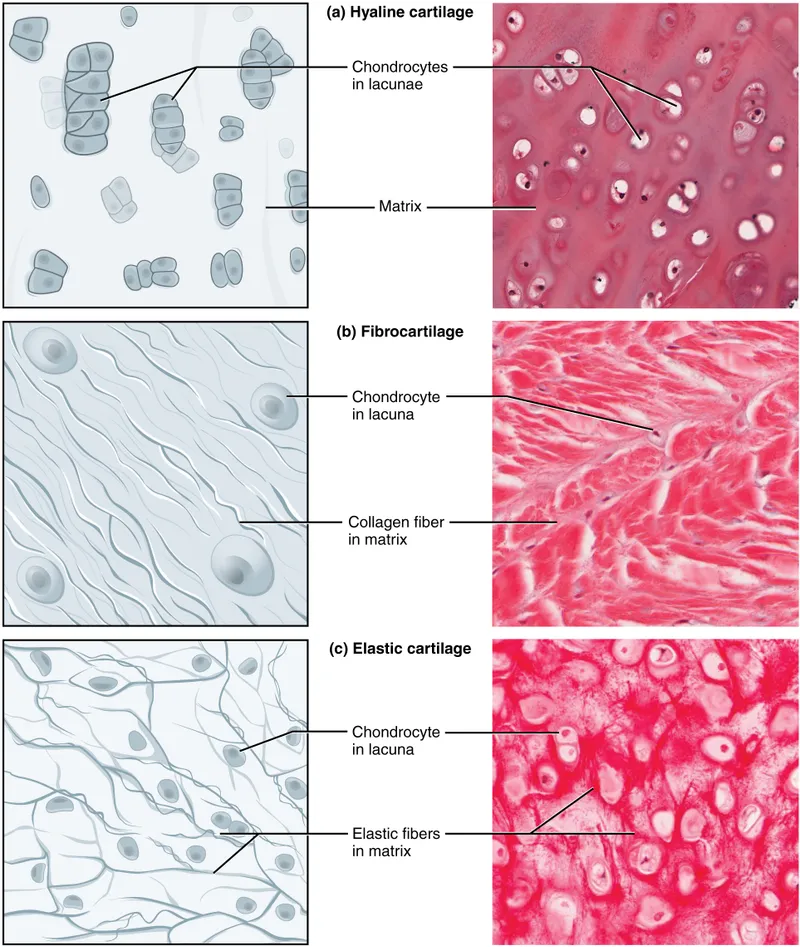
- **Type 2 collagen** is the main collagen type found in **hyaline cartilage** and elastic cartilage, providing resistance to pressure.
- It is not found in significant amounts in uterine tissue or scar tissue formed within the uterus.
*Elastin*
- **Elastin** is a protein that provides **elasticity** to tissues like blood vessels, skin, and lungs, allowing them to stretch and recoil.
- While present in the uterus for its contractile properties, it is not the primary constituent of **fibrotic scar tissue** forming adhesions.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old girl presents to her primary care physician for a routine check-up. The physician allows the medical student to perform a physical examination. The medical student notes hearing impairment as well as the findings show in Figures A and B. Radiographs show indications of multiple old fractures of the humerus that have healed. After questioning the girl’s parents, the medical student learns that in addition, the patient is extremely picky with her food and eats a diet consisting mainly of cereal and pasta. What is the most likely etiology of the patient’s disease?
- A. Dietary deficiency of ascorbic acid
- B. Defect in type I collagen (Correct Answer)
- C. Defective mineralization of cartilage
- D. Decreased bone mineral density
- E. Non-accidental trauma
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Defect in type I collagen***
- The constellation of **frequent fractures**, **hearing impairment**, and **blue sclerae** (as indicated by Figure A, which shows a bluish tint to the white part of the eye) is characteristic of **osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)**, a genetic disorder caused by mutations in COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes leading to **defective type I collagen synthesis**.
- Type I collagen is the primary structural protein in bone, and defects result in brittle bones, blue sclerae (due to thin sclera allowing choroid visibility), and conductive hearing loss (from ossicle abnormalities).
- While the patient's diet is described as "picky," the primary features point towards a genetic collagen defect rather than a nutritional deficiency as the underlying cause for the bone and connective tissue abnormalities.
*Dietary deficiency of ascorbic acid*
- A deficiency in **ascorbic acid (vitamin C)** leads to **scurvy**, characterized by **gingivitis**, **poor wound healing**, **petechiae**, and easy bruising due to impaired collagen synthesis.
- While collagen synthesis is affected, the specific presentation of blue sclerae, hearing impairment, and multiple fractures as primary symptoms is not typical for scurvy.
*Defective mineralization of cartilage*
- **Defective mineralization of cartilage** often points to **rickets in children** or **osteomalacia in adults**, usually due to **vitamin D deficiency** or disorders of phosphate metabolism.
- While these conditions can cause bone fragility, they do not typically present with blue sclerae or hearing impairment as defining features. The "old fractures" suggest a chronic bone fragility predating any acute nutritional issues.
*Decreased bone mineral density*
- **Decreased bone mineral density (BMD)** is a general term seen in many conditions, including **osteoporosis** and **osteogenesis imperfecta**.
- While the patient likely has decreased BMD due to their frequent fractures, this option describes a symptom rather than the **underlying etiology** of the disorder.
*Non-accidental trauma*
- **Non-accidental trauma (child abuse)** should always be considered in a child with multiple fractures.
- However, the presence of other systemic findings like **blue sclerae** and **hearing impairment** strongly suggests an underlying genetic disorder like osteogenesis imperfecta, making non-accidental trauma less likely as the primary cause for all observed symptoms.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 3: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician with acute, severe pain in the middle of her lower back. She also complains of constipation and trouble sleeping recently. Menses occur regularly at 28-day intervals. Examination shows localized tenderness to palpation over the lumbar spine. Serum calcium is 14 mg/dL and serum phosphorus is 1.5 mg/dL. An x-ray of the lumbar spine shows a compression fracture of the L4 vertebral body and osteopenia. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's decreased bone mineral density?
- A. Increase in parathyroid hormone secretion (Correct Answer)
- B. Decrease in RANKL expression
- C. Decrease in osteoblast activity
- D. Increase in calcitonin secretion
- E. Decrease in estrogen production
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Increase in parathyroid hormone secretion***
- This patient presents with the classic triad of **primary hyperparathyroidism**: hypercalcemia (14 mg/dL), hypophosphatemia (1.5 mg/dL), and bone disease (compression fracture with osteopenia).
- **PTH excess** causes increased bone resorption by stimulating osteoclast activity, leading to decreased bone mineral density and pathologic fractures.
- PTH increases renal phosphate excretion (causing hypophosphatemia) and increases calcium reabsorption and bone resorption (causing hypercalcemia).
- The **constipation is a manifestation of hypercalcemia** ("stones, bones, abdominal groans, and psychiatric overtones").
- Primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common cause of hypercalcemia in outpatients and frequently presents with osteopenia/osteoporosis.
*Decrease in estrogen production*
- While estrogen deficiency causes osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, this patient has **regular menses at 28-day intervals**, indicating she is not menopausal.
- Estrogen deficiency causes **normocalcemic osteoporosis**, not the hypercalcemia (14 mg/dL) and hypophosphatemia (1.5 mg/dL) seen in this patient.
- The laboratory abnormalities clearly point to a different etiology.
*Decrease in RANKL expression*
- RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand) stimulates osteoclast differentiation and activity.
- A **decrease** in RANKL would **reduce** osteoclast activity and **increase** bone mineral density, which is opposite to this patient's presentation.
- PTH actually works partly by increasing RANKL expression, further supporting hyperparathyroidism as the diagnosis.
*Decrease in osteoblast activity*
- While decreased osteoblast activity can contribute to low bone density, this is typically seen in conditions like multiple myeloma or aging.
- This mechanism does not explain the **hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia** seen in this patient.
- The primary pathology here is **increased osteoclast activity** driven by excess PTH.
*Increase in calcitonin secretion*
- Calcitonin **lowers** serum calcium by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
- An increase in calcitonin would cause **hypocalcemia**, not the hypercalcemia (14 mg/dL) observed in this patient.
- This is physiologically opposite to the patient's presentation.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 5: A 60-year-old male presents with fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, and lower extremity edema. Physical examination reveals an elevated jugular venous pressure and an S3 heart sound. Which of the following medications is most likely to improve this patient's symptoms?
- A. Metoprolol
- B. Furosemide (Correct Answer)
- C. Losartan
- D. Lisinopril
- E. Spironolactone
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Correct: Furosemide***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **heart failure with fluid overload**: dyspnea on exertion, lower extremity edema, elevated jugular venous pressure, and an S3 heart sound (indicating volume overload).
- **Furosemide**, a **loop diuretic**, is the most effective medication for **rapid symptomatic relief** in heart failure with congestion. It works by blocking sodium and water reabsorption in the loop of Henle, promoting diuresis and reducing **pulmonary congestion** and **peripheral edema**.
- While other medications like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists are crucial for **long-term mortality reduction** and disease modification, loop diuretics provide the **fastest and most direct symptomatic improvement** for fluid overload.
*Incorrect: Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a **beta-blocker** that is essential for chronic HFrEF management, providing **mortality reduction** and **reverse cardiac remodeling**.
- However, beta-blockers take **weeks to months** to show symptomatic benefit and can initially **worsen symptoms** due to negative inotropic effects, especially in acute decompensation.
- While important for long-term management, metoprolol does not provide immediate symptomatic relief from fluid overload.
*Incorrect: Losartan*
- **Losartan** is an **angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)** used as an alternative to ACE inhibitors in HFrEF, particularly in patients who develop cough with ACE inhibitors.
- ARBs reduce **afterload** and prevent **cardiac remodeling**, contributing to improved long-term outcomes and mortality reduction.
- However, they do not directly address fluid overload and do not provide rapid symptomatic relief compared to diuretics.
*Incorrect: Spironolactone*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that improves mortality in HFrEF by preventing myocardial fibrosis, reducing cardiac remodeling, and preventing potassium loss.
- While beneficial for long-term management, spironolactone has **weak diuretic effects** and takes weeks to provide symptomatic benefit.
- It is not the first-line choice for **acute symptomatic relief** of volume overload, though it is an important component of chronic HFrEF therapy.
*Incorrect: Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor** and a cornerstone of HFrEF therapy, reducing **mortality**, **hospitalizations**, and preventing **cardiac remodeling** by reducing afterload and preload.
- While ACE inhibitors improve symptoms over time, they do not provide the **rapid diuretic effect** needed for immediate relief of dyspnea and edema.
- Lisinopril is essential for long-term management but is not the most effective option for acute symptomatic improvement of fluid overload.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying the structural integrity of collagen. Human fibroblasts are cultured on a medium and different enzymes are applied. One of the cultures is supplemented with an enzyme that inhibits lysyl oxidase, preventing the formation of covalent cross-links between collagen α-chains. Which of the following processes is most likely to be impaired as a result?
- A. Internal elastic lamina formation
- B. Ligament relaxation
- C. Osteoclast activation
- D. Bone matrix synthesis (Correct Answer)
- E. Cartilaginous growth plate mineralization
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Bone matrix synthesis***
* **Collagen** is the primary organic component of the bone matrix (osteoid), and its proper cross-linking through **lysyl oxidase-mediated covalent bonds** is crucial for structural integrity and subsequent mineralization.
* **Lysyl oxidase** converts lysine and hydroxylysine residues to aldehydes (allysine and hydroxyallysine), which then form **aldol condensations and Schiff bases** to create stable cross-links between collagen fibrils.
* Inhibiting lysyl oxidase directly compromises the formation of stable collagen fibrils, which are essential for **osteoid production** and bone strength, leading to conditions like **lathyrism** (seen with β-aminopropionitrile exposure).
*Incorrect Option: Internal elastic lamina formation*
* The **internal elastic lamina** is primarily composed of **elastin**, not collagen, and provides arterial elasticity.
* While elastin also requires lysyl oxidase for cross-linking (desmosine and isodesmosine formation), the question specifically asks about **collagen α-chains**, making bone matrix synthesis the more direct answer.
*Incorrect Option: Ligament relaxation*
* **Ligament relaxation** refers to increased laxity, primarily influenced by hormones like relaxin during pregnancy.
* Impairing collagen cross-linking would lead to **ligament weakness and fragility** rather than physiologic relaxation, potentially causing joint instability.
*Incorrect Option: Osteoclast activation*
* **Osteoclast activation** involves bone resorption, regulated by **RANK/RANKL/OPG signaling**, and is independent of newly synthesized collagen cross-linking.
* While collagen integrity affects bone quality, lysyl oxidase inhibition impairs **osteoblast-mediated bone formation**, not osteoclast function.
*Incorrect Option: Cartilaginous growth plate mineralization*
* **Growth plate mineralization** involves calcium phosphate crystal deposition within cartilage matrix, regulated by chondrocytes and factors like alkaline phosphatase.
* While collagen integrity is important in cartilage, the defect in collagen cross-linking most critically affects **bone matrix (osteoid)** synthesis, where type I collagen predominates and provides the scaffold for mineralization.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old male presents with left hip pain and stiffness. Radiographs are shown in Figures A and B. Serum alkaline phosphatase levels are elevated. A biopsy of the left femur is performed and shown in Figure C. Which of the following cells are initially responsible for this condition?
- A. T-Cells
- B. Fibroblasts
- C. Osteoblasts
- D. Osteoclasts (Correct Answer)
- E. Neutrophils
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Osteoclasts***
- The presented images and elevated **alkaline phosphatase** strongly suggest **Paget's disease of bone**, which is characterized by abnormal bone remodeling initially driven by excessive osteoclastic activity.
- In Paget's disease, the initial phase involves a chaotic increase in **osteoclast** number and activity, leading to focal areas of excessive bone resorption.
*T-Cells*
- **T-cells** are primarily involved in immune responses and cell-mediated immunity rather than direct bone remodeling in Paget's disease.
- While immune factors may play a role in the pathogenesis of Paget's disease, **T-cells** are not the primary cells responsible for the initial destructive phase.
*Fibroblasts*
- **Fibroblasts** are connective tissue cells involved in producing collagen and extracellular matrix, important for tissue repair and scarring.
- They are not the main cells responsible for the initial abnormal bone resorption observed in Paget's disease.
*Osteoblasts*
- **Osteoblasts** are bone-forming cells responsible for synthesizing and depositing new bone matrix.
- In Paget's disease, osteoblastic activity is increased in a compensatory and disorganized manner following the initial osteoclastic hyperactivity, but they are not the cells _initially_ responsible for the condition.
*Neutrophils*
- **Neutrophils** are a type of white blood cell primarily involved in acute inflammatory responses to infections.
- They have no direct role in the primary pathogenesis of Paget's disease of bone.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 8: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 9: A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset severe pain in the right shoulder that occurred when he threw a bowling ball 2 hours ago. He has a history of dislocations in both shoulders and subluxation of the right knee and left wrist. There is no history of fractures. On physical examination, the right arm is slightly abducted and externally rotated. An anterior bulge is seen near the shoulder joint. The neurovascular examination of the right arm shows no abnormalities. The skin examination shows multiple widened atrophic scars around the knees, elbows, and ankles. The skin of the neck and around the elbow can easily be extended up to 4 cm. The sclera is white. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. A defect in which of the following proteins is the most likely cause of the findings in this patient?
- A. Collagen (Correct Answer)
- B. Keratin
- C. Fibrillin-1
- D. Tau
- E. Elastin
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Collagen***
- This patient's symptoms, including **recurrent dislocations**, easy **skin extensibility**, and **atrophic scars**, are classic signs of **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)**, which is primarily caused by defects in **collagen synthesis or processing**.
- The shoulder dislocation from a minor activity (throwing a bowling ball), along with multisystem hypermobility (shoulders, knee, wrist), strongly points to a **connective tissue disorder** affecting collagen.
*Keratin*
- **Keratin** is a structural protein primarily found in **epithelial cells**, forming hair, skin, and nails.
- Defects in keratin typically manifest as disorders of **skin fragility**, such as **epidermolysis bullosa**, not joint hypermobility or tissue extensibility.
*Fibrillin-1*
- **Fibrillin-1** defects cause **Marfan syndrome**, characterized by **tall stature**, **arachnodactyly**, **aortic root dilation**, and **lens dislocation**.
- While Marfan syndrome involves connective tissue, the patient's presentation of easy skin extensibility and atrophic scars is not characteristic of fibrillin-1 defects, and there is no mention of cardiovascular or ocular issues typical of Marfan.
*Tau*
- **Tau protein** is a **microtubule-associated protein** primarily found in neurons and is involved in stabilizing microtubules.
- Defects or abnormal aggregation of tau protein are associated with **neurodegenerative diseases** like **Alzheimer's disease** and **frontotemporal dementia**, not connective tissue disorders.
*Elastin*
- **Elastin** provides elasticity to tissues, allowing them to stretch and recoil. Defects can lead to conditions like **cutis laxa** or **Williams syndrome**.
- While some features of increased skin extensibility might overlap, the constellation of recurrent joint dislocations and specific atrophic scars seen in this patient is more indicative of **collagen defects** common in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old man presents with a complaint of breathlessness while jogging. He says that he recently started marathon training. He does not have any family history of asthma nor has any allergies. He currently takes no medication. The blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and the heart rate is 67/min. With each heartbeat, he experiences pounding in his chest, and his head bobs. On physical examination, he has long fingers, funnel chest, and disproportionate body proportions with a decreased upper-to-lower segment ratio. On auscultation over the 2nd right intercostal space, an early diastolic murmur is heard, and 3rd and 4th heart sounds are heard. Echocardiography shows aortic root dilatation. The patient is scheduled for surgery. Which of the following is associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Klinefelter syndrome
- B. Intravenous drug abuse
- C. Marfan's Syndrome (Correct Answer)
- D. Kawasaki syndrome
- E. Gonorrhea
Specialized connective tissues Explanation: ***Marfan's Syndrome***
- The patient presents with **tall stature**, **long fingers (arachnodactyly)**, **funnel chest (pectus excavatum)**, and **aortic root dilation** with **aortic regurgitation** (early diastolic murmur, head bobbing, pounding in the chest), all classic features of Marfan syndrome.
- This is a **connective tissue disorder** caused by a mutation in the **FBN1 gene**, leading to defective **fibrillin-1**, which is crucial for structural integrity in the heart, blood vessels, eyes, and skeleton.
*Klinefelter syndrome*
- Characterized by a **47, XXY karyotype** and typically presents with infertility, small testes, gynecomastia, and tall stature, but not the specific cardiovascular or skeletal features described.
- While it can cause tall stature, it does not explain the **arachnodactyly**, **pectus excavatum**, or the severe **aortic root dilation** and regurgitation.
*Intravenous drug abuse*
- Primarily associated with **infective endocarditis**, particularly affecting the **tricuspid valve**, leading to heart murmurs related to infection, not the skeletal and aortic root abnormalities seen here.
- This history would lead to a different clinical presentation, potentially involving fever, chills, and vegetations on valve leaflets, none of which are mentioned.
*Kawasaki syndrome*
- An **acute inflammatory vasculitis** primarily affecting young children, characterized by fever, rash, conjunctivitis, lymphadenopathy, and oral mucosal changes.
- While it can cause **coronary artery aneurysms**, it does not explain the skeletal abnormalities or the specific presentation of aortic root dilation with regurgitation in an adult.
*Gonorrhea*
- A **sexually transmitted infection** that can lead to disseminated gonococcal infection, causing arthritis, tenosynovitis, and dermatitis.
- It does not cause the specific skeletal abnormalities or the primary cardiac pathology of aortic root dilation and regurgitation described in this patient.
More Specialized connective tissues US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.