Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Simple epithelial tissues. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 1: Which of the following cells in the body depends on dynein for its unique functioning?
- A. Small intestinal mucosal cell
- B. Skeletal muscle cell
- C. Adipocyte
- D. Lower esophageal mucosal cell
- E. Fallopian tube mucosal cell (Correct Answer)
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Fallopian tube mucosal cell***
- Dynein is a **motor protein** that facilitates the movement of **cilia** along microtubules.
- The ciliary action in fallopian tube mucosal cells is crucial for **transporting the ovum** from the ovary to the uterus.
*Small intestinal mucosal cell*
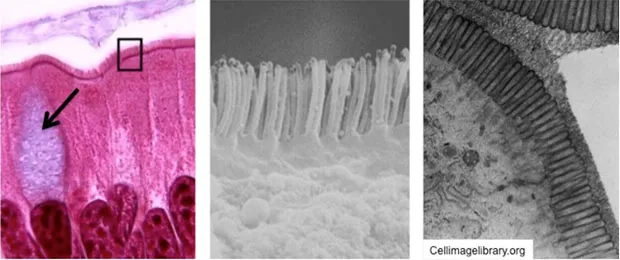
- These cells primarily depend on **microvilli** for absorption, which are actin-based structures and do not directly involve dynein for their primary function of absorption.
- While they have some cilia, their unique and defining function is nutrient absorption, not movement dependent on dynein.
*Skeletal muscle cell*
- Skeletal muscle cells rely on the interaction of **actin and myosin** filaments for **contraction**.
- Dynein is not directly involved in the mechanism of muscle contraction.
*Adipocyte*
- Adipocytes are specialized in **lipid storage** and release, a process that does not involve dynein.
- Their unique function does not depend on intracellular or extracellular movement facilitated by dynein.
*Lower esophageal mucosal cell*
- These cells primarily provide a **protective barrier** against gastric acid reflux.
- Their function involves **stratified squamous epithelium** and mucus production, not ciliary movement dependent on dynein.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 2: A pathologist examining a tissue sample notes the presence of pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells and cilia. This tissue was most likely obtained from which of the following locations?
- A. Bronchi (Correct Answer)
- B. Small intestine
- C. Skin
- D. Esophagus
- E. Urinary bladder
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Bronchi***
- The **bronchi**, as part of the respiratory tract, are lined with **pseudostratified columnar epithelium** that contains abundant **goblet cells** and **cilia** [1].
- **Cilia** help propel mucus and trapped particles out of the respiratory system, while **goblet cells** produce mucus to trap foreign substances [1].
*Small intestine*
- The small intestine is lined with **simple columnar epithelium** with **microvilli** (forming a brush border) and goblet cells, but it lacks **cilia**.
- Its primary function is nutrient absorption, not particulate clearance.
*Skin*
- The skin is covered by **stratified squamous epithelium**, specifically **keratinized stratified squamous epithelium**, which provides protection against abrasion and dehydration.
- It does not contain **goblet cells**, **cilia**, or **pseudostratified columnar epithelium**.
*Esophagus*
- The esophagus is lined with **non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium**, designed to protect against mechanical abrasion during food passage.
- It lacks **goblet cells**, **cilia**, and **pseudostratified columnar epithelium**.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator studying hormone synthesis and transport uses immunocytochemical techniques to localize a carrier protein in the central nervous system of an experimental animal. The investigator finds that this protein is synthesized together with a specific hormone from a composite precursor. The protein is involved in the transport of the hormone from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei to its destination. The hormone transported by these carrier proteins is most likely responsible for which of the following functions?
- A. Stimulation of thyroglobulin cleavage
- B. Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels (Correct Answer)
- C. Hyperplasia of the adrenal zona fasciculata
- D. Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production
- E. Maturation of primordial germ cells
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels***
- The description of a hormone synthesized in the **supraoptic** and **paraventricular nuclei** and transported by a carrier protein refers to **antidiuretic hormone (ADH)**, also known as vasopressin.
- ADH's primary function in the kidney is to **increase water reabsorption** by upregulating **aquaporin-2 channels** in the principal cells of the collecting ducts.
*Stimulation of thyroglobulin cleavage*
- **Thyroglobulin cleavage** and subsequent release of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) are stimulated by **thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)**, which is produced by the anterior pituitary, not the hypothalamus.
- The described origin in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei is inconsistent with TSH.
*Hyperplasia of the adrenal zona fasciculata*
- **Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)** from the anterior pituitary stimulates the adrenal cortex, including the zona fasciculata, to produce cortisol.
- The hormone described here originates in the hypothalamus and is transported to the posterior pituitary, not stimulating adrenal hyperplasia.
*Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production*
- **Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)** production is stimulated primarily by **growth hormone (GH)**, which is secreted by the anterior pituitary.
- This function is not associated with hormones produced in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.
*Maturation of primordial germ cells*
- The maturation of **primordial germ cells** is regulated by **gonadotropins (FSH and LH)**, which are secreted by the anterior pituitary, and sex steroids.
- This process is not directly controlled by hormones originating from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 4: A 34-year-old man with worsening refractory epigastric pain secondary to long-standing gastroesophageal reflux disease presents for endoscopic evaluation. Past medical history is also significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus that was diagnosed 3 years ago, managed medically. Current medications are metformin, metoclopramide, and omeprazole. Which of the following best describes this patient’s most likely endoscopic findings?
- A. Esophageal smooth muscle atrophy
- B. Metaplasia of the esophageal mucosa (Correct Answer)
- C. A malignant proliferation of squamous cells
- D. Hypertrophy of the esophageal mucosa protruding into the lumen of the lower esophagus
- E. Longitudinal lacerations of the esophageal mucosa
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Metaplasia of the esophageal mucosa***
- Long-standing **gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)** can lead to **Barrett's esophagus**, a condition where the normal **squamous epithelium** of the esophagus is replaced by **columnar epithelium** (intestinal metaplasia) due to chronic acid exposure.
- This endoscopic finding is significant as **Barrett's esophagus** is a well-known **premalignant condition** for esophageal adenocarcinoma.
*Esophageal smooth muscle atrophy*
- This is commonly seen in conditions like **scleroderma** or other **motility disorders**, where the smooth muscle of the esophagus degenerates, leading to impaired peristalsis.
- While GERD can be a complication of such disorders, **smooth muscle atrophy** is not the primary endoscopic finding directly related to long-standing refractory GERD itself.
*A malignant proliferation of squamous cells*
- This describes **squamous cell carcinoma** of the esophagus, which is typically associated with risk factors like **smoking** and **alcohol consumption**.
- While Barrett's esophagus can progress to adenocarcinoma, direct squamous cell carcinoma is not the *most likely* initial finding after chronic reflux.
*Hypertrophy of the esophageal mucosa protruding into the lumen of the lower esophagus*
- **Hypertrophy** (enlargement) of the esophageal mucosa is not a typical finding in chronic GERD; rather, the mucosa undergoes changes like **inflammation**, **erosion**, or **metaplasia**.
- Protrusions into the lumen in this context would more likely suggest a **polyp** or **tumor**, which are less common primary findings than metaplasia in long-standing GERD.
*Longitudinal lacerations of the esophageal mucosa*
- **Longitudinal lacerations** of the esophageal mucosa, often near the gastroesophageal junction, are characteristic of **Mallory-Weiss tears**, which result from forceful vomiting or retching.
- These are acute injuries and not directly indicative of the chronic changes expected in long-standing refractory GERD.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 5: A 68-year-old male smoker dies suddenly in a car accident. He had smoked 2 packs per day for 40 years. His past medical history is notable for a frequent, very productive cough, recurrent respiratory infections and occasional wheezing. He had no other medical problems. At autopsy, which of the following is most likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Increased number and activity of goblet cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Ferruginous bodies
- C. Mucous gland atrophy
- D. Interstitial fibrosis of the lung
- E. Pleural plaques
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Increased number and activity of goblet cells***
- The patient's history of a **productive cough**, **recurrent respiratory infections**, and **wheezing** in a chronic smoker strongly indicates **chronic bronchitis**.
- **Chronic bronchitis** is pathologically characterized by **hypertrophy of mucous glands** and an **increase in goblet cell number and activity**, leading to excessive mucus production.
*Ferruginous bodies*
- **Ferruginous bodies** are typically found in **asbestosis**, a lung disease caused by asbestos exposure.
- While asbestos exposure can cause respiratory symptoms, the sudden death and clinical picture without specific exposure history do not point to asbestosis as the primary diagnosis.
*Mucous gland atrophy*
- **Mucous gland atrophy** is generally not associated with chronic smoking and the symptoms described.
- In conditions like chronic bronchitis, there is actually **hypertrophy** and **hyperplasia** of the mucous glands, leading to increased mucus production.
*Interstitial fibrosis of the lung*
- **Interstitial fibrosis** is characteristic of conditions like **idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis** or other **interstitial lung diseases**.
- While smoking is a risk factor for some forms of fibrosis, the predominant symptoms of a productive cough and recurrent infections are more indicative of chronic bronchitis rather than diffuse interstitial fibrosis.
*Pleural plaques*
- **Pleural plaques** are **fibrous thickenings of the pleura**, almost exclusively associated with **asbestos exposure**.
- They are usually asymptomatic and do not directly explain the productive cough, recurrent infections, and wheezing presented in this patient's history.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 6: A researcher is studying proteins that contribute to intestinal epithelial permeability. He has isolated intestinal tissue from several mice. After processing the tissue into its individual components, he uses a Western blot analysis to identify a protein that forms part of a multi-protein complex at the apical aspect of epithelial cells. The complex is known to provide a diffusion barrier between the apical and basolateral aspects of epithelial cells. Which of the following proteins is this researcher most likely investigating?
- A. Integrin
- B. Connexon
- C. Desmoglein
- D. E-cadherin
- E. Claudin (Correct Answer)
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Claudin***
- **Claudins** are integral membrane proteins that are primary components of **tight junctions** (zonulae occludentes), which form a diffusion barrier at the **apical aspect** of epithelial cells.
- They regulate **paracellular permeability**, crucial for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier.
*Integrin*
- **Integrins** are transmembrane receptors that mediate cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion and cell-cell adhesion, but they are not the primary components of tight junction diffusion barriers.
- They are involved in cell signaling and structural support, rather than forming a direct paracellular seal.
*Connexon*
- A **connexon** is a protein assembly that forms a **gap junction**, allowing direct communication and passage of small molecules between adjacent cells.
- Gap junctions facilitate intercellular communication, but do not primarily contribute to sealing the paracellular space as a diffusion barrier.
*Desmoglein*
- **Desmoglein** is a cadherin family protein found in **desmosomes** (maculae adherens), which are cell-cell adhesion complexes that provide strong mechanical attachments between cells.
- Desmosomes resist shearing forces and provide structural integrity but do not regulate paracellular permeability as tight junctions do.
*E-cadherin*
- **E-cadherin** is a crucial component of **adherens junctions** (zonula adherens), which provide cell-cell adhesion and help establish and maintain cell polarity.
- While important for epithelial integrity, E-cadherin primarily links cells to the actin cytoskeleton and is not directly responsible for forming the selective diffusion barrier itself.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 7: A 52-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of an ongoing cough. He reports that the cough started 1 year ago after a "bad cold" and then never resolved. He feels the cough is getting worse, sometimes the cough is dry, but often the cough will bring up a clear to white mucus, especially in the morning. The patient has hypertension and peripheral artery disease. He takes aspirin and lisinopril. He started smoking at age 16, and now smokes 2 packs of cigarettes a day. He has 1-2 beers a couple nights of the week with dinner. He denies illicit drug use. Which of the following cell types within the lung is most likely to undergo metaplasia caused by smoking?
- A. Pseudostratified columnar (Correct Answer)
- B. Simple cuboidal
- C. Transitional
- D. Simple squamous
- E. Stratified squamous
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Pseudostratified columnar***
- The **tracheobronchial tree** is lined with **pseudostratified columnar epithelium** containing cilia and goblet cells, which are crucial for clearing mucus and inhaled particles.
- Exposure to chronic irritants like cigarette smoke causes these cells to undergo **squamous metaplasia**, transforming into more resilient but less functional stratified squamous epithelium.
*Simple cuboidal*
- **Simple cuboidal epithelium** lines the **bronchioles** and is involved in secretion and absorption, but it is not the primary site for metaplastic changes due to smoking.
- While smoking can affect bronchioles, the characteristic metaplasia seen with chronic irritation primarily occurs in the larger airways.
*Transitional*
- **Transitional epithelium** is found in the **urinary bladder** and other parts of the urinary tract, allowing for stretching.
- It is not found in the respiratory tract and thus is not affected by smoking-induced metaplasia in the lungs.
*Simple squamous*
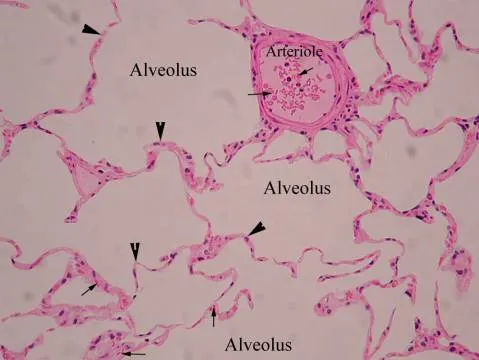
- **Simple squamous epithelium** lines the **alveoli**, facilitating gas exchange due to its thin, flat structure.
- While smoking can damage alveolar cells, the primary metaplastic change in response to chronic irritation occurs in the conducting airways, not in the alveoli.
*Stratified squamous*
- **Stratified squamous epithelium** is the *result* of metaplasia in the airways due to smoking, not the cell type undergoing the initial change.
- **Pseudostratified columnar epithelium** transforms into stratified squamous epithelium as a protective response to chronic irritation.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-month-old girl is brought by her mother to the local walk-in clinic after noticing a mass protruding from her vagina. The mass had the appearance of "a bunch of grapes". She also says that she has been having a vaginal discharge for the past 6 months. Her family and personal history are not significant for malignancies or inherited disorders. The physical examination is unremarkable except for the presence of soft nodules protruding from the vaginal canal. A tissue sample is obtained for histologic evaluation. Several weeks later the patient returns to the walk-in clinic for a scheduled follow-up visit. The pathology report describes a polypoid mass beneath an epithelial surface with atypical stromal cells positive for polyclonal desmin. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- B. Verrucous carcinoma
- C. Sarcoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Adenocarcinoma
- E. Melanoma
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Sarcoma***
- The description of a **"bunch of grapes"** mass in a young girl, along with **atypical stromal cells** positive for **polyclonal desmin**, is highly characteristic of **embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma** (a type of sarcoma botryoides).
- **Desmin positivity** indicates a muscle cell origin, and the **polypoid mass** is consistent with the gross appearance of this aggressive childhood tumor.
*Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)*
- SCC of the vagina is extremely rare in a **19-month-old girl** and typically affects older women.
- Histologically, SCC would show **dysplastic squamous epithelial cells** with **keratinization** or intercellular bridges, not atypical stromal cells positive for desmin.
*Verrucous carcinoma*
- This is a rare, well-differentiated variant of SCC, also typically occurring in **older individuals** and associated with HPV infection.
- It presents as a **warty, exophytic lesion** with minimal cellular atypia, distinct from a "bunch of grapes" mass and desmin positivity.
*Adenocarcinoma*
- Vaginal adenocarcinoma can occur in young girls, particularly **clear cell adenocarcinoma** associated with **diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure**; however, this patient has no such history.
- Histology would show glandular differentiation and mucin production, not atypical stromal cells expressing desmin.
*Melanoma*
- Vaginal melanoma is very rare, typically presenting as a **pigmented lesion** in postmenopausal women.
- Histopathology would reveal malignant melanocytes with **positive S-100 and HMB-45 staining**, not atypical stromal cells positive for desmin.
Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG Question 10: A 35-year-old woman presents to a pre-operative evaluation clinic prior to an elective cholecystectomy. She has a 5 pack-year smoking history. The anesthesiologist highly recommends to discontinue smoking for at least 8 weeks prior to the procedure for which she is compliant. What is the most likely histology of her upper respiratory tract's epithelial lining at the time of her surgery?
- A. Simple squamous
- B. Simple columnar
- C. Pseudostratified columnar (Correct Answer)
- D. Stratified squamous
- E. Stratified columnar
Simple epithelial tissues Explanation: ***Pseudostratified columnar***
- The upper respiratory tract is normally lined by **pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium** with goblet cells, which is crucial for mucociliary clearance.
- While smoking can initially cause **squamous metaplasia**, discontinuing smoking for 8 weeks allows for significant, if not complete, **reversal of these changes** back to the normal pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
*Simple squamous*
- This type of epithelium is found in areas designed for efficient **gas exchange** (e.g., alveoli of the lungs) and is not typical for the conductive airways of the upper respiratory tract.
- It lacks the **cilia and goblet cells** necessary for clearing inhaled particles and pathogens.
*Simple columnar*
- **Simple columnar epithelium** is found in regions like the lining of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., stomach, small and large intestines) and is not characteristic of the upper respiratory tract.
- While it can have goblet cells, it typically lacks **cilia** for respiratory clearance.
*Stratified squamous*
- **Stratified squamous epithelium** is found in areas subject to friction and abrasion, such as the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus.
- While chronic smoking can induce **squamous metaplasia** in the respiratory tract, an 8-week cessation period would likely result in the reversal of this change back to the normal type.
*Stratified columnar*
- **Stratified columnar epithelium** is a relatively rare type found in specific locations like parts of the male urethra and some large excretory ducts.
- It is not the normal or even a common metaplastic lining for the human upper respiratory tract.
More Simple epithelial tissues US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.