Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Extracellular matrix components. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 1: A 15-year-old boy presents with shortness of breath on exertion for the past 2 weeks. Although he does not have any other complaints, he is concerned about not gaining much weight despite a good appetite. His height is 188 cm (6 ft 2 in) and weight is 58 kg (124 lb). His blood pressure is 134/56 mm Hg and his pulse rate is 78/min. On cardiac auscultation, his apex beat is displaced laterally with a diastolic murmur lateral to the left sternal border. Slit-lamp examination shows an upward and outward displacement of both lenses. Synthesis of which of the following proteins is most likely defective in this patient?
- A. Fibronectin
- B. Elastin
- C. Fibrillin (Correct Answer)
- D. Reticular fibers
- E. Laminin
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Fibrillin***
- The patient's presentation with **tall stature**, **arachnodactyly** (implied by tall, thin build), **ectopia lentis** (upward and outward lens displacement), and a **diastolic murmur** (suggesting aortic root dilation or dissection, or mitral valve prolapse) are classic features of **Marfan syndrome**.
- **Marfan syndrome** is caused by a defect in the gene encoding **fibrillin-1**, a glycoprotein essential for the formation of elastic fibers and connective tissue integrity.
*Fibronectin*
- **Fibronectin** is involved in cell adhesion, growth, migration, and differentiation, and plays a crucial role in wound healing and embryonic development.
- While essential for connective tissue, defects in fibronectin are not typically associated with the constellation of symptoms seen in Marfan syndrome.
*Elastin*
- **Elastin** works in conjunction with fibrillin to provide elasticity to tissues like the skin, lungs, and blood vessels.
- While Marfan syndrome affects elastic fibers, the primary defect is in fibrillin, which then impairs the proper formation and function of elastin-containing microfibrils.
*Reticular fibers*
- **Reticular fibers** are fine collagen fibers (primarily type III collagen) that form a delicate supporting network in various tissues and organs.
- Defects in reticular fibers are not characteristic of Marfan syndrome; Marfan syndrome is specifically linked to fibrillin defects.
*Laminin*
- **Laminins** are major proteins of the **basal lamina**, essential for cell adhesion and differentiation in epithelial and endothelial tissues.
- Genetic defects in laminin components are often associated with muscular dystrophies or epidermolysis bullosa, not the Marfanoid features presented.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 2: Collagen is a very critical structural protein in many of our connective tissues. Defects in collagen produce diseases such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, where there is a defective lysyl hydroxylase gene, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where there is a defect in the production of type I collagen. Which of the following represents the basic repeating tripeptide of collagen?
- A. Gly-X-Y (Correct Answer)
- B. Asp-X-Y
- C. Met-X-Y
- D. Ser-X-Y
- E. Glu-X-Y
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Gly-X-Y***
- The **basic repeating tripeptide unit of collagen** is **Glycine-X-Y**, where X and Y are often **proline** and **hydroxyproline**, respectively.
- **Glycine** is essential at every third position because its small side chain allows for the tight packing of the **collagen triple helix**.
*Asp-X-Y*
- **Aspartate (Asp)** is an **acidic amino acid** and is not typically found at the first position of the repeating tripeptide unit of collagen.
- Its bulky side chain would hinder the tight coiling of the **collagen helix**.
*Met-X-Y*
- **Methionine (Met)** is a **hydrophobic amino acid** and, while important in other proteins, it does not occupy the critical first position in the repeating collagen tripeptide.
- The unique structural requirements of collagen favor **glycine** at this position for optimal packing.
*Ser-X-Y*
- **Serine (Ser)** is a **polar, uncharged amino acid** and, like aspartate and methionine, is not the primary amino acid found at the first position of the repeating collagen tripeptide.
- The small size of **glycine** is crucial for collagen's characteristic triple helix.
*Glu-X-Y*
- **Glutamate (Glu)** is another **acidic amino acid** that is not typically found at the first position of the repeating tripeptide in collagen.
- Large or charged amino acids at this position would destabilize the **collagen secondary structure**.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 3: A 62-year-old man with prostate cancer comes to the physician because of low back pain for 2 weeks and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows localized tenderness over the lumbar spine. An x-ray of the lumbar spine shows several osteoblastic lesions at the level of L2 and L4 vertebrae. Microscopic examination of a bone biopsy specimen from the L4 vertebra shows irregular bone trabeculae and star-shaped cells with long, cytoplasmic processes located deep within the lacunae. Exchange of nutrients and waste products between these cells most likely occurs through which of the following structures?
- A. Zonula adherens
- B. Macula adherens
- C. Macula communicans (Correct Answer)
- D. Zonula occludens
- E. Hemidesmosomes
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Macula communicans***
- The description of **star-shaped cells with long, cytoplasmic processes** located deep within lacunae refers to **osteocytes**. These cells communicate and exchange nutrients/waste products via **gap junctions**, also known as **macula communicans**.
- **Gap junctions** are essential for maintaining the viability of osteocytes embedded in the mineralized bone matrix by allowing the passage of small molecules and ions.
*Zonula adherens*
- This is an **adherens junction** that provides strong cell-to-cell adhesion, typically forming a continuous belt-like structure around the cell.
- Its primary role is mechanical adhesion, not the direct exchange of nutrients and waste products between cells.
*Macula adherens*
- Also known as a **desmosome**, this junction provides strong focal adhesion between cells, often in tissues subjected to mechanical stress.
- Like adherens junctions, its main function is structural integrity, not transepithelial transport or communication.
*Zonula occludens*
- This is a **tight junction**, which forms a seal between adjacent cells, preventing paracellular transport of molecules and maintaining cell polarity.
- While crucial for creating barriers, it does not facilitate direct communication or nutrient exchange between the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
*Hemidesmosomes*
- These junctions anchor epithelial cells to the **basement membrane**, providing strong adhesion between the cell and the extracellular matrix.
- Their function is cell-matrix adhesion, distinct from cell-to-cell communication for nutrient exchange.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 4: A 6-year-old boy with a history of multiple fractures is brought to his pediatrician by his mother, because she is concerned her child cannot hear her. On physical exam, kyphoscoliosis, poor dentition, bowing of long bones, and conductive hearing loss is noted. On genetic analysis, the patient has a COL1A1 gene mutation. The defect found in this patient is most likely associated with impaired formation of which of the following?
- A. Cartilage
- B. Vitreous body of the eye
- C. Lens
- D. Bone (Correct Answer)
- E. Sclera
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Bone***
- This patient has **osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)** due to a **COL1A1 gene mutation** affecting **Type I collagen** synthesis.
- **Bone** is composed primarily of Type I collagen (~90% of the organic matrix), and its formation is **severely impaired** in OI.
- The major clinical manifestations all result from defective bone formation: **multiple fractures**, **kyphoscoliosis**, **bowing of long bones**, and poor bone mineralization.
- The **conductive hearing loss** results from abnormal ossicle development and otosclerosis-like changes in the temporal bone.
- **Poor dentition** is also related to defective Type I collagen in dentin (dentinogenesis imperfecta).
*Sclera*
- While the **sclera** does contain Type I collagen and appears **blue** in OI due to thinning (allowing choroidal vessels to show through), this is a clinical sign rather than the primary site of impaired formation.
- Blue sclera is a diagnostic feature but not the main pathology - it's a visible manifestation of the collagen defect, not the primary tissue with impaired formation.
*Cartilage*
- **Cartilage** is primarily composed of **Type II collagen**, not Type I collagen.
- Defects in Type II collagen cause **chondrodysplasias**, which present differently from this clinical picture.
*Vitreous body of the eye*
- The **vitreous body** is primarily composed of **Type II collagen** and hyaluronic acid.
- It is not primarily affected by Type I collagen defects.
*Lens*
- The **lens** relies primarily on **crystallin proteins** for its structure, not collagen.
- **Lens dislocation** (ectopia lentis) is associated with **Marfan syndrome** (defective fibrillin-1) and **homocystinuria**, not osteogenesis imperfecta.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 5: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He started walking at 20 months of age. He can use a cup to drink but cannot use silverware. He speaks in 2-word sentences and can build a tower of 4 blocks. He can scribble but cannot draw a circle. He is above the 99th percentile for height and at the 15th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows bilateral inferior lens dislocation. His fingers are long and slender. He has a high-arched palate. The thumb and 5th finger overlap when he grips a wrist with the opposite hand. The skin over the neck can be extended and stretched easily. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency
- B. Galactokinase deficiency
- C. Fibrillin 1 deficiency
- D. Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Type V collagen deficiency
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Cystathionine synthase deficiency***
- The combination of **inferior lens dislocation**, **marfanoid habitus** (tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate), **developmental delay** (late walking, speech delay), and **hyperelastic skin** is highly suggestive of **homocystinuria** due to cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- **Homocystinuria** is an autosomal recessive disorder causing accumulation of **homocysteine**, leading to multisystem involvement.
*Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**, characterized by **gout, intellectual disability, choreoathetosis, and self-mutilation**.
- It does not present with lens dislocation or marfanoid features.
*Galactokinase deficiency*
- This is a rare form of **galactosemia** primarily causing **cataracts**.
- It does not explain the developmental delay, marfanoid features, or lens dislocation.
*Fibrillin 1 deficiency*
- This causes **Marfan syndrome**, which shares features like **tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate, and lens dislocation**.
- However, in Marfan syndrome, lens dislocation is typically **superior**, while in this case, it is **inferior**, pointing towards homocystinuria.
*Type V collagen deficiency*
- This can be associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome**, which features **hyperelastic skin** and joint hypermobility.
- However, it does not typically cause lens dislocation or the specific marfanoid habitus described, and developmental delay is not a primary feature.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 6: A 5-year-old boy presents to a pediatric orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of spinal curvature. His primary care physician noticed during an annual checkup that the boy's shoulders were uneven, and radiograph revealed early onset scoliosis. His past medical history is significant for multiple fractures as well as short stature. Based on the early presentation of scoliosis and the unusual history of fractures, the surgeon orders further workup and discovers a genetic mutation in an extracellular protein. This protein exists in two different forms. The first is an insoluble dimer that is linked by disulfide bonds and links integrins to the extracellular matrix. The second is a soluble protein that assists with clotting. Based on these descriptions, which of the following proteins is most likely mutated in this patient?
- A. Type 1 collagen
- B. Type 3 collagen
- C. Fibronectin (Correct Answer)
- D. Fibrillin
- E. Elastin
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Fibronectin***
- **Fibronectin** uniquely exists in **two distinct forms**: an **insoluble dimeric form** (linked by disulfide bonds) in the extracellular matrix that binds **integrins** and connects them to matrix components, AND a **soluble plasma form** that participates in **blood clotting, wound healing, and opsonization**.
- This dual existence (insoluble ECM dimer + soluble plasma protein involved in clotting) is the **key distinguishing feature** that matches the biochemical description in the question.
- Fibronectin mutations can affect connective tissue integrity and skeletal development, though they are rare.
*Type 1 collagen*
- **Type 1 collagen** is the most abundant collagen, crucial for **bone, skin, tendons**, and ligaments. Mutations cause **osteogenesis imperfecta** with brittle bones, fractures, and short stature.
- While clinically this matches the patient's presentation, Type 1 collagen does **NOT exist as a soluble protein involved in clotting**, which is explicitly stated in the question stem.
- It forms insoluble triple-helix fibrils but lacks the soluble clotting form described.
*Type 3 collagen*
- **Type 3 collagen** is found in **distensible tissues** (blood vessels, intestines, skin). Mutations cause **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV** with vascular fragility.
- It forms fibrillar structures in the ECM but does **NOT have a soluble form involved in blood clotting**.
- Does not match the dual-form requirement in the question.
*Fibrillin*
- **Fibrillin** is a major component of **microfibrils** in elastic fibers, providing structural support. Mutations cause **Marfan syndrome** (tall stature, arachnodactyly, cardiovascular issues).
- While it is an ECM component, fibrillin does **NOT exist as a soluble clotting protein**.
- Does not fulfill both biochemical criteria stated in the question.
*Elastin*
- **Elastin** provides **elasticity and resilience** to tissues (skin, blood vessels, lungs) and forms the core of elastic fibers.
- Elastin does **NOT link integrins to the ECM** in the manner described, nor does it have a **soluble form involved in clotting**.
- Does not match either key biochemical feature described.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 7: A 69-year-old man comes to the physician with a 2-year history of progressive hearing loss. His hearing is worse in crowded rooms, and he has noticed that he has more difficulty understanding women than men. He has no history of serious illness and does not take any medications. A Rinne test shows air conduction is greater than bone conduction bilaterally. This condition is most likely associated with damage closest to which of the following structures?
- A. Tympanic membrane
- B. Round window
- C. Base of the stapes
- D. External acoustic meatus
- E. Basal turn of the cochlea (Correct Answer)
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Basal turn of the cochlea***
- The patient's presentation of progressive hearing loss, difficulty hearing in crowded rooms (**presbycusis**), and trouble understanding women's voices (higher frequencies) is characteristic of **sensorineural hearing loss**.
- The **basal turn of the cochlea** is responsible for detecting high-frequency sounds, making it the most likely site of damage in presbycusis.
*Tympanic membrane*
- Damage to the **tympanic membrane** would typically result in a **conductive hearing loss**, characterized by bone conduction being greater than air conduction (abnormal Rinne test).
- The patient's Rinne test shows air conduction greater than bone conduction, indicating a sensorineural or normal hearing pattern.
*Round window*
- The **round window** plays a role in relieving pressure in the cochlea, allowing fluid movement and sound transmission.
- While damage here can affect hearing, it's not the primary site of progressive, age-related high-frequency sensorineural loss.
*Base of the stapes*
- Issues at the **base of the stapes**, particularly **otosclerosis**, cause **conductive hearing loss** due to the ossification of the oval window, hindering sound transmission.
- This would present with an abnormal Rinne test (BC > AC), which is not observed in this patient.
*External acoustic meatus*
- Obstruction or damage to the **external acoustic meatus** (e.g., earwax impaction, otitis externa) would cause a **conductive hearing loss**.
- The Rinne test would show bone conduction greater than air conduction, which is inconsistent with the patient's findings.
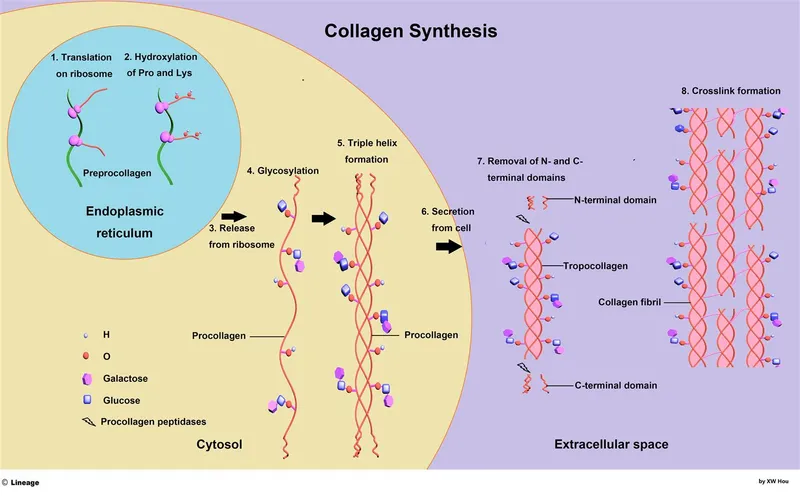
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 8: A 3-month-old infant presents with severe joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and delayed wound healing. Skin biopsy shows abnormal collagen fibril organization with irregular diameter and reduced tensile strength. Genetic testing reveals a mutation affecting lysyl hydroxylase, an enzyme involved in collagen post-translational modification. The family asks about prognosis and potential complications. Synthesize the biochemical defect with clinical manifestations to determine the most critical pathophysiological mechanism.
- A. Impaired collagen synthesis at the ribosomal level
- B. Defective hydroxylation of lysine residues preventing stable collagen cross-linking (Correct Answer)
- C. Excessive collagen degradation by matrix metalloproteinases
- D. Abnormal glycosylation affecting collagen secretion
- E. Impaired procollagen cleavage preventing fibril formation
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Defective hydroxylation of lysine residues preventing stable collagen cross-linking***
- **Lysyl hydroxylase** is essential for the post-translational hydroxylation of lysine; its deficiency impairs the formation of **hydroxylysine**, which is crucial for stable **covalent cross-linking**.
- This biochemical defect results in **reduced tensile strength** of collagen fibrils, leading to the classic clinical triad of **joint hypermobility**, **skin hyperextensibility**, and **delayed wound healing** seen in Kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
*Impaired collagen synthesis at the ribosomal level*
- Ribosomal synthesis pertains to the translation of **pre-procollagen** alpha chains; however, this patient has a post-translational enzyme mutation.
- Defects at the **ribosomal level** would lead to a quantitative lack of protein rather than the **abnormal fibril organization** and diameter irregularities described.
*Excessive collagen degradation by matrix metalloproteinases*
- **Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)** are involved in tissue remodeling and chronic inflammation, not primary genetic collagen disorders.
- While MMP activity can affect tissue integrity, the clinical presentation and **genetic testing** specifically point to a synthesis/modification defect, not an overactive degradation pathway.
*Abnormal glycosylation affecting collagen secretion*
- **Glycosylation** occurs on hydroxylysine residues in the Golgi apparatus; while related to post-translational modification, it is not the primary function of **lysyl hydroxylase**.
- Primary defects in collagen **glycosylation** or **secretion** usually present with more severe multi-systemic growth delays rather than the specific mechanical fragility seen here.
*Impaired procollagen cleavage preventing fibril formation*
- This mechanism describes **Arthrochalasia** or **Dermatosparaxis** types of EDS, where **procollagen N-peptidase** or C-peptidase is deficient.
- Failure to cleave **terminal propeptides** prevents the formation of insoluble tropocollagen, but this is distinct from the **lysyl hydroxylase** deficiency identified by this patient's genetic testing.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 9: A 58-year-old woman undergoes cervical biopsy following an abnormal Pap smear. Histology shows full-thickness epithelial atypia with loss of cellular polarity, increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, and numerous mitotic figures, but the basement membrane remains intact. Her oncologist discusses treatment options. The patient is concerned about progression risk versus overtreatment. Evaluate the most appropriate management strategy considering the tissue diagnosis and natural history.
- A. Observation only as basement membrane is intact
- B. Excisional procedure (LEEP or cone biopsy) with close surveillance (Correct Answer)
- C. Immediate radical hysterectomy
- D. Radiation therapy to prevent invasion
- E. Chemotherapy followed by reassessment
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Excisional procedure (LEEP or cone biopsy) with close surveillance***
- The histology describes **CIN 3 (full-thickness atypia)**; since the **basement membrane is intact**, it is a high-grade pre-invasive lesion requiring definitive treatment to prevent progression to invasive cancer.
- An **excisional procedure** like **LEEP** or **cone biopsy** is the standard management to both treat the lesion and provide a complete specimen for histological review to rule out occult invasion.
*Observation only as basement membrane is intact*
- Observation is inappropriate for **CIN 3** because the risk of spontaneous progression to **invasive carcinoma** is significantly high.
- **Full-thickness atypia** necessitates active intervention, unlike lower-grade lesions (CIN 1) which may be monitored via surveillance.
*Immediate radical hysterectomy*
- A **radical hysterectomy** is considered overtreatment for a diagnosis where the **basement membrane is intact** (carcinoma in situ/CIN 3).
- Such invasive surgery is reserved for confirmed **invasive cervical cancer** cases, not for pre-invasive lesions that can be managed by local excision.
*Radiation therapy to prevent invasion*
- **Radiation therapy** is not indicated for **pre-invasive lesions** and is associated with significant long-term morbidity in the pelvic region.
- Primary management for **HSIL/CIN 3** is surgical excision, reserving radiation for higher-stage **invasive malignancies**.
*Chemotherapy followed by reassessment*
- There is no clinical role for **neoadjuvant chemotherapy** in the management of **cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)**.
- Management is strictly **surgical (excisional or ablative)** to remove the dysplastic cells before they can acquire the ability to invade the stroma.
Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old woman with Marfan syndrome presents to the emergency department with acute chest pain. CT angiography reveals a Type A aortic dissection. The cardiothoracic surgeon explains that her underlying connective tissue disorder predisposed her to this complication. During surgery, the aortic wall appears thin and fragile. Evaluate which molecular defect best explains the compromised structural integrity of her aortic wall.
- A. Deficient type I collagen synthesis reducing tensile strength
- B. Abnormal fibrillin-1 causing defective elastic fiber assembly and excessive TGF-β signaling (Correct Answer)
- C. Excessive collagenase activity degrading structural proteins
- D. Impaired proteoglycan synthesis reducing ground substance
- E. Defective type IV collagen affecting basement membrane stability
Extracellular matrix components Explanation: ***Abnormal fibrillin-1 causing defective elastic fiber assembly and excessive TGF-β signaling***
- **Marfan syndrome** results from mutations in the **FBN1 gene**, which codes for **fibrillin-1**, a glycoprotein that serves as a scaffold for **elastin** in the extracellular matrix.
- Defects in fibrillin-1 lead to impaired **microfibril** assembly and increased **TGF-β** bioavailability, causing **cystic medial necrosis** and structural failure of the aortic wall.
*Deficient type I collagen synthesis reducing tensile strength*
- This defect is the hallmark of **Osteogenesis Imperfecta**, which presents with **fragile bones**, blue sclerae, and hearing loss.
- While **Type I collagen** provides tensile strength to many tissues, it is not the primary molecular deficit responsible for the aortic fragility seen in **Marfan syndrome**.
*Excessive collagenase activity degrading structural proteins*
- Excessive **matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)** activity can contribute to tissue remodeling, but it is a secondary process rather than the primary genetic defect.
- This mechanism is more associated with inflammatory conditions or the late stages of **atherosclerotic aneurysm** formation rather than Marfan-specific dissection.
*Impaired proteoglycan synthesis reducing ground substance*
- While the aortic media in Marfan syndrome shows an accumulation of **glycosaminoglycans** (mucoid material), this is a result of the pathology (**cystic medial necrosis**) rather than impaired synthesis.
- Proteoglycans normally provide compressive strength, and their reduction is not the root cause of the **elastic fiber** fragmentation seen in this patient.
*Defective type IV collagen affecting basement membrane stability*
- Mutations in **Type IV collagen** are characteristic of **Alport syndrome**, which primarily affects the **glomerular basement membrane**, eyes, and inner ear.
- Type IV collagen is a major component of **basement membranes** and does not play a chief role in the large-vessel structural integrity of the **aortic media**.
More Extracellular matrix components US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.