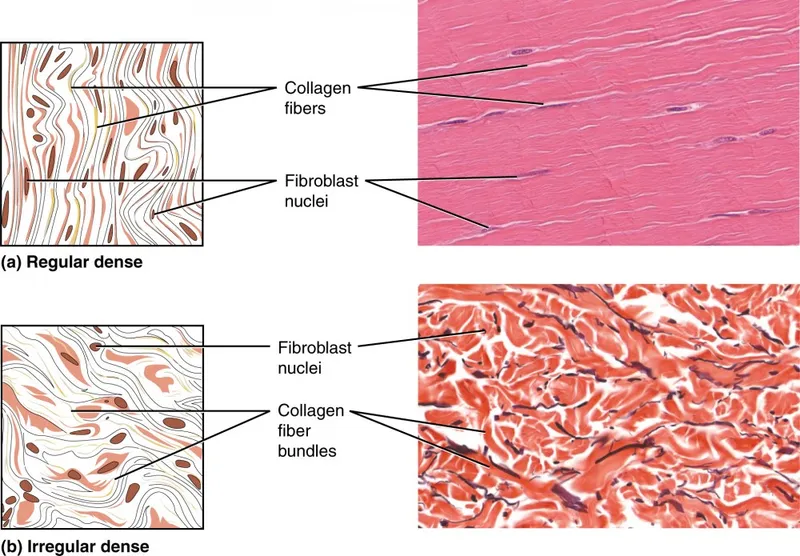
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Dense connective tissue. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old man comes to his doctor because of 2 weeks of progressively worsening pain on the outer side of his right elbow. He does not recall any trauma to the area. The patient plays tennis recreationally and has recently gone from playing weekly to playing daily in preparation for a local tournament. He has had some pain relief with ibuprofen. On physical examination, there is tenderness over the lateral surface of the right distal humerus. The pain is reproduced by supinating the forearm against resistance. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Bursal inflammation
- B. Nerve compression at the elbow
- C. Repeated wrist flexion
- D. Repeated wrist extension (Correct Answer)
- E. Excessive stress to bone
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Repeated wrist extension***
- This patient's symptoms (pain on the **outer side of the elbow**, tenderness over the **lateral epicondyle**, pain with resisted **supination**) are classic for **lateral epicondylitis**, also known as **tennis elbow**.
- Lateral epicondylitis is an **overuse injury** caused by repetitive microtrauma to the **extensor tendons** of the forearm, particularly the **extensor carpi radialis brevis**, which originate from the **lateral epicondyle** and are heavily involved in **wrist extension** and supination (as seen in tennis activities).
*Bursal inflammation*
- **Bursitis** at the elbow typically presents as swelling and tenderness over the **olecranon bursa** (posterior elbow) rather than the lateral epicondyle.
- Pain is usually reproduced by direct compression of the bursa or flexion of the elbow, not specifically by resisted supination.
*Nerve compression at the elbow*
- **Nerve compression** at the elbow (e.g., ulnar neuropathy, radial tunnel syndrome) typically causes **neuropathic symptoms** such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the distribution of the affected nerve.
- While radial tunnel syndrome can cause pain near the lateral epicondyle, it is often described as a deeper, aching pain and does not typically involve tenderness directly over the epicondyle or pain with resisted supination in the same manner as epicondylitis.
*Repeated wrist flexion*
- Repeated wrist flexion is associated with **medial epicondylitis** (golfer's elbow), which causes pain on the **inner side of the elbow** and tenderness over the **medial epicondyle**.
- This condition affects the **flexor-pronator mass** of the forearm, not the extensor tendons on the lateral side.
*Excessive stress to bone*
- While excessive stress can lead to **stress fractures**, these are less common in the elbow joint in this context and typically present with persistent, localized bone pain that worsens with activity and may show up on imaging.
- The patient's specific symptoms of **tenderness at the epicondyle** and pain with resisted movement are more indicative of a soft tissue, **tendinous injury** rather than a primary bone pathology.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 2: A 30-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 month after sustaining a chemical burn over the dorsum of his right hand and forearm. Physical examination shows hyperextension of the hand at the wrist. The skin over the dorsum of the wrist is tense and there is a thick, epithelialized scar. Range of motion of the right wrist is restricted. This patient's contracture is most likely due to activity of which of the following cells?
- A. Fibroblasts
- B. Myofibroblasts (Correct Answer)
- C. Neutrophils
- D. Macrophages
- E. Endothelial cells
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Myofibroblasts***
- The patient presents with a **contracture** (restricted range of motion and hyperextension of the hand due to a thick scar) after a burn, which is characteristic of the action of **myofibroblasts**.
- Myofibroblasts are specialized cells that possess features of both fibroblasts (synthesizing **collagen** and extracellular matrix) and smooth muscle cells (containing **actin microfilaments**), allowing them to exert contractile force which leads to scar contraction.
*Fibroblasts*
- While fibroblasts are crucial for **wound healing** by producing collagen and other extracellular matrix components, they primarily lay down the foundation for scar tissue.
- They lack the strong contractile capabilities that lead to significant **tissue retraction** and contracture.
*Neutrophils*
- Neutrophils are **acute inflammatory cells** that primarily function in the early stages of wound healing to phagocytose debris and pathogens.
- They do not play a direct role in the formation of **scar tissue** or **contractures**.
*Macrophages*
- Macrophages are important **immune cells** involved in clearing debris, presenting antigens, and releasing growth factors during the later stages of wound healing.
- They also influence fibroblast activity, but they do not directly cause **tissue contraction** or scar formation.
*Endothelial cells*
- Endothelial cells line **blood vessels** and are essential for **angiogenesis** (formation of new blood vessels) during wound healing.
- They are not involved in the **contractile process** that leads to scar contracture.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 3: A 5-year-old girl accompanied by her mother presents to the emergency department after suffering a fall on the elementary school playground. Her mother reports that a child on the playground pushed her daughter who fell on her right side, after which she screamed and was found clutching her right leg. The girl's past medical history is significant for a fracture of the left femur and right radius over the past 2 years and an auditory deficit requiring hearing aid use starting 6 months ago. Inspection reveals a relatively short girl in moderate distress. She has brown opalescent teeth. She refuses to bear weight on her right lower extremity. Radiography of the right lower extremity reveals a femoral midshaft fracture. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of the patient's condition?
- A. Decreased cystathionine beta synthase activity
- B. Vitamin D deficiency
- C. Fibrillin gene defect
- D. Defective type I collagen production (Correct Answer)
- E. Type III collagen gene defect
Dense connective tissue Explanation: **Defective type I collagen production**
- The patient's history of **recurrent fractures** from minor trauma, **auditory deficit**, and **brown opalescent teeth** (dentinogenesis imperfecta) are classic manifestations of **osteogenesis imperfecta**, a genetic disorder characterized by **defective type I collagen production**.
- **Type I collagen** is a major component of bone, dentin, and the sclera, and its deficiency leads to brittle bones, hearing loss due to ossicle abnormalities, and dental defects.
*Decreased cystathionine beta synthase activity*
- This condition describes **homocystinuria**, which can present with skeletal abnormalities and developmental delays.
- However, typical features include **marfanoid habitus**, **lens luxation**, and **thromboembolic events**, which are not reported in this patient.
*Vitamin D deficiency*
- **Vitamin D deficiency** leads to **rickets** in children, characterized by bone pain, muscle weakness, and skeletal deformities but typically presents with **bowing of legs**, **rachitic rosary**, and **craniotabes**, not recurrent fractures from minor trauma or opalescent teeth.
- While it weakens bones, the constellation of symptoms here, especially dental and auditory deficits, points away from simple vitamin D deficiency.
*Fibrillin gene defect*
- A **fibrillin gene defect** is characteristic of **Marfan syndrome**, which presents with **long limbs**, **arachnodactyly**, **lens luxation**, and **aortic root dilation**.
- While it involves connective tissue, it does not typically cause the bone fragility and dental findings seen in this patient.
*Type III collagen gene defect*
- A **type III collagen gene defect** is associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, vascular type**, which features **easy bruising**, **fragile blood vessels**, and **organ rupture**.
- This condition leads to hypermobility and skin hyperextensibility, but not the specific combination of brittle bones, hearing loss, and dental defects seen in this patient.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 4: During the examination of a gunshot wound, the forensic pathologist notes an entrance wound with abrasion collar and soot deposition. The wound shows a stellate-shaped pattern with irregular margins. This pattern most likely indicates which of the following?
- A. Ricochet injury
- B. Long-range firing
- C. Intermediate-range firing
- D. Contact wound (Correct Answer)
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Contact wound***
- A **stellate-shaped pattern with irregular margins** is the pathognomonic feature of a **contact wound** where the muzzle is pressed directly against the skin.
- When the weapon is fired in contact with skin, **hot gases expand beneath the skin surface**, causing it to burst outward in a characteristic **stellate or cruciate laceration pattern**.
- The presence of **soot deposition** and **abrasion collar** further supports a contact or near-contact gunshot wound.
- In contact wounds over bone (e.g., skull), the stellate pattern is most pronounced due to resistance from underlying bone.
*Intermediate-range firing*
- **Intermediate-range firing** (typically 6 inches to 3 feet) shows **powder tattooing** (stippling) and may show soot deposition around a round or oval entrance wound.
- However, intermediate-range wounds do **NOT produce stellate-shaped patterns** because the gases disperse before impact and don't expand beneath the skin.
- The entrance wound remains relatively round with surrounding powder stippling.
*Ricochet injury*
- A **ricochet injury** has an irregular, asymmetrical entrance wound due to bullet deformation and altered trajectory after striking another surface.
- Would not show the characteristic stellate pattern or typical soot distribution of direct firing.
*Long-range firing*
- **Long-range firing** produces only a clean entrance wound with an **abrasion collar**, without soot or powder tattooing.
- The distance is too great for combustion byproducts to reach the target.
- The wound is typically round or oval without stellate laceration.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 5: A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room by his parents after slipping on a rug at home and experiencing exquisite pain and swelling of his arms. Radiographs reveal a new supracondylar fracture of the humerus, as well as indications of multiple, old fractures that have healed. His parents note that an inherited disorder is present in their family history. A comprehensive physical exam also reveals blue-tinted sclera and yellow-brown, discolored teeth. What is the etiology of the patient’s disorder?
- A. Defect in the glycoprotein that forms a sheath around elastin
- B. Deficiency of type 3 procollagen
- C. Defect in the hydroxylation step of collagen synthesis
- D. Deficiency of type 1 collagen (Correct Answer)
- E. Deficiency of type 5 collagen
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Deficiency of type 1 collagen***
- This patient presents with a history of **multiple fractures**, **blue sclera**, and **discolored teeth**, which are classic signs of **osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)**.
- OI is most commonly caused by **mutations in COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes**, leading to **quantitative or qualitative defects in type I collagen synthesis**, which is a major structural component of bone, sclera, and dentin.
- This represents the primary molecular defect in the majority of OI cases.
*Defect in the glycoprotein that forms a sheath around elastin*
- This defect is characteristic of **Marfan syndrome**, which typically presents with **tall stature**, **arachnodactyly**, and **cardiovascular abnormalities** (e.g., aortic root dilation).
- The clinical presentation with multiple fractures and blue sclera does not align with Marfan syndrome.
*Deficiency of type 3 procollagen*
- A deficiency in type III procollagen is associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, vascular type**, which primarily involves **fragile blood vessels**, **rupture of internal organs**, and **easy bruising**.
- This does not explain the patient's severe bone fragility or blue sclera.
*Defect in the hydroxylation step of collagen synthesis*
- Defects in collagen hydroxylation can occur due to **vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)** or mutations in hydroxylase enzymes (e.g., **LEPRE1** in some rare OI types).
- While certain rare forms of OI can involve hydroxylation defects, the **classic presentation** with blue sclera and dentinogenesis imperfecta is most characteristic of **primary structural mutations in type I collagen genes** (COL1A1/COL1A2), making "deficiency of type 1 collagen" the more precise answer for this patient's etiology.
*Deficiency of type 5 collagen*
- Deficiency of type V collagen is associated with the **classical type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome**, characterized primarily by **skin hyperextensibility** and **joint hypermobility**.
- While it is a collagen disorder, it does not typically present with the severe bone fragility and blue sclera seen in this patient.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old man with prostate cancer comes to the physician because of low back pain for 2 weeks and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows localized tenderness over the lumbar spine. An x-ray of the lumbar spine shows several osteoblastic lesions at the level of L2 and L4 vertebrae. Microscopic examination of a bone biopsy specimen from the L4 vertebra shows irregular bone trabeculae and star-shaped cells with long, cytoplasmic processes located deep within the lacunae. Exchange of nutrients and waste products between these cells most likely occurs through which of the following structures?
- A. Zonula adherens
- B. Macula adherens
- C. Macula communicans (Correct Answer)
- D. Zonula occludens
- E. Hemidesmosomes
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Macula communicans***
- The description of **star-shaped cells with long, cytoplasmic processes** located deep within lacunae refers to **osteocytes**. These cells communicate and exchange nutrients/waste products via **gap junctions**, also known as **macula communicans**.
- **Gap junctions** are essential for maintaining the viability of osteocytes embedded in the mineralized bone matrix by allowing the passage of small molecules and ions.
*Zonula adherens*
- This is an **adherens junction** that provides strong cell-to-cell adhesion, typically forming a continuous belt-like structure around the cell.
- Its primary role is mechanical adhesion, not the direct exchange of nutrients and waste products between cells.
*Macula adherens*
- Also known as a **desmosome**, this junction provides strong focal adhesion between cells, often in tissues subjected to mechanical stress.
- Like adherens junctions, its main function is structural integrity, not transepithelial transport or communication.
*Zonula occludens*
- This is a **tight junction**, which forms a seal between adjacent cells, preventing paracellular transport of molecules and maintaining cell polarity.
- While crucial for creating barriers, it does not facilitate direct communication or nutrient exchange between the cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
*Hemidesmosomes*
- These junctions anchor epithelial cells to the **basement membrane**, providing strong adhesion between the cell and the extracellular matrix.
- Their function is cell-matrix adhesion, distinct from cell-to-cell communication for nutrient exchange.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He started walking at 20 months of age. He can use a cup to drink but cannot use silverware. He speaks in 2-word sentences and can build a tower of 4 blocks. He can scribble but cannot draw a circle. He is above the 99th percentile for height and at the 15th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows bilateral inferior lens dislocation. His fingers are long and slender. He has a high-arched palate. The thumb and 5th finger overlap when he grips a wrist with the opposite hand. The skin over the neck can be extended and stretched easily. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency
- B. Galactokinase deficiency
- C. Fibrillin 1 deficiency
- D. Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Type V collagen deficiency
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Cystathionine synthase deficiency***
- The combination of **inferior lens dislocation**, **marfanoid habitus** (tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate), **developmental delay** (late walking, speech delay), and **hyperelastic skin** is highly suggestive of **homocystinuria** due to cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- **Homocystinuria** is an autosomal recessive disorder causing accumulation of **homocysteine**, leading to multisystem involvement.
*Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**, characterized by **gout, intellectual disability, choreoathetosis, and self-mutilation**.
- It does not present with lens dislocation or marfanoid features.
*Galactokinase deficiency*
- This is a rare form of **galactosemia** primarily causing **cataracts**.
- It does not explain the developmental delay, marfanoid features, or lens dislocation.
*Fibrillin 1 deficiency*
- This causes **Marfan syndrome**, which shares features like **tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate, and lens dislocation**.
- However, in Marfan syndrome, lens dislocation is typically **superior**, while in this case, it is **inferior**, pointing towards homocystinuria.
*Type V collagen deficiency*
- This can be associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome**, which features **hyperelastic skin** and joint hypermobility.
- However, it does not typically cause lens dislocation or the specific marfanoid habitus described, and developmental delay is not a primary feature.
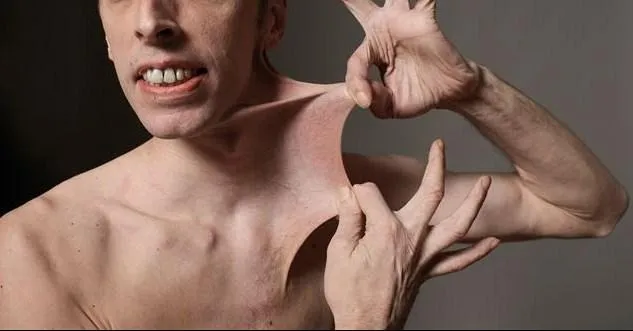
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset severe pain in the right shoulder that occurred when he threw a bowling ball 2 hours ago. He has a history of dislocations in both shoulders and subluxation of the right knee and left wrist. There is no history of fractures. On physical examination, the right arm is slightly abducted and externally rotated. An anterior bulge is seen near the shoulder joint. The neurovascular examination of the right arm shows no abnormalities. The skin examination shows multiple widened atrophic scars around the knees, elbows, and ankles. The skin of the neck and around the elbow can easily be extended up to 4 cm. The sclera is white. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. A defect in which of the following proteins is the most likely cause of the findings in this patient?
- A. Collagen (Correct Answer)
- B. Keratin
- C. Fibrillin-1
- D. Tau
- E. Elastin
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Collagen***
- This patient's symptoms, including **recurrent dislocations**, easy **skin extensibility**, and **atrophic scars**, are classic signs of **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS)**, which is primarily caused by defects in **collagen synthesis or processing**.
- The shoulder dislocation from a minor activity (throwing a bowling ball), along with multisystem hypermobility (shoulders, knee, wrist), strongly points to a **connective tissue disorder** affecting collagen.
*Keratin*
- **Keratin** is a structural protein primarily found in **epithelial cells**, forming hair, skin, and nails.
- Defects in keratin typically manifest as disorders of **skin fragility**, such as **epidermolysis bullosa**, not joint hypermobility or tissue extensibility.
*Fibrillin-1*
- **Fibrillin-1** defects cause **Marfan syndrome**, characterized by **tall stature**, **arachnodactyly**, **aortic root dilation**, and **lens dislocation**.
- While Marfan syndrome involves connective tissue, the patient's presentation of easy skin extensibility and atrophic scars is not characteristic of fibrillin-1 defects, and there is no mention of cardiovascular or ocular issues typical of Marfan.
*Tau*
- **Tau protein** is a **microtubule-associated protein** primarily found in neurons and is involved in stabilizing microtubules.
- Defects or abnormal aggregation of tau protein are associated with **neurodegenerative diseases** like **Alzheimer's disease** and **frontotemporal dementia**, not connective tissue disorders.
*Elastin*
- **Elastin** provides elasticity to tissues, allowing them to stretch and recoil. Defects can lead to conditions like **cutis laxa** or **Williams syndrome**.
- While some features of increased skin extensibility might overlap, the constellation of recurrent joint dislocations and specific atrophic scars seen in this patient is more indicative of **collagen defects** common in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 9: A 16-year-old male presents to an ophthalmologist as a new patient with a complaint of blurry vision. He reports that over the past several months he has had increasing difficulty seeing the board from the back of the classroom at school. The patient is otherwise doing well in school and enjoys playing basketball. His past medical history is otherwise significant for scoliosis which is managed by an orthopedic surgeon. His family history is significant for a mother with type II diabetes mellitus, and a father who underwent aortic valve replacement last year. On physical exam, the patient is tall for his age and has long arms. He has 20 degrees of thoracic scoliosis, which is stable from previous exams. On slit-lamp examination, the patient is found to have bilateral upward lens subluxation and is prescribed corrective lenses.
Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Extra copy of sex chromosome
- B. Mutation of gene on chromosome 15 (Correct Answer)
- C. Mutation of COL5A1 or COL5A2
- D. Defective metabolism of methionine
- E. Mutation of RET proto-oncogene
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Mutation of gene on chromosome 15***
- The patient's presentation with **tall stature**, **long arms** (dolichostenomelia), **scoliosis**, and **bilateral upward lens subluxation** are classic features of **Marfan syndrome**.
- Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a mutation in the *FBN1* gene located on **chromosome 15**, which encodes for **fibrillin-1**, a glycoprotein essential for connective tissue formation.
*Extra copy of sex chromosome*
- An extra copy of a sex chromosome, such as in **Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)**, is associated with tall stature and disproportionately long limbs, but it typically presents with **hypogonadism**, infertility, and learning difficulties, not lens subluxation or significant scoliosis as the primary features.
- Patients with Klinefelter syndrome often have a **eunuchoid body habitus** and gynecomastia, which are not described in this patient.
*Mutation of COL5A1 or COL5A2*
- Mutations in *COL5A1* or *COL5A2* are associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (classical type)**, which primarily features **skin hyperextensibility**, delayed wound healing, and **joint hypermobility**.
- While some forms of Ehlers-Danlos can have ocular involvement (e.g., easy bruising, scleral fragility), **lens subluxation** and the specific tall, slender build with scoliosis are not characteristic clinical features.
*Defective metabolism of methionine*
- A defective metabolism of methionine is characteristic of **homocystinuria**, an autosomal recessive disorder.
- Homocystinuria also causes **tall stature**, **scoliosis**, and **lens subluxation**, but the subluxation is typically **downward and inward**, differentiating it from the upward subluxation seen in Marfan syndrome. Patients also have an increased risk of **thromboembolic events** and **intellectual disability**.
*Mutation of RET proto-oncogene*
- Mutations of the *RET* proto-oncogene are associated with **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2)**.
- MEN2 presents with specific endocrine tumors such as **medullary thyroid carcinoma**, **pheochromocytoma**, and **parathyroid hyperplasia**, and does not involve the skeletal or ocular abnormalities described in this patient.
Dense connective tissue US Medical PG Question 10: A 1-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for the evaluation of recurrent seizures. He is at the 5th percentile for height and 10th percentile for weight. Examination shows coarse pale hair, inelastic hypopigmented skin, and generalized hypotonia. Laboratory studies show low serum ceruloplasmin levels. Decreased activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
- A. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
- B. Lysyl oxidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Glucocerebrosidase
- D. Prolyl hydroxylase
- E. Homogentisate oxidase
Dense connective tissue Explanation: ***Lysyl oxidase***
- This patient's presentation with **recurrent seizures**, **growth failure**, **coarse pale hair**, **hypopigmented skin**, **generalized hypotonia**, and **low serum ceruloplasmin** is highly suggestive of **Menkes disease**.
- **Menkes disease** is an X-linked recessive disorder of copper metabolism, resulting from a defect in the **ATP7A gene**. This defect leads to impaired copper transport from intestinal cells, causing copper deficiency, which in turn reduces the activity of copper-dependent enzymes, including **lysyl oxidase**.
*Phenylalanine hydroxylase*
- A deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase** causes **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which involves an accumulation of phenylalanine.
- PKU typically presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor, but not the specific skin and hair findings or low ceruloplasmin seen in this case.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- A deficiency in **glucocerebrosidase** is responsible for **Gaucher disease**, a lysosomal storage disorder.
- Gaucher disease presents with hepatosplenomegaly, bone crises, and neurological symptoms in some types, which are not the primary features here.
*Prolyl hydroxylase*
- **Prolyl hydroxylase** is involved in the hydroxylation of proline residues during collagen synthesis.
- Deficiencies or dysfunction of this enzyme are typically associated with collagen disorders or scurvy (due to vitamin C deficiency affecting its activity) and do not manifest with the specific constellation of symptoms described.
*Homogentisate oxidase*
- A deficiency in **homogentisate oxidase** causes **alkaptonuria**.
- Alkaptonuria is characterized by dark urine upon standing, ochronosis (darkening of connective tissues), and arthritis in adulthood, which are not consistent with the patient's presentation.
More Dense connective tissue US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.