Limb development US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Limb development. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 1: A 10-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents for a follow-up examination. He has had a short stature since birth and underwent diagnostic testing. Genetic analyses showed a gain of function mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene. He has met all developmental milestones. He is at the 10th percentile for height and 90th percentile for weight. Which of the following additional findings is most likely on physical examination?
- A. Frontal bossing (Correct Answer)
- B. Absent collar bones
- C. Long extremities
- D. Blue sclerae
- E. Small genitalia
Limb development Explanation: ***Frontal bossing***
- A gain of function mutation in the **FGFR3 gene** is characteristic of **achondroplasia**, which is a common cause of short stature.
- **Frontal bossing** (prominent forehead) and midface hypoplasia are classical craniofacial features seen in individuals with achondroplasia.
*Absent collar bones*
- **Absent or hypoplastic clavicles** (collar bones) are a hallmark feature of **cleidocranial dysostosis**, a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the *RUNX2* gene, not typically associated with FGFR3 mutations.
- This condition also presents with delayed closure of fontanelles and dental anomalies, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
*Long extremities*
- Patients with achondroplasia characteristically have **rhizomelic short stature**, meaning the **proximal limbs** (femur and humerus) are disproportionately shorter than the trunk, leading to short extremities overall, not long ones.
- Long extremities are characteristic of conditions like **Marfan syndrome**, which has distinct genetic and clinical features.
*Blue sclerae*
- **Blue sclerae** are a common finding in **osteogenesis imperfecta**, a genetic disorder characterized by bone fragility due to defects in type I collagen synthesis.
- This condition is not caused by FGFR3 mutations and typically presents with recurrent fractures and other connective tissue abnormalities.
*Small genitalia*
- **Micropenis** (small genitalia) can be associated with various endocrine disorders, such as **hypogonadism** or congenital adrenal hyperplasia, or certain genetic syndromes.
- It is not a characteristic feature of achondroplasia or FGFR3-related skeletal dysplasias.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 2: A 25-year-old female comes to her obstetrician’s office for a prenatal visit. She has a transvaginal ultrasound that correlates with her last menstrual period and dates her pregnancy at 4 weeks. She has no complaints except some nausea during the morning that is improving. She comments that she has had some strange food cravings, but has no issues with eating a balanced diet. Her BMI is 23 kg/m^2 and she has gained 1 pound since the start of her pregnancy. She is curious about her pregnancy and asks the physician what her child is now able to do. Which of the following developments is expected of the fetus during this embryological phase?
- A. Formation of male genitalia
- B. Closure of the neural tube (Correct Answer)
- C. Movement of limbs
- D. Creation of the notochord
- E. Cardiac activity visible on ultrasound
Limb development Explanation: ***Closure of the neural tube***
- At **4 weeks gestation**, the **neural tube** is in the process of closing, forming the precursor for the brain and spinal cord, making this a critical developmental milestone.
- This period is vital for the prevention of neural tube defects like **spina bifida** and **anencephaly**.
*Formation of male genitalia*
- The differentiation of **external genitalia** (male or female) occurs much later, typically around weeks **9-12 of gestation**, much later than the 4-week mark discussed here.
- Prior to this, the genital ridges are bipotential and do not yet show sex-specific characteristics.
*Movement of limbs*
- While limb buds begin to appear around 4-5 weeks, coordinated **limb movements** are typically observed much later, around **10-12 weeks** of gestation, as muscular and neurological systems further develop.
- Early movements are typically subtle and reflex-like, rather than purposeful.
*Creation of the notochord*
- The **notochord** is formed during **gastrulation**, which occurs predominantly in the **third week of gestation**, prior to the 4-week mark.
- It serves as the primary axial support for the embryo and induces the formation of the neural tube.
*Cardiac activity visible on ultrasound*
- **Cardiac activity** typically becomes detectable on transvaginal ultrasound between **5 and 6 weeks gestation**, shortly after the 4-week mark.
- At 4 weeks, the heart tube may have started to form, but discernible beating is usually not yet evident.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old man presents for his annual physical exam. The physician fails to palpate a ductus deferens on the left side. An ultrasound confirms absence of the left ductus deferens and further reveals absence of the left epididymis, seminal vesicle, and kidney. Spermogram and reproductive hormones panel are within normal limits. Left-sided agenesis of an embryonic anlage is suspected. Which two structures are connected by this anlage during embryogenesis?
- A. Metanephros and coelom
- B. Mesonephros and coelom
- C. Pronephros and cloaca
- D. Mesonephros and cloaca (Correct Answer)
- E. Pronephros and coelom
Limb development Explanation: ***Mesonephros and cloaca***
- The **mesonephros** forms the **mesonephric (Wolffian) duct**, which connects to the **cloaca**.
- In males, this duct gives rise to the **epididymis**, **vas deferens**, **seminal vesicles**, and **ureteric bud** (which forms the kidney collecting system). The simultaneous absence of the kidney, epididymis, and seminal vesicle indicates a defect in this developmental pathway.
*Metanephros and coelom*
- The **metanephros** is a later stage of kidney development, forming the definitive kidney parenchyma, but it does **not connect directly to the coelom**.
- Its excretory ducts develop from an interaction with the ureteric bud (derived from the mesonephric duct), not directly from the coelom.
*Mesonephros and coelom*
- While the **mesonephros** develops within the intermediate mesoderm adjacent to the **coelom**, its primary connection relevant to these structures is to the cloaca via the mesonephric duct.
- The **coelom** is the primitive body cavity, and direct connections to the adult reproductive/urinary tracts in this manner are not embryologically accurate for this defect.
*Pronephros and cloaca*
- The **pronephros** is a transient, non-functional embryonic kidney structure that degenerates early in development and does **not form the definitive male reproductive or urinary structures** seen here.
- Its connection to the cloaca is not as direct or as developmentally critical for the structures described in the case.
*Pronephros and coelom*
- Similar to the previous option, the **pronephros** is an early and transient structure.
- It does **not develop into the adult genitourinary structures** affected in this patient, and its relationship with the coelom is not the key to understanding this specific congenital anomaly.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 4: A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency room with severe right shoulder pain following a painful overhead swing during a competitive volleyball match. On physical examination, the patient has limited active range of motion of the right shoulder and significant pain with passive motion. Suspecting a rotator cuff injury, the physician obtains an MRI, which indicates a minor tear in the tendon of the rotator cuff muscle that is innervated by the axillary nerve. Which of the following muscles was affected?
- A. Teres major
- B. Supraspinatus
- C. Teres minor (Correct Answer)
- D. Infraspinatus
- E. Subscapularis
Limb development Explanation: ***Correct: Teres minor***
- **Teres minor** is the only rotator cuff muscle innervated by the **axillary nerve** (C5-C6)
- Functions as an **external rotator** of the shoulder and stabilizes the humeral head
- The axillary nerve courses through the **quadrangular space** (bordered by teres minor superiorly, teres major inferiorly, long head of triceps medially, and surgical neck of humerus laterally)
- Injury to this muscle can occur with overhead activities, though less commonly injured than supraspinatus
*Incorrect: Supraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle, particularly with overhead activities
- Functions primarily in **abduction** (initiates first 15° of abduction)
*Incorrect: Infraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as the primary **external rotator** of the shoulder
- Second most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle
*Incorrect: Subscapularis*
- Innervated by the **upper and lower subscapular nerves** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Only rotator cuff muscle on the **anterior** surface of the scapula
- Functions as an **internal rotator** of the shoulder
*Incorrect: Teres major*
- **NOT part of the rotator cuff** (forms part of the posterior axillary fold)
- Innervated by the **lower subscapular nerve** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as an **internal rotator, adductor, and extensor** of the shoulder
Limb development US Medical PG Question 5: A 5-year-old boy presents for a regularly scheduled check-up. The child is wheelchair bound due to lower extremity paralysis and suffers from urinary incontinence. At birth, it was noted that the child had lower limbs of disproportionately small size in relation to the rest of his body. Radiograph imaging at birth also revealed several abnormalities in the spine, pelvis, and lower limbs. Complete history and physical performed on the child's birth mother during her pregnancy would likely have revealed which of the following?
- A. Maternal use of nicotine
- B. Maternal use of tetracyclines
- C. Maternal hyperthyroidism
- D. Maternal use of lithium
- E. Uncontrolled maternal diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
Limb development Explanation: ***Uncontrolled maternal diabetes mellitus***
- **Maternal diabetes** is a significant risk factor for **caudal regression syndrome**, which presents with **lower limb paralysis**, **urinary incontinence**, and **spinal/pelvic abnormalities**.
- The combination of disproportionately small lower limbs and the associated neurological and skeletal issues strongly points to a congenital anomaly linked to **poor glycemic control** during pregnancy.
*Maternal use of nicotine*
- Maternal nicotine use is associated with a range of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including **low birth weight**, **premature birth**, and **respiratory problems**, but not typically caudal regression syndrome.
- While concerning, it does not directly explain the specific constellation of skeletal, neurological, and urological abnormalities described.
*Maternal use of tetracyclines*
- **Tetracycline exposure** during pregnancy can lead to **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, particularly in the developing fetus.
- It is not known to cause the severe spinal and lower limb malformations, paralysis, or urinary incontinence seen in this case.
*Maternal hyperthyroidism*
- Uncontrolled maternal hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as **fetal tachycardia**, **goiter**, and **preterm birth**.
- It is not directly associated with congenital malformations like caudal regression syndrome that affect the lower spine and limbs.
*Maternal use of lithium*
- Maternal lithium use is most notably associated with an increased risk of **Ebstein's anomaly**, a congenital **heart defect**.
- It does not explain the specific musculoskeletal, neurological, and urological abnormalities presented in the case.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 6: A 13-year-old girl presents to an orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of a spinal curvature that was discovered during a school screening. She has otherwise been healthy and does not take any medications. On presentation, she is found to have significant asymmetry of her back and is sent for a spine radiograph. The radiograph reveals a unilateral rib attached to the left transverse process of the C7 vertebrae. Abnormal expression of which of the following genes is most likely responsible for this finding?
- A. WNT7
- B. FGF
- C. Homeobox (Correct Answer)
- D. PAX
- E. Sonic hedgehog
Limb development Explanation: ***Homeobox***
- **Homeobox genes (HOX genes)** play a crucial role in specifying the identity of vertebral segments along the **craniocaudal axis** during embryonic development.
- An abnormal expression of these genes can lead to **skeletal malformations**, such as the formation of a **cervical rib**, by altering the segmental identity of the C7 vertebra.
*WNT7*
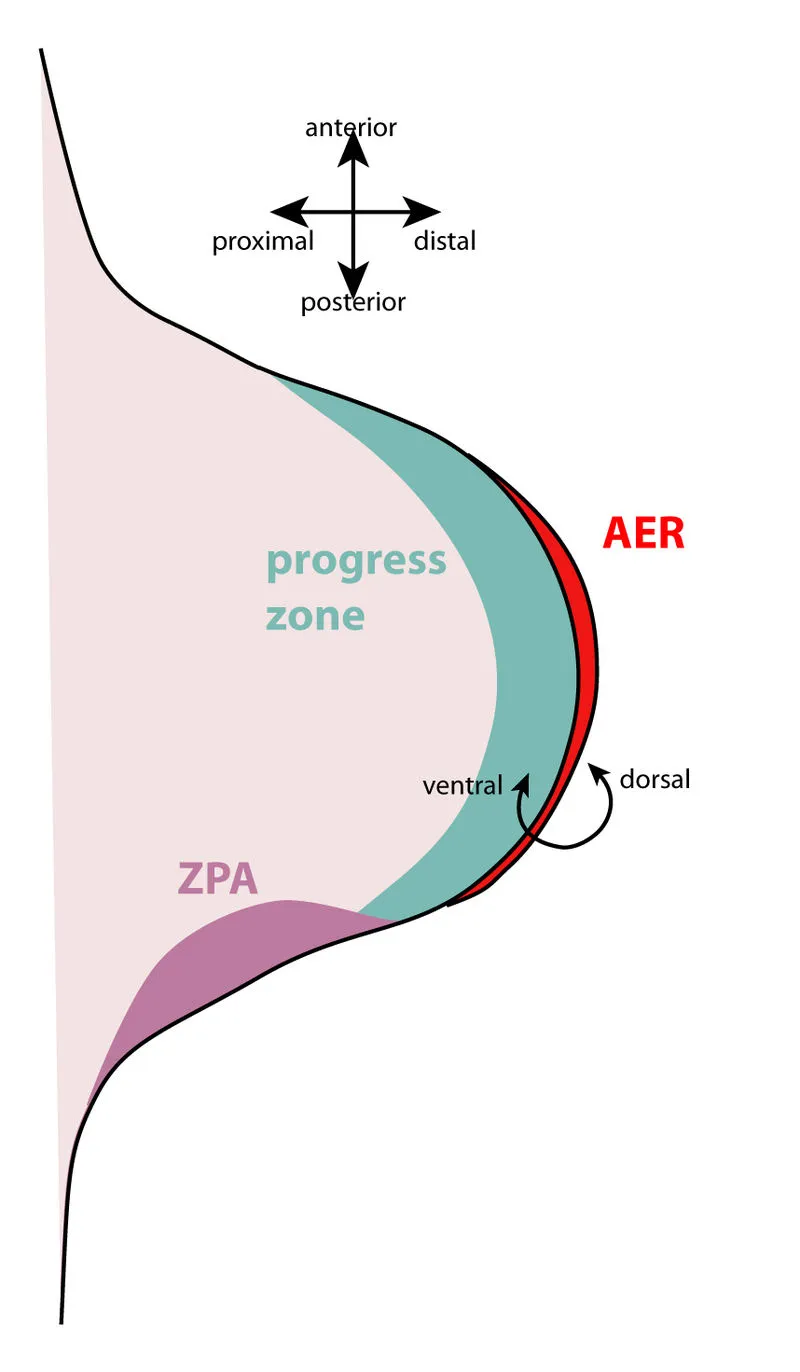
- **WNT7 genes** are involved in limb patterning and have a role in the formation of the **dorsoventral axis** of the limb and kidney development.
- They are not primarily associated with vertebral segmentation or the formation of cervical ribs.
*FGF*
- **Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) genes** are essential for various processes, including limb development, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis.
- While they are involved in numerous developmental pathways, they are not the primary genes responsible for specifying vertebral identity and thus cervical rib formation.
*PAX*
- **PAX genes** are a family of transcription factors critical for organ development, especially of the eye, brain, and kidney.
- While important for development, they are not directly implicated in the specification of vertebral segments or the pathogenesis of cervical ribs.
*Sonic hedgehog*
- **Sonic hedgehog (SHH)** signaling is a key pathway in embryonic development, particularly for pattern formation in the neural tube, limbs, and facial structures.
- While crucial for body axis development and segmentation, **HOX genes** have a more direct role in determining the specific identity of vertebral segments and causing cervical ribs.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 7: A research team is studying certain congenital anomalies of the respiratory tract. The method consists of marking a certain germinal layer with an isotope, following its development stages in chicken embryos, and finally analyzing the specimen. A given specimen of tissue is presented in the exhibit. Which of the following germinal structures most likely gave rise to the epithelial lining of this specimen?
- A. Ectoderm
- B. Neural crest
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Surface ectoderm
Limb development Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **epithelial lining** of the entire respiratory tract, including the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, is derived from the **endoderm**.
- The **laryngotracheal groove** develops from the ventral wall of the primitive foregut, which is endodermal in origin, further differentiating into the respiratory tree.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** primarily forms the epidermis, hair, nails, and the nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial lining of the respiratory tract.
*Neural crest*
- **Neural crest cells** contribute to a wide variety of structures, including components of the peripheral nervous system, head mesenchyme, and melanocytes.
- They are not involved in forming the epithelial lining of the respiratory system.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** forms the connective tissue, cartilage, and muscle components of the respiratory tract, such as the smooth muscle and cartilage rings of the trachea and bronchi, and the visceral pleura.
- However, it does not form the epithelial lining itself.
*Surface ectoderm*
- **Surface ectoderm** specifically gives rise to the epidermis, hair, nails, and glands of the skin, as well as the oral cavity epithelium.
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial structures of the respiratory tract.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 8: A male newborn is delivered at term to a 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 3. The mother has no medical insurance and did not receive prenatal care. Physical examination shows microcephaly and ocular hypotelorism. There is a single nostril, cleft lip, and a solitary central maxillary incisor. An MRI of the head shows a single large ventricle and fused thalami. This patient's condition is most likely caused by abnormal expression of which of the following protein families?
- A. Wnt
- B. Hedgehog (Correct Answer)
- C. Homeobox
- D. Fibroblast growth factor
- E. Transforming growth factor
Limb development Explanation: ***Hedgehog***
- The presented clinical features—**microcephaly**, **ocular hypotelorism**, **single nostril**, **cleft lip**, **solitary central maxillary incisor**, and neuroimaging findings of a **single large ventricle and fused thalami**—are classic manifestations of **holoprosencephaly**.
- **Holoprosencephaly** is a severe developmental anomaly caused by the incomplete division of the prosencephalon (forebrain) and is strongly associated with mutations in genes involved in the **Hedgehog signaling pathway**, particularly the **Sonic Hedgehog (SHH)** gene.
*Wnt*
- The **Wnt signaling pathway** is crucial for various developmental processes, including **neural tube closure**, limb patterning, and organogenesis.
- Abnormalities in Wnt signaling are associated with conditions like **neural tube defects** and specific cancers, but not typically with the facial and brain malformations seen in holoprosencephaly.
*Homeobox*
- **Homeobox (Hox) genes** are a family of transcription factors that play a critical role in patterning the body axis during embryonic development, determining the identity of body segments.
- Mutations in **Hox genes** are linked to various congenital anomalies, especially affecting the **skeletal system** and **limbs**, but do not directly cause the classic features of holoprosencephaly.
*Fibroblast growth factor*
- **Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs)** and their receptors are involved in a wide range of developmental processes, including **limb development**, **bone formation**, and **neurogenesis**.
- Dysregulation of FGF signaling is associated with conditions like **craniosynostosis** and various skeletal dysplasias, but not the specific brain and facial abnormalities observed in holoprosencephaly.
*Transforming growth factor*
- The **Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily** includes a diverse group of growth factors involved in cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix production.
- Dysfunction in TGF-β signaling is implicated in conditions like **Marfan syndrome** and various fibrotic disorders, but it is not the primary pathway linked to the pathogenesis of holoprosencephaly.
Limb development US Medical PG Question 9: A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician because she has not had a menstrual period for 5 weeks. Menarche was at the age of 14 years and menses occurred at regular 30-day intervals. She reports having unprotected sexual intercourse 3 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Which of the following best describes the stage of development of the embryo at this time?
- A. Fetal heart is beating, but cardiac activity is not yet visible on ultrasound
- B. Limb buds have formed, but fetal movements have not begun
- C. Sexual differentiation has begun, but fetal movement has not started
- D. Neural crest has formed, but limb buds have not yet formed (Correct Answer)
- E. Implantation has occurred, but notochord has not yet formed
Limb development Explanation: ***Neural crest has formed, but limb buds have not yet formed***
- At **5 weeks gestational age (3 weeks post-fertilization)**, neurulation is completing or recently completed
- **Neural crest cells** migrate from the neural folds during weeks 3-4 post-fertilization and are definitely present by this time
- **Limb buds** appear later, around week 4-5 post-fertilization (week 6-7 gestational age), making this the most accurate description for the current developmental stage
*Fetal heart is beating, but cardiac activity is not yet visible on ultrasound*
- The primitive heart tube begins contracting around day 22-23 post-fertilization (early week 4)
- At 3 weeks post-fertilization (5 weeks gestational age), the heart may just be starting to beat, but this timing is less precise
- Cardiac activity becomes visible on transvaginal ultrasound around 5.5-6 weeks gestational age, so this option is close but less precise than the correct answer
*Limb buds have formed, but fetal movements have not begun*
- **Limb buds** typically appear around week 4-5 post-fertilization (week 6-7 gestational age)
- This is **too advanced** for 3 weeks post-fertilization
- While fetal movements aren't perceptible to the mother until 16-20 weeks, they begin much later than the current stage
*Sexual differentiation has begun, but fetal movement has not started*
- **Sexual differentiation** of the gonads begins around week 7 post-fertilization (week 9 gestational age)
- External genitalia differentiation occurs even later (weeks 9-12 post-fertilization)
- This stage is **far too advanced** for the current 3-week post-fertilization timeframe
*Implantation has occurred, but notochord has not yet formed*
- **Implantation** occurs 6-12 days after fertilization, which is approximately 2-3 weeks before a positive pregnancy test
- The **notochord** forms during gastrulation in the **3rd week post-fertilization** (5th week gestational age)
- By the time of this positive pregnancy test (5 weeks gestational age), the notochord has **already formed**, making this statement incorrect
Limb development US Medical PG Question 10: During the third week of development, the blastocyst undergoes a variety of differentiation processes responsible for the formation of the gastrula and, eventually, the embryo. This differentiation creates cell lineages that eventually become a variety of body systems. What cell lineage, present at this date, is responsible for the formation of the liver?
- A. Neuroectoderm
- B. Syncytiotrophoblasts
- C. Ectoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Mesoderm
Limb development Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that develops during gastrulation and is responsible for forming the lining of the **gastrointestinal tract** and associated organs, including the **liver** and pancreas.
- Liver development begins from an outgrowth of the **foregut endoderm**, which differentiates into hepatocytes and bile duct cells, forming the hepatic parenchyma.
*Neuroectoderm*
- **Neuroectoderm** is a specialized part of the ectoderm that gives rise to the entire **nervous system**, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
- It does not contribute to the formation of visceral organs like the liver.
*Syncytiotrophoblasts*
- **Syncytiotrophoblasts** are a layer of the **trophoblast** that form part of the placenta, specifically involved in hormone production and nutrient exchange between the mother and fetus.
- They are part of the supporting structures for pregnancy and do not contribute to the embryonic germ layers or organ formation within the embryo itself.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** is the outermost germ layer and gives rise to the **epidermis of the skin**, hair, nails, nervous system, and sensory organs.
- While it forms the outer coverings and nervous system, it does not directly form internal organs like the liver.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** is the middle germ layer, responsible for forming **muscle**, **bone**, connective tissue, the circulatory system, kidneys, and gonads.
- While mesoderm contributes supporting structures to the liver (blood vessels, connective tissue, hematopoietic cells), the **hepatic parenchyma** (hepatocytes and bile ducts) is derived from the endoderm, making endoderm the primary cell lineage responsible for liver formation.
More Limb development US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.