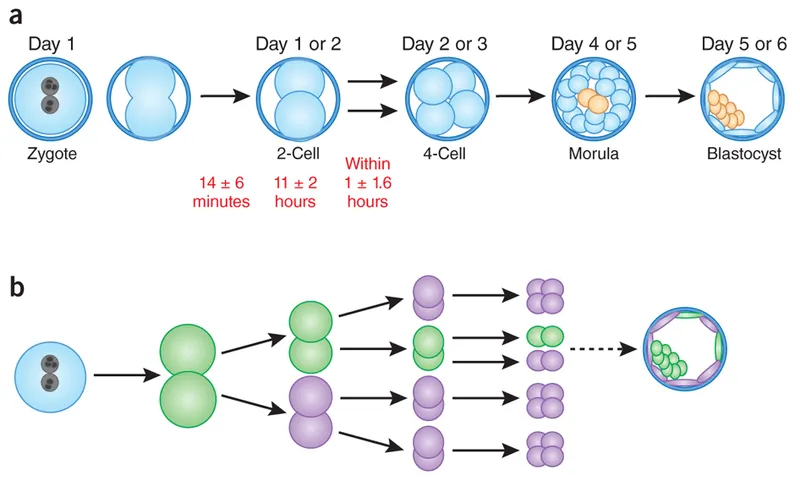
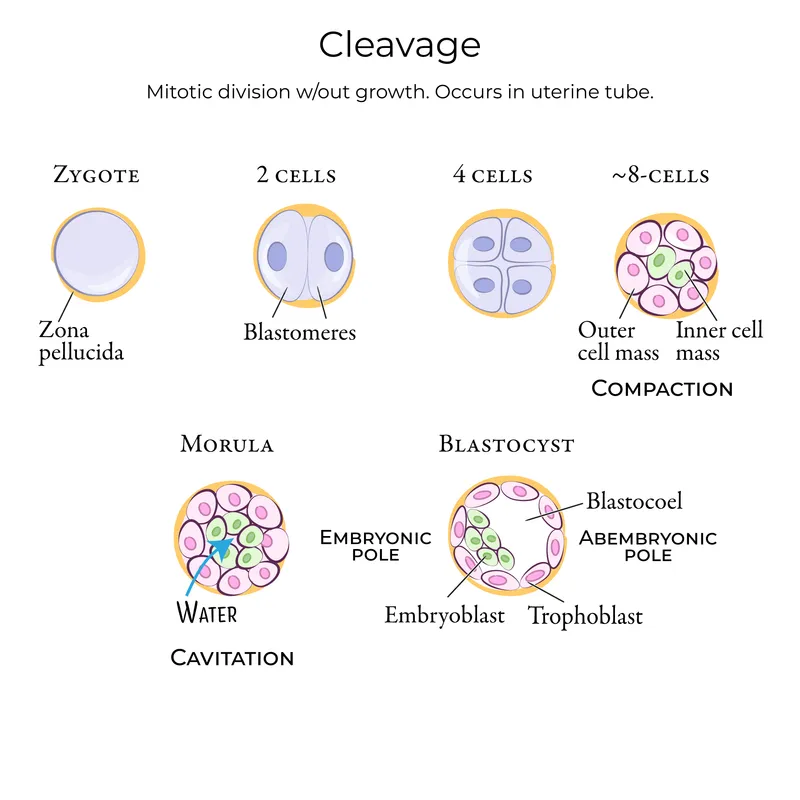
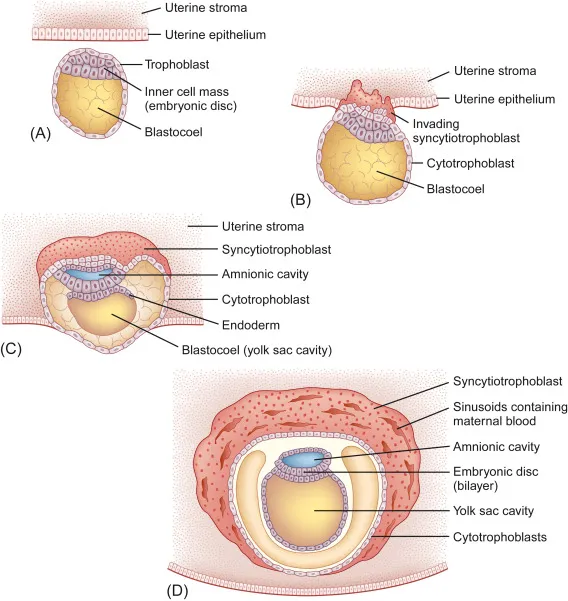
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cleavage and blastocyst formation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. Her last menstrual period was 9 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy consistent in size with a 7-week gestation. The hormone that was measured in this patient's urine to detect the pregnancy is also directly responsible for which of the following processes?
- A. Development of breast tissue
- B. Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation
- C. Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions
- D. Maintenance of the corpus luteum (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of ovulation
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Maintenance of the corpus luteum***
- The hormone measured in the urine pregnancy test is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**.
- **hCG** acts like **luteinizing hormone (LH)** to maintain the **corpus luteum** in early pregnancy, ensuring continued progesterone production until the placenta takes over.
*Development of breast tissue*
- **Estrogen** and **progesterone** are the primary hormones responsible for the development of breast tissue during pregnancy, preparing the breasts for lactation.
- While hCG indirectly supports these hormones, it does not directly cause breast tissue development.
*Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation*
- The **preparation of the uterine endometrium** for implantation is primarily driven by **progesterone**, produced by the corpus luteum initially and later by the placenta.
- hCG’s role is to maintain the corpus luteum, thus indirectly supporting progesterone production.
*Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions*
- **Progesterone** is the main hormone responsible for **inhibiting uterine contractions** during pregnancy to prevent preterm labor.
- While hCG supports progesterone production, it does not directly inhibit uterine contractions itself.
*Inhibition of ovulation*
- High levels of **estrogen** and **progesterone** during pregnancy suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thereby **inhibiting ovulation**.
- While hCG maintains the corpus luteum which produces these hormones, hCG itself is not the direct inhibitor of ovulation.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 2: A 2250-g (5.0-lb) male newborn and a 2900-g (6.4-lb) male newborn are delivered at 36 weeks' gestation to a 24-year-old, gravida 1, para 1 woman. The mother had no prenatal care. Examination of the smaller newborn shows low-set ears, retrognathia, and right-sided clubfoot. The hematocrit is 41% for the smaller newborn and 69% for the larger newborn. This pregnancy was most likely which of the following?
- A. Monochorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic
- B. Conjoined twins
- C. Dichorionic-diamniotic monozygotic
- D. Monochorionic-diamniotic monozygotic (Correct Answer)
- E. Dichorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Monochorionic-diamniotic monozygotic***
- This is the most likely scenario given the significant **weight discordance**, **malformations** in one twin (low-set ears, retrognathia, clubfoot), and divergent hematocrit values suggesting **twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS)**.
- **Monochorionic** indicates a shared placenta, allowing for vascular anastomoses that cause TTTS; **diamniotic** means separate amniotic sacs, which is typical for division between days 4-8 post-fertilization.
*Monochorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic*
- This type of twinning occurs with division after day 8-13 post-fertilization and would result in **both twins sharing the same amniotic sac**, increasing the risk of cord entanglement.
- While it's monochorionic and thus prone to TTTS, the presence of two distinct newborns without signs of cord entanglement makes diamniotic more likely.
*Conjoined twins*
- **Conjoined twins** result from incomplete separation of a monozygotic embryo after day 13, leading to physically connected infants.
- The description of two distinct newborns, despite the size and health differences, rules out physical fusion.
*Dichorionic-diamniotic monozygotic*
- While dichorionic-diamniotic twins can be monozygotic (splitting within the first 3 days post-fertilization), they typically have **separate placentas** or at least separate chorions.
- This arrangement significantly **reduces the risk of TTTS**, which is strongly suggested by the differing hematocrits and growth discordance.
*Dichorionic-monoamniotic monozygotic*
- **Dichorionic** means two separate chorions, implying separate placentas or at least separate chorionic membranes, making the significant vascular connection for TTTS unlikely.
- **Monoamniotic** (sharing one amniotic sac) with two chorions is a rare and highly unusual combination for monozygotic twins; it usually implies a very early split before chorion differentiation but without separate amnions.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 3: A 12-year-old boy follows up with his primary care physician for ongoing management of a urinary tract infection. He recently started middle school and has been having a difficult time navigating the school since he ambulates with leg braces and crutches. Consequently, he has not had sufficient time to use his urinary catheter appropriately. Otherwise, he has been unchanged from the previous visit with both sensory and motor defects in his lower extremities. He has had these defects since birth and has undergone surgeries to repair a bony defect in his spine with protrusion of a membrane through the defect. During what days of embryonic development did the defect responsible for this patient's symptoms most likely occur?
- A. Days 21-35 (Correct Answer)
- B. Days 0-7
- C. Days 8-20
- D. Days 90-birth
- E. Days 36-90
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Days 21-35***
- This period during embryogenesis is crucial for **neurulation**, the process where the **neural tube** forms and closes. Failure of neural tube closure, particularly in the caudal region, leads to conditions like **spina bifida** (which aligns with the patient's described bony defect and neurological symptoms).
- The patient's history of a **bony defect in the spine with protrusion of a membrane**, along with **sensory and motor defects in the lower extremities** and issues with bladder control (recurrent UTIs and catheter use), strongly indicates a **neural tube defect (NTD)**. Most NTDs occur between days 21 and 28 of embryonic development, encompassing the neural tube closure.
*Days 0-7*
- This initial period involves **fertilization, cleavage**, and **blastulation**. Cellular differentiation and major organ formation have not yet begun.
- Defects during this stage typically result in early embryonic loss or very broad, systemic issues rather than specific structural defects like neural tube closure abnormalities.
*Days 8-20*
- This period includes implantation and early **gastrulation**, where the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) are established.
- While important developmental events occur, **neurulation**, the specific process affected in this patient, primarily begins around day 18-20 and continues into the next period.
*Days 90-birth*
- This period represents the **fetal stage**, characterized by growth and maturation of already formed organs and systems.
- Major structural defects like spina bifida would have already occurred and been established much earlier in embryonic development.
*Days 36-90*
- This period, often referred to as the **fetal period of organogenesis**, involves significant growth and differentiation of organs.
- By this stage, the neural tube would have already closed. While further development and refinement of the nervous system occur, the primary defect of **neural tube closure** would have happened before day 36.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 4: A previously healthy 29-year-old Taiwanese woman comes to the emergency department with vaginal bleeding and pelvic pressure for several hours. Over the past 2 weeks, she had intermittent nausea and vomiting. A home urine pregnancy test was positive 10 weeks ago. She has had no prenatal care. Her pulse is 80/min and blood pressure is 150/98 mm Hg. Physical examination shows warm and moist skin. Lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. Her abdomen is soft and non-distended. Bimanual examination shows a uterus palpated at the level of the umbilicus. Her serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin concentration is 110,000 mIU/mL. Urine dipstick is positive for protein and ketones. Transvaginal ultrasound shows a central intrauterine mass with hypoechoic spaces; there is no detectable fetal heart rate. An x-ray of the chest shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Serial beta-hCG measurement
- B. Bed rest and doxylamine therapy
- C. Methotrexate therapy
- D. Suction curettage (Correct Answer)
- E. Insulin therapy
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Suction curettage***
- The patient's symptoms (vaginal bleeding, pelvic pressure, nausea/vomiting), signs (hypertension, large for gestational age uterus at the umbilicus corresponding to 20 weeks gestation, proteinuria), and laboratory findings (markedly elevated beta-hCG of 110,000 mIU/mL) are highly suggestive of a **hydatidiform mole**.
- A **transvaginal ultrasound** showing a central intrauterine mass with **hypoechoic spaces** (often described as a 'snowstorm' or 'grape-like' appearance) and no fetal heart rate confirms the diagnosis of a **molar pregnancy**. The most appropriate and urgent management is **suction curettage** to remove the abnormal pregnancy tissue, which also serves a diagnostic purpose.
*Serial beta-hCG measurement*
- While **serial beta-hCG** measurements are crucial for monitoring after treatment of a molar pregnancy to detect persistent trophoblastic disease, they are not the initial management step for an active molar pregnancy with acute symptoms.
- This step would delay the necessary removal of the abnormal tissue and risk complications such as hemorrhage or progression to **gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN)**.
*Bed rest and doxylamine therapy*
- **Bed rest and doxylamine** are treatments for benign conditions like **hyperemesis gravidarum** or threatened abortion, which do not align with the severe symptoms, physical findings, and ultrasound characteristics of this patient's condition.
- This approach would be completely inadequate and inappropriate for a molar pregnancy.
*Methotrexate therapy*
- **Methotrexate** is a chemotherapy agent used to treat **persistent gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN)** or **choriocarcinoma** following molar pregnancy evacuation, or in cases of ectopic pregnancy.
- It is not the primary treatment for the initial removal of a molar pregnancy itself, which requires surgical evacuation.
*Insulin therapy*
- **Insulin therapy** is used to manage **gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)** or pre-existing diabetes in pregnancy.
- There is no clinical or laboratory evidence (e.g., elevated glucose) to suggest diabetes in this patient, and it is unrelated to the primary diagnosis of molar pregnancy.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 5: Research is being conducted on embryoblasts. The exact date of fertilization is unknown. There is the presence of a cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast, marking the time when implantation into the uterus would normally occur. Within the embryoblast, columnar and cuboidal cells are separated by a membrane. Which of these cell layers begins to line the yolk sac cavity?
- A. Hypoblast (Correct Answer)
- B. Epiblast
- C. Syncytiotrophoblast
- D. Inner cell mass
- E. Endoderm
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Hypoblast***
- The **hypoblast** is a layer of cuboidal cells that forms from the inner cell mass around day 8 post-fertilization.
- It plays a crucial role in forming the **primary yolk sac** by migrating to line the exocoelomic cavity.
*Epiblast*
- The **epiblast** is composed of columnar cells located dorsal to the hypoblast and forms the floor of the **amniotic cavity**.
- It is the source of the **three primary germ layers** during gastrulation (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), not the yolk sac lining itself.
*Syncytiotrophoblast*
- The **syncytiotrophoblast** is the outer, invasive layer of the trophoblast that facilitates implantation and forms the fetal component of the placenta.
- It is not involved in lining the yolk sac cavity but rather in **invading the uterine endometrium** and producing hCG.
*Inner cell mass*
- The **inner cell mass (ICM)** is the cluster of cells within the blastocyst that gives rise to the embryoblast (which further differentiates into epiblast and hypoblast).
- The ICM itself does not line the yolk sac; rather, its derivative, the hypoblast, does.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that forms during gastrulation from the epiblast derivative.
- It ultimately forms the linings of the **gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, not the primary yolk sac lining.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 6: A researcher is studying gamete production and oogenesis. For her experiment, she decides to cultivate primary oocytes in their arrested state and secondary oocytes just prior to fertilization. When she examines these gametes, she will find that the primary oocytes and secondary oocytes are arrested in which phases of meiosis, respectively?
- A. Anaphase I; anaphase II
- B. Interphase I; prophase II
- C. Metaphase I; metaphase II
- D. Metaphase I; prophase II
- E. Prophase I; metaphase II (Correct Answer)
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Prophase I; metaphase II***
- **Primary oocytes** are arrested in **prophase I** from embryonic development until puberty, when they resume meiosis in preparation for ovulation.
- **Secondary oocytes** are immediately arrested in **metaphase II** after completing meiosis I, and they will remain in this stage until fertilization occurs.
*Anaphase I; anaphase II*
- **Anaphase I** involves the separation of **homologous chromosomes**, and **anaphase II** involves the separation of **sister chromatids**. Neither primary nor secondary oocytes are arrested in these stages.
- Meiotic arrest occurs at earlier stages to prevent further division until specific triggers (ovulation or fertilization) are met.
*Interphase I; prophase II*
- **Interphase I** precedes meiosis I, during which DNA replication occurs, and it is not a stage of meiotic arrest for primary oocytes.
- **Prophase II** is a transient stage in meiosis II, and secondary oocytes are arrested later in **metaphase II**, not prophase II.
*Metaphase I; metaphase II*
- While **secondary oocytes** are indeed arrested in **metaphase II**, **primary oocytes** are arrested much earlier in **prophase I**, not metaphase I.
- The arrest in metaphase I is temporary for primary oocytes as they complete meiosis I to form secondary oocytes upon hormonal signaling.
*Metaphase I; prophase II*
- **Primary oocytes** are arrested in **prophase I**, not metaphase I. Meiosis I is completed before ovulation, leading to the formation of secondary oocytes.
- **Secondary oocytes** are arrested in **metaphase II**, not prophase II, awaiting fertilization to complete meiosis II.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 7: A male newborn is delivered at term to a 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 3. The mother has no medical insurance and did not receive prenatal care. Physical examination shows microcephaly and ocular hypotelorism. There is a single nostril, cleft lip, and a solitary central maxillary incisor. An MRI of the head shows a single large ventricle and fused thalami. This patient's condition is most likely caused by abnormal expression of which of the following protein families?
- A. Wnt
- B. Hedgehog (Correct Answer)
- C. Homeobox
- D. Fibroblast growth factor
- E. Transforming growth factor
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Hedgehog***
- The presented clinical features—**microcephaly**, **ocular hypotelorism**, **single nostril**, **cleft lip**, **solitary central maxillary incisor**, and neuroimaging findings of a **single large ventricle and fused thalami**—are classic manifestations of **holoprosencephaly**.
- **Holoprosencephaly** is a severe developmental anomaly caused by the incomplete division of the prosencephalon (forebrain) and is strongly associated with mutations in genes involved in the **Hedgehog signaling pathway**, particularly the **Sonic Hedgehog (SHH)** gene.
*Wnt*
- The **Wnt signaling pathway** is crucial for various developmental processes, including **neural tube closure**, limb patterning, and organogenesis.
- Abnormalities in Wnt signaling are associated with conditions like **neural tube defects** and specific cancers, but not typically with the facial and brain malformations seen in holoprosencephaly.
*Homeobox*
- **Homeobox (Hox) genes** are a family of transcription factors that play a critical role in patterning the body axis during embryonic development, determining the identity of body segments.
- Mutations in **Hox genes** are linked to various congenital anomalies, especially affecting the **skeletal system** and **limbs**, but do not directly cause the classic features of holoprosencephaly.
*Fibroblast growth factor*
- **Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs)** and their receptors are involved in a wide range of developmental processes, including **limb development**, **bone formation**, and **neurogenesis**.
- Dysregulation of FGF signaling is associated with conditions like **craniosynostosis** and various skeletal dysplasias, but not the specific brain and facial abnormalities observed in holoprosencephaly.
*Transforming growth factor*
- The **Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily** includes a diverse group of growth factors involved in cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix production.
- Dysfunction in TGF-β signaling is implicated in conditions like **Marfan syndrome** and various fibrotic disorders, but it is not the primary pathway linked to the pathogenesis of holoprosencephaly.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 8: A 13-year-old girl presents to an orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of a spinal curvature that was discovered during a school screening. She has otherwise been healthy and does not take any medications. On presentation, she is found to have significant asymmetry of her back and is sent for a spine radiograph. The radiograph reveals a unilateral rib attached to the left transverse process of the C7 vertebrae. Abnormal expression of which of the following genes is most likely responsible for this finding?
- A. WNT7
- B. FGF
- C. Homeobox (Correct Answer)
- D. PAX
- E. Sonic hedgehog
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Homeobox***
- **Homeobox genes (HOX genes)** play a crucial role in specifying the identity of vertebral segments along the **craniocaudal axis** during embryonic development.
- An abnormal expression of these genes can lead to **skeletal malformations**, such as the formation of a **cervical rib**, by altering the segmental identity of the C7 vertebra.
*WNT7*
- **WNT7 genes** are involved in limb patterning and have a role in the formation of the **dorsoventral axis** of the limb and kidney development.
- They are not primarily associated with vertebral segmentation or the formation of cervical ribs.
*FGF*
- **Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) genes** are essential for various processes, including limb development, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis.
- While they are involved in numerous developmental pathways, they are not the primary genes responsible for specifying vertebral identity and thus cervical rib formation.
*PAX*
- **PAX genes** are a family of transcription factors critical for organ development, especially of the eye, brain, and kidney.
- While important for development, they are not directly implicated in the specification of vertebral segments or the pathogenesis of cervical ribs.
*Sonic hedgehog*
- **Sonic hedgehog (SHH)** signaling is a key pathway in embryonic development, particularly for pattern formation in the neural tube, limbs, and facial structures.
- While crucial for body axis development and segmentation, **HOX genes** have a more direct role in determining the specific identity of vertebral segments and causing cervical ribs.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old woman sees you in your office with a complaint of new-onset headaches over the past few weeks. On exam, you find a 2 x 2 cm dark, irregularly shaped, pigmented lesion on her back. She is concerned because her father recently passed away from skin cancer. What tissue type most directly gives rise to the lesion this patient is experiencing?
- A. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Endoderm
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Ectoderm
- E. Neuroectoderm
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The suspected lesion, given its description and the patient's family history of skin cancer, is likely a **melanoma**.
- Melanoma originates from **melanocytes**, which are derived from **neural crest cells** during embryonic development.
*Endoderm*
- The endoderm gives rise to the **lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, as well as organs such as the liver and pancreas.
- It is not involved in the formation of melanocytes or skin lesions like melanoma.
*Mesoderm*
- The mesoderm forms tissues such as **muscle, bone, cartilage, connective tissue**, and the circulatory system.
- It does not directly give rise to melanocytes, which are the cells of origin for melanoma.
*Ectoderm*
- The ectoderm gives rise to the **epidermis, nervous system**, and sensory organs.
- While melanocytes are found in the epidermis, they are specifically derived from the **neural crest (a sub-population of ectoderm)**, not the general ectoderm.
*Neuroectoderm*
- Neuroectoderm specifically refers to the ectoderm that develops into the **nervous system**.
- While neural crest cells originate from the neuroectoderm, "neural crest cells" is a more precise answer for the origin of melanocytes.
Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG Question 10: A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician because she has not had a menstrual period for 5 weeks. Menarche was at the age of 14 years and menses occurred at regular 30-day intervals. She reports having unprotected sexual intercourse 3 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Which of the following best describes the stage of development of the embryo at this time?
- A. Fetal heart is beating, but cardiac activity is not yet visible on ultrasound
- B. Limb buds have formed, but fetal movements have not begun
- C. Sexual differentiation has begun, but fetal movement has not started
- D. Neural crest has formed, but limb buds have not yet formed (Correct Answer)
- E. Implantation has occurred, but notochord has not yet formed
Cleavage and blastocyst formation Explanation: ***Neural crest has formed, but limb buds have not yet formed***
- At **5 weeks gestational age (3 weeks post-fertilization)**, neurulation is completing or recently completed
- **Neural crest cells** migrate from the neural folds during weeks 3-4 post-fertilization and are definitely present by this time
- **Limb buds** appear later, around week 4-5 post-fertilization (week 6-7 gestational age), making this the most accurate description for the current developmental stage
*Fetal heart is beating, but cardiac activity is not yet visible on ultrasound*
- The primitive heart tube begins contracting around day 22-23 post-fertilization (early week 4)
- At 3 weeks post-fertilization (5 weeks gestational age), the heart may just be starting to beat, but this timing is less precise
- Cardiac activity becomes visible on transvaginal ultrasound around 5.5-6 weeks gestational age, so this option is close but less precise than the correct answer
*Limb buds have formed, but fetal movements have not begun*
- **Limb buds** typically appear around week 4-5 post-fertilization (week 6-7 gestational age)
- This is **too advanced** for 3 weeks post-fertilization
- While fetal movements aren't perceptible to the mother until 16-20 weeks, they begin much later than the current stage
*Sexual differentiation has begun, but fetal movement has not started*
- **Sexual differentiation** of the gonads begins around week 7 post-fertilization (week 9 gestational age)
- External genitalia differentiation occurs even later (weeks 9-12 post-fertilization)
- This stage is **far too advanced** for the current 3-week post-fertilization timeframe
*Implantation has occurred, but notochord has not yet formed*
- **Implantation** occurs 6-12 days after fertilization, which is approximately 2-3 weeks before a positive pregnancy test
- The **notochord** forms during gastrulation in the **3rd week post-fertilization** (5th week gestational age)
- By the time of this positive pregnancy test (5 weeks gestational age), the notochord has **already formed**, making this statement incorrect
More Cleavage and blastocyst formation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.