Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
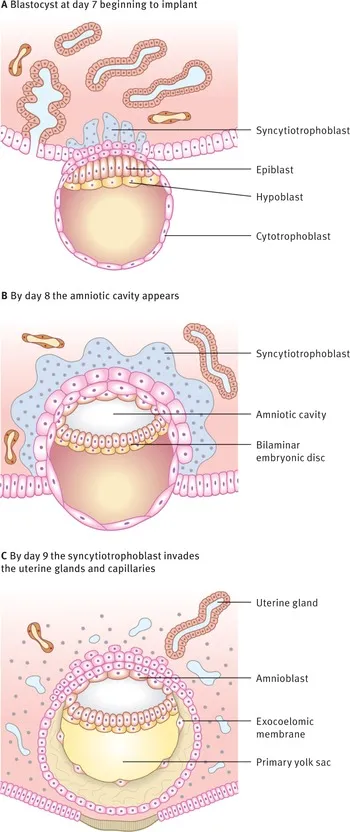
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 1: During the third week of development, the blastocyst undergoes a variety of differentiation processes responsible for the formation of the gastrula and, eventually, the embryo. This differentiation creates cell lineages that eventually become a variety of body systems. What cell lineage, present at this date, is responsible for the formation of the liver?
- A. Neuroectoderm
- B. Syncytiotrophoblasts
- C. Ectoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Mesoderm
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that develops during gastrulation and is responsible for forming the lining of the **gastrointestinal tract** and associated organs, including the **liver** and pancreas.
- Liver development begins from an outgrowth of the **foregut endoderm**, which differentiates into hepatocytes and bile duct cells, forming the hepatic parenchyma.
*Neuroectoderm*
- **Neuroectoderm** is a specialized part of the ectoderm that gives rise to the entire **nervous system**, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
- It does not contribute to the formation of visceral organs like the liver.
*Syncytiotrophoblasts*
- **Syncytiotrophoblasts** are a layer of the **trophoblast** that form part of the placenta, specifically involved in hormone production and nutrient exchange between the mother and fetus.
- They are part of the supporting structures for pregnancy and do not contribute to the embryonic germ layers or organ formation within the embryo itself.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** is the outermost germ layer and gives rise to the **epidermis of the skin**, hair, nails, nervous system, and sensory organs.
- While it forms the outer coverings and nervous system, it does not directly form internal organs like the liver.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** is the middle germ layer, responsible for forming **muscle**, **bone**, connective tissue, the circulatory system, kidneys, and gonads.
- While mesoderm contributes supporting structures to the liver (blood vessels, connective tissue, hematopoietic cells), the **hepatic parenchyma** (hepatocytes and bile ducts) is derived from the endoderm, making endoderm the primary cell lineage responsible for liver formation.
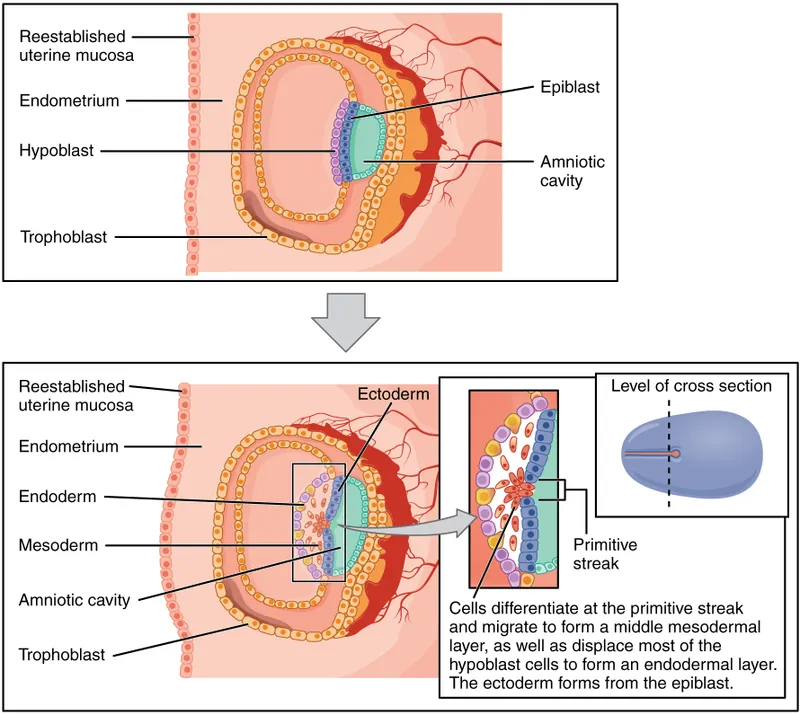
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 2: A 21-year-old G3P2 woman presents to her obstetrician at 6 weeks gestation for routine prenatal care. Her past medical history includes obesity and gestational diabetes. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries at term. One infant was macrosomic with hypoglycemia, but otherwise, she has had no complications. Her physician informs her that she must start taking a multivitamin with folic acid daily. The defect that folic acid supplementation protects against arises in tissue that is derived from which germ cell layer?
- A. Mesoderm
- B. Notochord
- C. Endoderm
- D. Mesenchyme
- E. Ectoderm (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Ectoderm***
- Folic acid supplementation primarily prevents **neural tube defects**, such as **spina bifida** and **anencephaly**.
- The **neural tube**, which forms the brain and spinal cord, is derived from the **ectoderm**.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** gives rise to structures like muscle, bone, connective tissue, and the cardiovascular system.
- Defects in mesodermal development are not primarily prevented by folic acid supplementation.
*Notochord*
- The **notochord** is a transient embryonic structure that induces the formation of the neural plate from the ectoderm.
- While critical for nervous system development, it is not a germ cell layer itself, and defects in its development are not directly prevented by folic acid.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** forms the lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, as well as glands like the thyroid and pancreas.
- Anomalies of these internal organs are not the primary target of folic acid supplementation.
*Mesenchyme*
- **Mesenchyme** is embryonic connective tissue, largely derived from the mesoderm, but can also come from neural crest (ectoderm).
- It differentiates into connective tissues, blood, and lymphatic vessels; neural tube defects are not considered mesenchymal in origin.
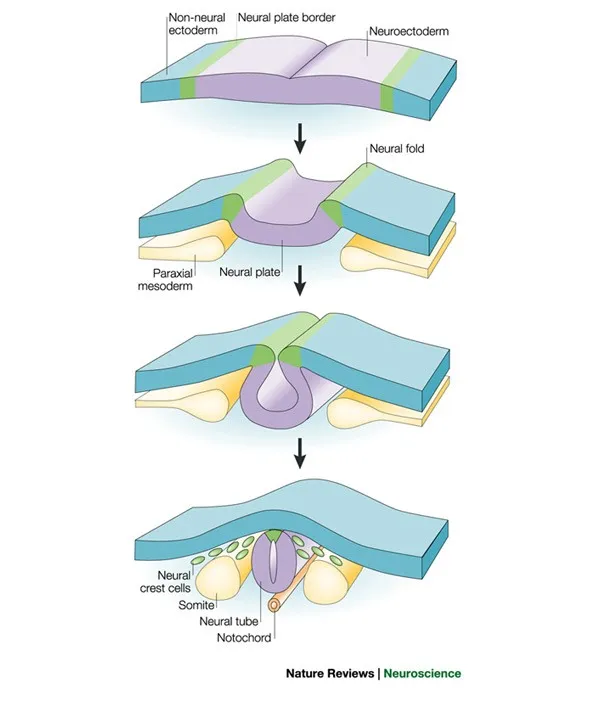
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old G1P0 woman undergoes her 2nd-trimester ultrasound in a community hospital. During her prenatal care, she was found to have mild anemia, low levels of folate, and serum alpha-fetoprotein levels greater than 2 multiples of the median (MoM) on 2 separate occasions. Her 1st-trimester ultrasound was significant for the absence of the intracranial lucency, no visualization of the cisterna magna, and posterior shift of the brain stem. These 2nd-trimester ultrasound reports reveal the widening of the lumbosacral spine ossification centers and the presence of a sac in proximity to the lumbosacral defect. Which of the following statements best describes the congenital defect in the fetus?
- A. Abnormal development of the caudal eminence
- B. Persistence of the anterior accessory neurenteric canal (ANC)
- C. Failure of the caudal neuropore to close (Correct Answer)
- D. Failure of mesenchymal cells to form a neural rod
- E. Failure of the rostral neuropore to close
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Failure of the caudal neuropore to close***
- The constellation of findings, including **elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, absence of intracranial lucency, no visualization of the cisterna magna, posterior shift of the brain stem, widening lumbosacral spine ossification centers, and a sac near a lumbosacral defect, points to a **neural tube defect**, specifically an **open spina bifida** (myelomeningocele).
- This condition results from the **incomplete closure of the neural tube**, particularly the **caudal neuropore**, which normally closes around day 27-28 of embryonic development.
*Abnormal development of the caudal eminence*
- **Caudal eminence defects** typically manifest as caudal regression syndrome, which involves abnormalities of the sacrum and lower limbs, but usually **not** an open neural tube defect with elevated AFP and characteristic cranial ultrasound findings.
- While there is a lumbosacral defect, the extensive features point away from an isolated caudal eminence issue.
*Persistence of the anterior accessory neurenteric canal (ANC)*
- **Persistent ANC** is a rare condition that can lead to **duplications of the neural tube** or gastrointestinal tract, often associated with a connection between the gut and the neural canal.
- This would not explain the high AFP, absence of intracranial lucency, or the specific sonographic features of an open neural tube defect like spina bifida.
*Failure of mesenchymal cells to form a neural rod*
- The formation of the neural tube is a complex process; while mesenchymal cells are involved in surrounding structures, the neural rod itself primarily forms from the **neuroectoderm**.
- This description does not accurately reflect the embryological origin of spina bifida, which is fundamentally a defect of neural tube closure rather than a failure of neural rod formation.
*Failure of the rostral neuropore to close*
- Failure of the **rostral (cranial) neuropore** to close leads to **anencephaly** or encephalocele, characterized by the absence of a significant portion of the brain and skull.
- While AFP levels would be high, the ultrasound findings of a sac in the lumbosacral region and the specific intracranial findings (e.g., absence of intracranial lucency, posterior shift of the brain stem, which are signs of Arnold-Chiari malformation type II) are much more consistent with a caudal defect like myelomeningocele.
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old gentleman passes away after a car accident. On routine autopsy it is incidentally noted that he has both a ventral and dorsal pancreatic duct. This incidental finding observed by the pathologist is generated due to failure of which of the following embryological processes?
- A. Apoptosis
- B. Stem cell differentiation
- C. Notochord signaling
- D. Neural crest cell migration
- E. Fusion (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Fusion***
- The pancreas develops from a **ventral and a dorsal bud** that typically **fuse** during development.
- Failure of these two pancreatic buds (and their associated ducts) to completely fuse can result in **pancreas divisum**, where two separate ductal systems persist, corresponding to the dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts.
*Apoptosis*
- **Apoptosis** (programmed cell death) is crucial for the removal of unwanted cells and sculpting tissues during embryogenesis, such as the formation of digits or the regression of certain structures.
- It does not directly explain the persistence of two separate pancreatic ducts due to non-fusion of developmental buds.
*Stem cell differentiation*
- **Stem cell differentiation** is the process by which less specialized stem cells become more specialized cell types, which is fundamental to organ development and tissue formation.
- While essential for pancreatic development, it doesn't specifically account for the anatomical anomaly of two persistent ducts.
*Notochord signaling*
- **Notochord signaling** is vital for inducing the formation of the neural tube and defining the dorsal-ventral axis of the embryo, as well as influencing the development of other nearby structures.
- This process is not directly related to the fusion of pancreatic buds, which occurs later and is influenced by interactions between mesenchymal and endodermal tissues.
*Neural crest cell migration*
- **Neural crest cells** are multipotent cells that migrate extensively throughout the embryo to form a wide variety of tissues, including parts of the peripheral nervous system, melanocytes, and bone/cartilage of the face and skull.
- Their migratory pathways and derivatives are not directly involved in the development and fusion of the pancreatic ductal system.
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 5: A 23-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of decreased hearing, dizziness, and ringing in his right ear for the past 6 months. Physical examination shows multiple soft, yellow plaques and papules on his arms, chest, and back. There is sensorineural hearing loss and weakness of facial muscles bilaterally. His gait is unsteady. An MRI of the brain shows a 3-cm mass near the right internal auditory meatus and a 2-cm mass at the left cerebellopontine angle. The abnormal cells in these masses are most likely derived from which of the following embryological structures?
- A. Surface ectoderm
- B. Neural tube
- C. Neural crest (Correct Answer)
- D. Notochord
- E. Mesoderm
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Neural crest***
- The patient's symptoms (bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, facial weakness, unsteady gait, central masses) along with cutaneous lesions (soft, yellow plaques) are highly suggestive of **Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)**.
- NF2 is characterized by **vestibular schwannomas** (acoustic neuromas) and other CNS tumors, which are derived from **Schwann cells**. Schwann cells, along with melanocytes and other peripheral nervous system components, originate from the **neural crest**.
*Surface ectoderm*
- The surface ectoderm forms structures such as the **epidermis**, hair, nails, and anterior pituitary.
- While the skin lesions are present, the primary tumors (schwannomas) are not derived from the surface ectoderm.
*Neural tube*
- The neural tube gives rise to the **central nervous system** (brain and spinal cord) and motor neurons.
- While the tumors affect the brain and cranial nerves, the specific cell type forming schwannomas (Schwann cells) does not originate directly from the neural tube.
*Notochord*
- The notochord induces the formation of the neural tube and eventually degenerates, contributing to the **nucleus pulposus** of the intervertebral discs.
- It is not involved in the pathogenesis or cellular origin of schwannomas.
*Mesoderm*
- The mesoderm gives rise to connective tissues, blood, bone, muscle, and most internal organs.
- While some tumors can have mesodermal origins, schwannomas are neuroectodermal in origin.
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 6: A 52-year-old woman sees you in your office with a complaint of new-onset headaches over the past few weeks. On exam, you find a 2 x 2 cm dark, irregularly shaped, pigmented lesion on her back. She is concerned because her father recently passed away from skin cancer. What tissue type most directly gives rise to the lesion this patient is experiencing?
- A. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Endoderm
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Ectoderm
- E. Neuroectoderm
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The suspected lesion, given its description and the patient's family history of skin cancer, is likely a **melanoma**.
- Melanoma originates from **melanocytes**, which are derived from **neural crest cells** during embryonic development.
*Endoderm*
- The endoderm gives rise to the **lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, as well as organs such as the liver and pancreas.
- It is not involved in the formation of melanocytes or skin lesions like melanoma.
*Mesoderm*
- The mesoderm forms tissues such as **muscle, bone, cartilage, connective tissue**, and the circulatory system.
- It does not directly give rise to melanocytes, which are the cells of origin for melanoma.
*Ectoderm*
- The ectoderm gives rise to the **epidermis, nervous system**, and sensory organs.
- While melanocytes are found in the epidermis, they are specifically derived from the **neural crest (a sub-population of ectoderm)**, not the general ectoderm.
*Neuroectoderm*
- Neuroectoderm specifically refers to the ectoderm that develops into the **nervous system**.
- While neural crest cells originate from the neuroectoderm, "neural crest cells" is a more precise answer for the origin of melanocytes.
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 7: A child is in the nursery one day after birth. A nurse notices a urine-like discharge being expressed through the umbilical stump. What two structures in the embryo are connected by the structure that failed to obliterate during the embryologic development of this child?
- A. Kidney - large bowel
- B. Liver - umbilical vein
- C. Bladder - small bowel
- D. Pulmonary artery - aorta
- E. Bladder - umbilicus (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Bladder - umbilicus***
- A **urine-like discharge** from the umbilical stump indicates a **patent urachus**, which is the embryonic remnant of the allantois.
- The **allantois** (which becomes the urachus) is an embryonic structure that connects the **fetal bladder** to the **umbilicus** during development.
- Normally, the allantois obliterates after birth to form the **median umbilical ligament**, but failure to obliterate results in a patent urachus allowing urine to discharge through the umbilicus.
*Kidney - large bowel*
- These two structures are not directly connected by an obliterating embryonic structure relevant to urine discharge from an umbilical stump.
- The kidneys form urine, and the large bowel is part of the digestive tract, with no direct embryonic communication to the umbilicus for urine expression.
*Liver - umbilical vein*
- The umbilical vein connects the **placenta to the fetal liver** (and ductus venosus) to transport oxygenated blood, not urine.
- Failure of the umbilical vein to obliterate would result in a patent umbilical vein, typically presenting as a vascular anomaly, not urine discharge.
*Pulmonary artery - aorta*
- These structures are connected by the **ductus arteriosus** in fetal circulation, bypassing the pulmonary circulation.
- While important for fetal development, a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a cardiovascular anomaly and would not manifest as urine discharge from the umbilical stump.
*Bladder - small bowel*
- While both structures are involved in waste elimination, there is no normal embryonic structure directly connecting the bladder and small bowel that obliterates to prevent urine discharge from the umbilicus.
- An abnormal connection between the bladder and bowel would typically involve a **fistula** and present with stool in urine or urine in stool, not umbilical discharge.
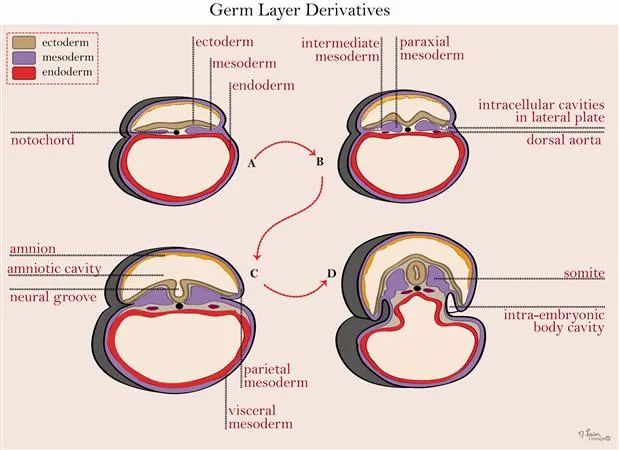
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 8: During development, a fetus is found to have incomplete fusion of the neural tube. Which of the following structures would most likely be affected by this developmental defect?
- A. Notochord
- B. Somites
- C. Vertebral bodies
- D. Spinal cord and meninges (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Spinal cord and meninges***
- Incomplete fusion of the neural tube directly results in defects of the **neural tube closure**, which include the formation of the **spinal cord** and its protective coverings, the **meninges**. [1, 2]
- Conditions like **spina bifida** (meningocele, myelomeningocele) are direct consequences of these fusion failures, exposing or abnormally developing the spinal cord and meninges. [1, 2]
*Notochord*
- The **notochord** is a transient embryonic structure that induces the formation of the neural tube by signaling to the overlying ectoderm; it is not directly formed by the neural tube itself.
- While it plays a critical role in neural tube development, its own structural integrity is typically not primarily affected by neural tube fusion defects.
*Somites*
- **Somites** are blocks of paraxial mesoderm that differentiate into sclerotome (vertebrae and ribs), myotome (skeletal muscle), and dermatome (dermis of the skin).
- While somite development is closely coordinated with neural tube formation, incomplete neural tube fusion primarily affects the neural structures themselves, not the somites directly.
*Vertebral bodies*
- **Vertebral bodies** develop from the sclerotome portion of the somites, which migrate to surround the neural tube and notochord.
- While vertebral defects can be associated with severe neural tube defects (e.g., in spina bifida, the vertebral arches may fail to close), the primary defect of incomplete neural tube fusion directly impacts the neural tissue (spinal cord and meninges), with skeletal defects being secondary or associated. [1, 2]
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG Question 10: An 11-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to complaint of intermittent and severe periumbilical pain for 1 day. She does not have any significant past medical history. She provides a history of a recent school trip to the suburbs. On physical examination, there is a mild tenderness around the umbilicus without any distension or discharge. There is no rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds are normal. An abdominal imaging shows enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes, and she is diagnosed with mesenteric lymphadenitis. However, incidentally, a mass of tissue was seen joining the inferior pole of both kidneys as shown in the image. Which of the following best describes this renal anomaly?
- A. Fused kidneys ascend beyond superior mesenteric artery.
- B. Rapid progression to acute renal failure
- C. Kidneys are usually non-functional.
- D. Increased risk of developing renal vein thrombosis
- E. Association with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) (Correct Answer)
Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation Explanation: ***Association with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO)***
- **Horseshoe kidney** is characterized by the fusion of the lower poles (most common) or upper poles of the kidneys, forming a U-shape. This anomaly is associated with an increased incidence of **ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO)** due to the abnormal course of the ureters over the isthmus.
- The abnormal ascent of the fused kidneys can also lead to an increased incidence of other anomalies such as **vesicoureteral reflux**, **renal calculi**, and recurrent urinary tract infections.
*Fused kidneys ascend beyond superior mesenteric artery.*
- The **horseshoe kidney** typically **fails to ascend** completely during development because its isthmus (the fused part) can get trapped under the **inferior mesenteric artery**.
- Therefore, fused kidneys in horseshoe kidney are often found in a **lower position** than normal, not ascended beyond the superior mesenteric artery.
*Rapid progression to acute renal failure*
- While horseshoe kidney can be associated with an increased risk of complications (like UPJO, stones, infections), it does not inherently lead to **rapid progression to acute renal failure**.
- Many individuals with a horseshoe kidney have **normal renal function** without significant clinical manifestations.
*Kidneys are usually non-functional.*
- The presence of a horseshoe kidney **does not typically mean the kidneys are non-functional**.
- In most cases, both renal units of a horseshoe kidney are **functional**, although they may be at increased risk for complications that could impact function over time.
*Increased risk of developing renal vein thrombosis*
- There is **no established increased risk** of developing **renal vein thrombosis** specifically associated with horseshoe kidney.
- The primary vascular anomalies associated with horseshoe kidney relate to the arterial supply and variations in the number and origin of renal arteries, not typically venous thrombosis.
More Bilaminar and trilaminar disc formation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.