Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Segmental innervation patterns. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old woman presents with sudden-onset pain in her lower back. She says she was exercising in the gym several hours ago when she felt a sharp pain. The pain is radiating down the side of her leg and into her foot. On physical exam, her vital signs are as follows: HR 95, BP 120/70, T 37.2 degrees C. She has extreme pain shooting down her leg with a straight leg raise. Her sensation to light touch and pin-prick is intact throughout. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Cauda equina syndrome
- B. Ankylosing spondylitis
- C. Osteomyelitis
- D. Spinal stenosis
- E. Disc herniation (Correct Answer)
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Disc herniation***
- The sudden onset of **sharp back pain** radiating down the leg (**radiculopathy**) after physical exertion, coupled with a positive **straight leg raise test**, is highly indicative of a disc herniation.
- Radiating pain suggests nerve root compression, and the straight leg raise test stretches the sciatic nerve, aggravating the pain in cases of disc herniation.
*Cauda equina syndrome*
- This is a neurological emergency characterized by **saddle anesthesia**, bowel or bladder dysfunction, and progressive motor weakness in both legs.
- These severe neurological deficits are not present in the patient's presentation; sensation is intact, and no mention of bowel/bladder issues.
*Ankylosing spondylitis*
- Typically presents with **chronic inflammatory back pain** that improves with exercise and worsens with rest, often in younger males.
- It is a systemic inflammatory condition, and the acute, exertion-related onset of pain with radiculopathy described here is not characteristic.
*Osteomyelitis*
- This is an **infection of the bone**, usually accompanied by fever, localized tenderness, and systemic signs of infection.
- The patient's vital signs are stable, and there is no indication of infection, making osteomyelitis less likely.
*Spinal stenosis*
- Characterized by **neurogenic claudication**, where leg pain and numbness worsen with walking and improve with sitting or leaning forward.
- The acute onset of pain after an intense activity and the presence of a positive straight leg raise are not typical features of spinal stenosis.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 2: A 68-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of a bulge in his scrotum that has enlarged over the past several months. He is found to have a right-sided inguinal hernia and undergoes elective hernia repair. At his first follow-up visit, he complains of a tingling sensation on his scrotum. Which of the following nerve roots communicates with the injured tissues?
- A. S1-S3
- B. L1-L2 (Correct Answer)
- C. S2-S4
- D. L4-L5
- E. L2-L3
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***L1-L2***
- The **ilioinguinal nerve** and **genitofemoral nerve**, which are commonly injured during inguinal hernia repair, arise from the **L1 and L2 spinal nerves**.
- These nerves provide sensory innervation to the **scrotum**, **inguinal region**, and **medial thigh**, explaining the patient's tingling sensation.
*S1-S3*
- These nerve roots typically contribute to the **sciatic nerve** and innervate the posterior thigh, leg, and foot, and are not directly involved in scrotal sensation relevant to an inguinal hernia repair.
- They also contribute to the **pudendal nerve**, which primarily supplies the perineum and external genitalia, but injury to this nerve is less common in routine inguinal hernia repair.
*S2-S4*
- These nerve roots primarily form the **pudendal nerve**, which innervates the **perineum** and external genitalia (including some scrotal sensation), but injury to these specific nerves is not a typical complication of routine inguinal hernia repair.
- They also contribute to the **pelvic splanchnic nerves**, controlling bladder and bowel function, which are unrelated to the described sensory deficit.
*L4-L5*
- These nerve roots primarily contribute to nerves supplying the **lower limb**, such as the **femoral nerve** and **sciatic nerve**, and do not directly innervate the scrotum.
- Injury to these roots would typically result in motor or sensory deficits of the **thigh and leg**, not isolated scrotal tingling.
*L2-L3*
- While L2 contributes to nerves supplying the inguinal region and scrotum (genitofemoral nerve), the **ilioinguinal nerve** originates from L1.
- The **lateral femoral cutaneous nerve**, which originates from L2-L3, innervates the **lateral thigh**, and its injury would cause tingling there, not in the scrotum.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of numbness in his left lower extremity. One month ago, he sustained a fracture of the neck of the left fibula during soccer practice that was treated with immobilization in a plaster cast. Physical examination of the left lower extremity is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Loss of sensation over the medial calf
- B. Impaired dorsiflexion of the foot (Correct Answer)
- C. Loss of sensation on the sole of the foot
- D. Inability to stand on tiptoes
- E. Decreased ankle reflex
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Impaired dorsiflexion of the foot***
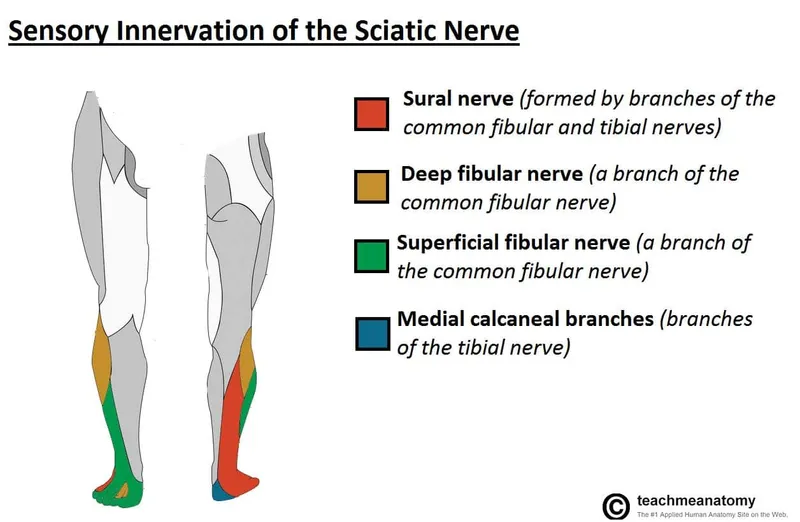
- A fracture of the **neck of the left fibula** can damage the **common fibular (peroneal) nerve**, which wraps around the fibular neck.
- Damage to the common fibular nerve specifically affects its deep branch, leading to weakness of the **tibialis anterior muscle** and **impaired dorsiflexion** (foot drop).
*Loss of sensation over the medial calf*
- **Sensation over the medial calf** is supplied by the **saphenous nerve**, a branch of the femoral nerve, which is not typically injured with a fibular neck fracture.
- Injury to the common fibular nerve primarily affects sensation over the **dorsum of the foot** and **lateral aspect of the leg**.
*Loss of sensation on the sole of the foot*
- **Sensation on the sole of the foot** is primarily mediated by the **tibial nerve** and its branches (medial and lateral plantar nerves).
- Trauma to the fibular neck is unlikely to directly compromise the tibial nerve to this extent.
*Inability to stand on tiptoes*
- The **ability to stand on tiptoes** is controlled by the **gastrocnemius and soleus muscles**, which are innervated by the **tibial nerve**.
- Injury to the common fibular nerve, rather than the tibial nerve, is associated with a fibular neck fracture.
*Decreased ankle reflex*
- The **ankle reflex** (Achilles reflex) is primarily mediated by the **S1 spinal nerve** via the **tibial nerve**.
- While severe fibular nerve compression could potentially have some indirect effects, a decreased ankle reflex is not a primary or direct symptom of common fibular nerve palsy.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 4: A 51-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressively worsening lower back pain. The pain radiates down the right leg to the lateral side of the foot. She has had no trauma, urinary incontinence, or fever. An MRI of the lumbar spine shows disc degeneration and herniation at the level of L5–S1. Which of the following is the most likely finding on physical examination?
- A. Difficulty walking on heels
- B. Exaggerated patellar tendon reflex
- C. Diminished sensation of the anus and genitalia
- D. Diminished sensation of the anterior lateral thigh
- E. Weak Achilles tendon reflex (Correct Answer)
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Weak Achilles tendon reflex***
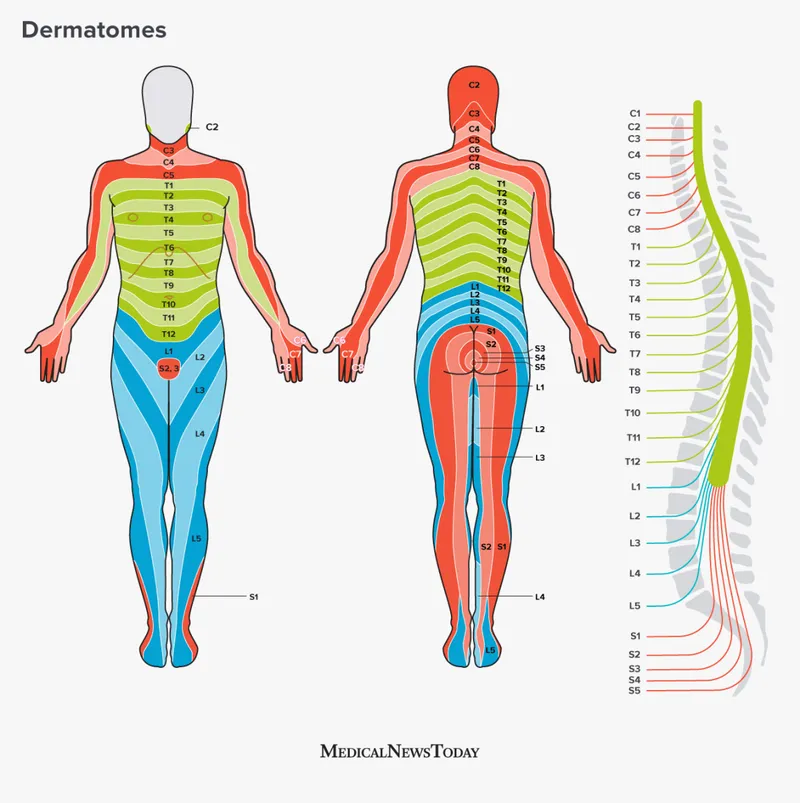
- A herniated disc at **L5-S1** typically compresses the **S1 nerve root**, which is responsible for the **Achilles tendon reflex**.
- **S1 radiculopathy** presents with weakness in plantarflexion, diminished or absent Achilles reflex, and sensory loss in the **lateral foot** (matching the patient's symptoms).
*Difficulty walking on heels*
- Difficulty walking on heels (**dorsiflexion weakness**) is primarily associated with **L4-L5 disc herniation** compressing the **L5 nerve root**.
- This symptom indicates **L5 radiculopathy**, which affects the tibialis anterior muscle, not S1.
*Exaggerated patellar tendon reflex*
- An exaggerated patellar tendon reflex (**hyperreflexia**) indicates an **upper motor neuron lesion** or spinal cord compression above the lumbar region.
- A disc herniation at **L5-S1** causes a **lower motor neuron lesion** with diminished reflexes, not hyperreflexia.
*Diminished sensation of the anus and genitalia*
- This symptom, along with urinary incontinence and saddle anesthesia, is characteristic of **cauda equina syndrome**, a surgical emergency.
- The patient lacks urinary incontinence and the specific unilateral pain pattern points to isolated **S1 radiculopathy**, not cauda equina syndrome.
*Diminished sensation of the anterior lateral thigh*
- Sensory loss in the **anterior lateral thigh** is associated with compression of the **lateral femoral cutaneous nerve** or **L2-L4 nerve roots**.
- This pattern is not consistent with **L5-S1 disc herniation**, which causes sensory changes in the lateral foot and posterior leg.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 5: A 78-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after she fell while gardening and experienced severe pain in her right arm. She has a history of well controlled hypertension and has been found to have osteoporosis. On presentation she is found to have a closed midshaft humerus fracture. No other major findings are discovered on a trauma survey. She is placed in a coaptation splint. The complication that is most associated with this injury has which of the following presentations?
- A. Hand of benediction
- B. Hypothenar atrophy
- C. Flattened deltoid
- D. Elbow flexion deficits
- E. Wrist drop (Correct Answer)
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Wrist drop***
- A **midshaft humerus fracture** is classically associated with injury to the **radial nerve**, which wraps around the humerus at this level.
- **Radial nerve injury** causes paralysis of the extensors of the wrist and fingers, leading to a characteristic **wrist drop** presentation.
*Hand of benediction*
- This presentation, where the **index and middle fingers remain extended** while the ring and little fingers flex, is characteristic of a **proximal median nerve injury**.
- A midshaft humerus fracture is less likely to cause a proximal median nerve injury given the anatomical course of the nerve.
*Hypothenar atrophy*
- **Hypothenar atrophy** is indicative of **ulnar nerve damage**, usually at the cubital tunnel or Guyon's canal.
- While the ulnar nerve courses near the humerus, it is less commonly injured in midshaft fractures compared to the radial nerve.
*Flattened deltoid*
- A **flattened deltoid** is a sign of **axillary nerve injury** or shoulder dislocation, leading to paralysis of the deltoid muscle.
- The axillary nerve is more commonly injured in **proximal humerus fractures** or shoulder trauma, not typically midshaft fractures.
*Elbow flexion deficits*
- **Elbow flexion deficits** are primarily associated with injury to the **musculocutaneous nerve** or the C5/C6 nerve roots.
- While a severe humeral fracture could potentially affect these structures, it is not the most direct or common neurological complication of a midshaft fracture, which targets the radial nerve.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 6: A 41-year-old woman presents with back pain for the past 2 days. She says that the pain radiates down along the posterior right thigh and leg. She says the pain started suddenly after lifting a heavy box 2 days ago. Past medical history is irrelevant. Physical examination reveals a straight leg raise (SLR) test restricted to 30°, inability to walk on her toes, decreased sensation along the lateral border of her right foot, and diminished ankle jerk on the same side. Which of the following nerve roots is most likely compressed?
- A. Fourth lumbar nerve root (L4)
- B. Second sacral nerve root (S2)
- C. Third sacral nerve root (S3)
- D. Fifth lumbar nerve root (L5)
- E. First sacral nerve root (S1) (Correct Answer)
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***First sacral nerve root (S1)***
- **Inability to walk on toes** (weakness of gastrocnemius and soleus), **decreased sensation along the lateral border of the foot**, and a **diminished ankle jerk** are classic signs of S1 radiculopathy.
- The radiating pain down the posterior leg, restricted straight leg raise due to a sudden onset after lifting, points towards a **disc herniation** compressing the S1 nerve root.
*Fourth lumbar nerve root (L4)*
- Compression of L4 typically causes **weakness in knee extension** (quadriceps), diminished patellar reflex, and sensory loss over the medial aspect of the shin.
- The patient's symptoms (inability to walk on toes, diminished ankle jerk) are not consistent with L4 nerve root involvement.
*Second sacral nerve root (S2)*
- S2 radiculopathy primarily affects sensation in the posterior thigh and calf and can cause **weakness in knee flexion** and **plantarflexion**, but the complete constellation of symptoms (especially ankle jerk reflex) is more indicative of S1.
- Isolated S2 compression without S1 involvement is less common with these specific signs.
*Third sacral nerve root (S3)*
- S3 nerve root compression typically presents with **perineal numbness** and issues with bowel or bladder function due to its involvement in these functions.
- The described motor and sensory deficits are not characteristic of S3 radiculopathy.
*Fifth lumbar nerve root (L5)*
- L5 radiculopathy is characterized by **weakness in foot dorsiflexion** (foot drop) and toe extension, leading to inability to walk on heels, and sensory loss on the dorsum of the foot.
- While L5 compression can cause radiating pain and a restricted straight leg raise, the specific deficit of **inability to walk on toes** and a **diminished ankle jerk** are not typical of L5 involvement.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 7: An MRI of a patient with low back pain reveals compression of the L5 nerve root. Which of the following muscles would most likely show weakness during physical examination?
- A. Tibialis posterior
- B. Tibialis anterior (Correct Answer)
- C. Gastrocnemius
- D. Quadriceps femoris
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Tibialis anterior***
- The **L5 nerve root** primarily innervates muscles responsible for **dorsiflexion** of the foot, with the **tibialis anterior** being the primary dorsiflexor.
- Weakness of the tibialis anterior would manifest as difficulty lifting the front of the foot, potentially leading to a **foot drop** gait.
*Tibialis posterior*
- The **tibialis posterior** is primarily innervated by the **tibial nerve** (S1-S2) and is responsible for **plantarflexion** and **inversion** of the foot.
- Weakness in this muscle would not be the most likely presentation of L5 nerve root compression.
*Gastrocnemius*
- The **gastrocnemius** muscle is primarily innervated by the **tibial nerve** (S1-S2) and is a powerful **plantarflexor** of the foot.
- Weakness in this muscle would indicate an S1 or S2 nerve root issue, not typically L5.
*Quadriceps femoris*
- The **quadriceps femoris** is innervated by the **femoral nerve**, predominantly originating from the **L2, L3, and L4 nerve roots**.
- Weakness would manifest as difficulty extending the knee, which is not characteristic of L5 compression.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 8: A 57-year-old man presents to the ED complaining of back and left leg pain. He was lifting heavy furniture while helping his daughter move into college when all of sudden he felt a sharp pain at his back. The pain is described as severe, worse with movement, and shoots down his lateral thigh. The patient denies any bowel/urinary incontinence, saddle anesthesia, weight loss, or weakness. He denies any past medical history but endorses a family history of osteoporosis. He has been smoking 1 pack per day for the past 20 years. Physical examination demonstrated decreased sensation at the left knee, decreased patellar reflex, and a positive straight leg test. There is diffuse tenderness to palpation at the lower back but no vertebral step-offs were detected. What is the most likely etiology for this patient’s pain?
- A. Vertebral compression fracture
- B. Disc herniation at the L4/L5 vertebra
- C. Spinal metastasis from lung cancer
- D. Disc herniation at the L3/L4 vertebra (Correct Answer)
- E. Lumbar muscle sprain
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Disc herniation at the L3/L4 vertebra***
- The patient's symptoms of **acute back pain radiating down the lateral thigh** after lifting, combined with **decreased sensation at the left knee** and a **decreased patellar reflex**, are classic signs of L3/L4 nerve root compression.
- A **positive straight leg test** also supports nerve root irritation, and the absence of red flag symptoms like incontinence or saddle anesthesia makes a simple disc herniation more likely than other serious conditions.
*Vertebral compression fracture*
- While lifting heavy objects can cause compression fractures, these usually present with more **severe, localized pain** that is not typically radiating with specific dermatomal or reflex changes.
- Absence of **vertebral step-offs** or significant predisposing factors for a fracture (e.g., severe osteoporosis, trauma) makes this less likely given the specific neurological findings.
*Disc herniation at the L4/L5 vertebra*
- An L4/L5 disc herniation would typically cause symptoms related to the **L5 nerve root**, such as pain radiating down the **lateral leg into the foot**, **weakness in dorsiflexion of the ankle** or **big toe**, and potentially a **decreased medial hamstring reflex**.
- The patient's reported symptoms (lateral thigh pain, decreased knee sensation, decreased patellar reflex) are more consistent with **L4 nerve root** involvement.
*Spinal metastasis from lung cancer*
- Although the patient has a **smoking history** and could be at risk for lung cancer, this diagnosis typically presents with more **insidious onset** of unexplained back pain, often with **weight loss**, and sometimes with more profound neurological deficits or bone pain not relieved by rest.
- The acute onset after an inciting event and specific neurological findings of a single nerve root are less suggestive of metastasis.
*Lumbar muscle sprain*
- A muscle sprain would typically present with **localized back pain**, often worsened by movement, but would **not involve radicular pain** shooting down the leg, nor would it cause specific **neurological deficits** like decreased sensation or reflex changes.
- The positive straight leg test and neurological findings rule out a simple muscle sprain.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 9: A 75-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of sharp, stabbing pain in the lower back that radiates to the back of his left leg. He also has had a loss of sensitivity around his buttocks and inner thighs as well as increased trouble urinating the last week. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with prostate cancer and was treated with radiation therapy. Neurologic examination shows reduced strength and reflexes in the left lower extremity; the right side is normal. The resting anal sphincter tone is normal but the squeeze tone is reduced. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Central cord syndrome
- B. Conus medullaris syndrome
- C. Anterior spinal cord syndrome
- D. Brown-sequard syndrome
- E. Cauda equina syndrome (Correct Answer)
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Cauda equina syndrome***
- The patient presents with **bilateral sensory loss in the perineal region** (**saddle anesthesia**) and **new-onset urinary dysfunction** (trouble urinating, reduced squeeze tone), which are classic symptoms of cauda equina syndrome.
- The **sharp, stabbing radicular pain** radiating down the leg indicates nerve root involvement, characteristic of cauda equina rather than conus medullaris.
- The **asymmetric motor weakness** (left leg only) supports cauda equina syndrome, as compression can preferentially affect specific nerve roots, whereas conus medullaris typically causes more symmetric bilateral deficits.
- The history of **prostate cancer** and **radiation therapy** suggests a potential metastatic lesion compressing the cauda equina nerves.
*Central cord syndrome*
- This syndrome primarily affects the **upper extremities more than the lower extremities** and typically results from hyperextension injuries in older individuals.
- It often presents with **dissociated sensory loss** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) below the level of the lesion, which is not the primary complaint here.
*Conus medullaris syndrome*
- Affects the **sacral spinal cord segments (S3-S5)**, leading to **symmetrical motor and sensory deficits**, often with prominent early **bowel and bladder dysfunction**.
- While it causes saddle anesthesia and urinary symptoms, the **asymmetrical motor weakness** (left leg only) and **prominent radicular pain** extending down the leg are more characteristic of cauda equina syndrome.
- Conus lesions typically present with more **symmetric bilateral deficits** rather than the unilateral pattern seen here.
*Anterior spinal cord syndrome*
- Characterized by **bilateral motor paralysis** and **loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the lesion, with **preservation of proprioception and vibratory sensation**.
- It would not typically present with the isolated **saddle anesthesia** and **radicular pain** described in the patient.
*Brown-sequard syndrome*
- Results from a **hemicord lesion**, causing **ipsilateral motor paralysis** and loss of proprioception/vibration below the lesion, and **contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation**.
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral saddle anesthesia** and **bowel/bladder dysfunction** do not align with the characteristic unilateral sensory and motor presentation of Brown-Sequard syndrome.
Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG Question 10: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her father because of a 1-month history of pain in her right knee. She is a competitive volleyball player and has missed several games recently due to pain. Examination shows swelling distal to the right knee joint on the anterior surface of the proximal tibia; there is no overlying warmth or deformity. Extension of the right knee against resistance is painful. Which of the following structures is attached to the affected anterior tibial area?
- A. Patellar ligament (Correct Answer)
- B. Iliotibial band
- C. Pes anserinus tendon
- D. Quadriceps tendon
- E. Anterior cruciate ligament
Segmental innervation patterns Explanation: ***Patellar ligament***
- The symptoms described, particularly **pain in the right knee worse with activity** in a young, active individual with **swelling distal to the knee joint on the anterior surface of the proximal tibia**, are classic for **Osgood-Schlatter disease**.
- This condition involves inflammation of the **patellar ligament** (also known as the patellar tendon) insertion onto the **tibial tuberosity**, which is the bony prominence on the anterior proximal tibia.
*Iliotibial band*
- The **iliotibial band (IT band)** runs along the lateral aspect of the thigh and inserts on the **lateral condyle of the tibia (Gerdy's tubercle)**, not the anterior proximal tibia.
- **IT band syndrome** typically causes lateral knee pain, often seen in runners, and not central anterior tibial swelling.
*Pes anserinus tendon*
- The **pes anserinus tendon** is formed by the conjoined tendons of the **sartorius**, **gracilis**, and **semitendinosus muscles**, inserting on the **medial proximal tibia**.
- Inflammation here (**pes anserinus bursitis/tendinitis**) would cause pain and swelling on the medial side of the knee, not the anterior aspect.
*Quadriceps tendon*
- The **quadriceps tendon** connects the quadriceps muscles to the **superior pole of the patella**, not the anterior proximal tibia.
- Conditions affecting this tendon typically cause pain above or at the patella, not distal to the knee joint.
*Anterior cruciate ligament*
- The **anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)** is an intra-articular ligament that connects the **femur to the tibia within the knee joint**.
- An **ACL injury** typically presents with acute pain, instability, and a "popping" sensation, not chronic swelling on the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia.
More Segmental innervation patterns US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.