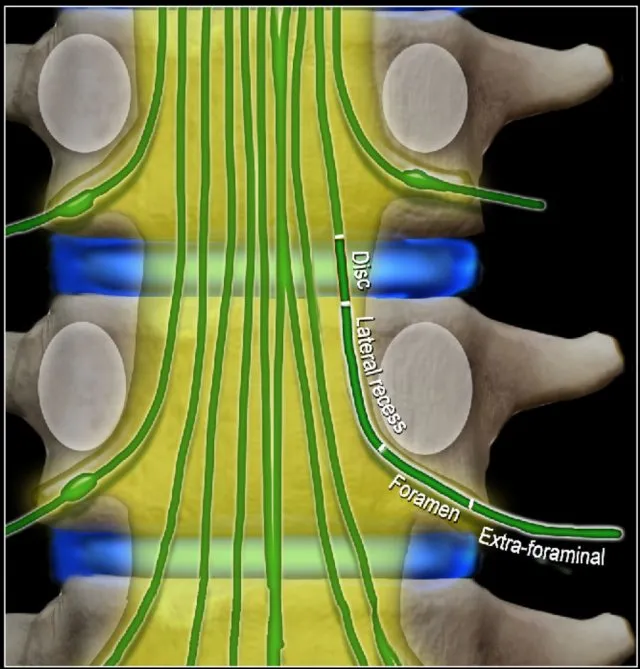
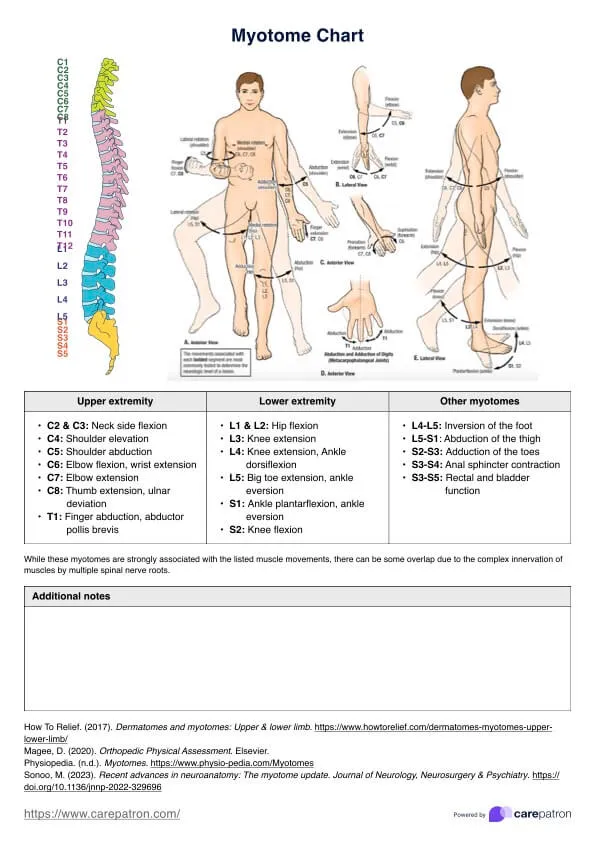
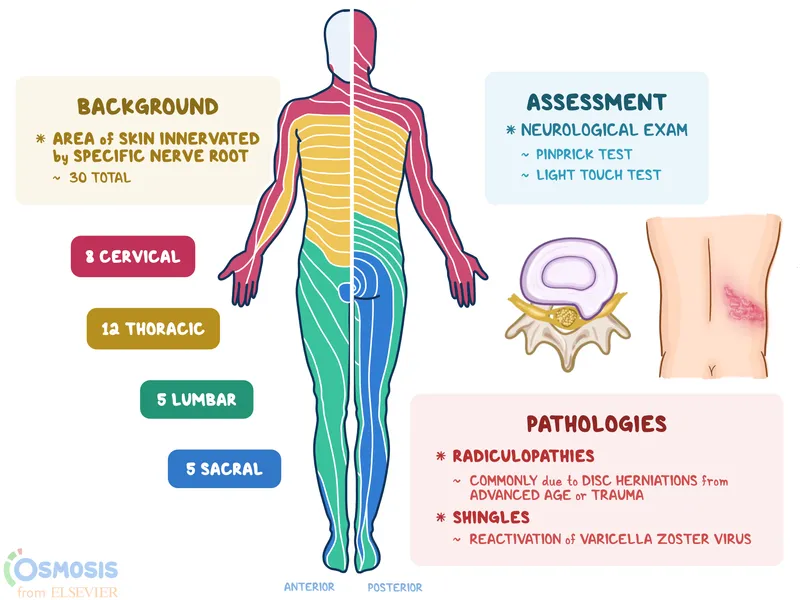
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Radiculopathy patterns by level. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 1: Seven hours after undergoing left hip arthroplasty for chronic hip pain, a 67-year-old woman reports a prickling sensation in her left anteromedial thigh and lower leg. Neurologic examination shows left leg strength 3/5 on hip flexion and 2/5 on knee extension. Patellar reflex is decreased on the left. Sensation to pinprick and light touch are decreased on the anteromedial left thigh as well as medial lower leg. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Femoral nerve injury (Correct Answer)
- B. L5 radiculopathy
- C. Sural nerve injury
- D. S1 radiculopathy
- E. Fibular nerve injury
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Femoral nerve injury***
- The patient's symptoms—weakness in **hip flexion** (iliopsoas via femoral nerve) and **knee extension** (quadriceps via femoral nerve), decreased **patellar reflex** (femoral nerve), and sensory loss in the **anteromedial thigh** (femoral nerve) and **medial lower leg** (saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve)—are all consistent with femoral nerve dysfunction.
- **Hip arthroplasty procedures** can sometimes lead to iatrogenic femoral nerve damage due to retraction, compression, or direct injury during surgery, especially when positioning or using surgical instruments.
*L5 radiculopathy*
- L5 radiculopathy typically causes weakness in **foot dorsiflexion**, **eversion**, and **toe extension**, along with sensory loss over the **dorsum of the foot** and lateral lower leg, which does not match the patient's presentation.
- While it can cause hip abductor weakness, it would not explain the prominent **quadriceps weakness** and **decreased patellar reflex**.
*Sural nerve injury*
- The sural nerve provides sensation to the **posterolateral aspect of the lower leg** and lateral malleolus, and has no motor function to the hip or knee.
- Injury to this nerve would not account for the patient's **proximal weakness** or sensory loss in the anteromedial thigh.
*S1 radiculopathy*
- S1 radiculopathy typically leads to weakness in **plantarflexion**, **hip extension**, and an absent **Achilles reflex**, along with sensory loss over the lateral foot and sole.
- It would not explain the significant **quadriceps weakness**, **decreased patellar reflex**, or sensory changes in the anteromedial thigh.
*Fibular nerve injury*
- Fibular (peroneal) nerve injury primarily results in **foot drop** (weakness in dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot) and sensory loss over the **dorsum of the foot** and anterolateral lower leg.
- It does not affect hip flexion, knee extension, or the patellar reflex, nor does it cause sensory loss in the anteromedial thigh.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old woman presents with sudden-onset pain in her lower back. She says she was exercising in the gym several hours ago when she felt a sharp pain. The pain is radiating down the side of her leg and into her foot. On physical exam, her vital signs are as follows: HR 95, BP 120/70, T 37.2 degrees C. She has extreme pain shooting down her leg with a straight leg raise. Her sensation to light touch and pin-prick is intact throughout. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Cauda equina syndrome
- B. Ankylosing spondylitis
- C. Osteomyelitis
- D. Spinal stenosis
- E. Disc herniation (Correct Answer)
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Disc herniation***
- The sudden onset of **sharp back pain** radiating down the leg (**radiculopathy**) after physical exertion, coupled with a positive **straight leg raise test**, is highly indicative of a disc herniation.
- Radiating pain suggests nerve root compression, and the straight leg raise test stretches the sciatic nerve, aggravating the pain in cases of disc herniation.
*Cauda equina syndrome*
- This is a neurological emergency characterized by **saddle anesthesia**, bowel or bladder dysfunction, and progressive motor weakness in both legs.
- These severe neurological deficits are not present in the patient's presentation; sensation is intact, and no mention of bowel/bladder issues.
*Ankylosing spondylitis*
- Typically presents with **chronic inflammatory back pain** that improves with exercise and worsens with rest, often in younger males.
- It is a systemic inflammatory condition, and the acute, exertion-related onset of pain with radiculopathy described here is not characteristic.
*Osteomyelitis*
- This is an **infection of the bone**, usually accompanied by fever, localized tenderness, and systemic signs of infection.
- The patient's vital signs are stable, and there is no indication of infection, making osteomyelitis less likely.
*Spinal stenosis*
- Characterized by **neurogenic claudication**, where leg pain and numbness worsen with walking and improve with sitting or leaning forward.
- The acute onset of pain after an intense activity and the presence of a positive straight leg raise are not typical features of spinal stenosis.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 3: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of burning pain in his neck and arms for a year. He has also had paresthesias in his hands during this period. He has had increasing weakness in both hands during the past 3 months. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension. He was involved in a motor vehicle collision 3 years ago. Current medications include metformin, sitagliptin, enalapril, atorvastatin, and aspirin. He has had 7 sexual partners in his lifetime; he uses condoms inconsistently. He is oriented to time, place, and person. Vital signs are within normal limits. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Examination of the upper extremities shows decreased muscle strength, absent reflexes, and decreased hand grip with fasciculations bilaterally. Sensation to temperature and pain is absent over the chest and bilateral upper arms. Vibration and joint position sensations are present in the upper limbs. Cranial nerve examination shows no focal findings. Examination of the lower extremities show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Brown-Séquard syndrome
- B. Tabes dorsalis
- C. Multiple sclerosis
- D. Syringomyelia (Correct Answer)
- E. Cervical disk prolapse
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Syringomyelia***
- This condition is characterized by a central canal cavitation (syrinx) in the spinal cord, leading to damage to the **spinothalamic tracts** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) and anterior horn cells (weakness, fasciculations, absent reflexes). The **'cape-like' distribution** of sensory loss over the chest and arms, along with hand weakness, is classic.
- The sensation loss to temperature and pain over the chest and bilateral upper arms with preserved vibration and joint position sensation in upper limbs is a **dissociated sensory loss**, a hallmark of syringomyelia, as the dorsal columns (responsible for vibration and proprioception) are typically spared.
*Brown-Séquard syndrome*
- This syndrome results from **hemitransaction of the spinal cord**, causing ipsilateral loss of motor function and proprioception/vibration sensation, and contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation below the lesion.
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral sensory loss** and **bilateral weakness** do not fit this unilateral lesion pattern.
*Tabes dorsalis*
- This is a late manifestation of **syphilis**, primarily affecting the posterior columns of the spinal cord (dorsal columns), leading to loss of **proprioception and vibration sensation**, along with ataxia and shooting pains.
- The patient presents with loss of pain and temperature sensation, not primarily proprioception and vibration, and has **motor weakness with fasciculations**, which are not typical for tabes dorsalis.
*Multiple sclerosis*
- MS is characterized by **demyelination in the central nervous system**, presenting with diverse neurological symptoms that often wax and wane, affecting multiple areas of the brain and spinal cord.
- While it can cause sensory and motor deficits, the **dissociated sensory loss** (pain/temperature vs. vibration/proprioception) in a "cape-like" distribution with prominent fasciculations points away from MS.
*Cervical disk prolapse*
- A cervical disk prolapse typically causes **radicular pain and neurological deficits** (motor weakness, sensory loss, reflex changes) in a dermatomal or myotomal distribution corresponding to the compressed nerve root.
- While it can cause arm pain and weakness, the **bilateral, "cape-like" dissociated sensory loss** over the chest and arms is not characteristic of a single or multiple cervical nerve root compressions.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 4: A 30-year-old man presents with weakness in his right hand. He says he has been an avid cyclist since the age of 20. He denies any recent trauma. Physical examination reveals decreased sensations over the 4th and 5th digits with difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits. Strength is 4 out of 5 in the extensor muscles of the right hand and wrist. When the patient is asked to extend his fingers, the result is shown in the image. Which of the following nerves is most likely damaged in this patient?
- A. Median nerve
- B. Musculocutaneous nerve
- C. Axillary nerve
- D. Ulnar nerve (Correct Answer)
- E. Radial nerve
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Ulnar nerve***
- The symptoms, including weakness in the **right hand**, decreased sensation over the **4th and 5th digits**, and difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits (which suggests **ulnar claw**), are characteristic of **ulnar nerve damage**.
- **Avid cycling** can lead to compression of the ulnar nerve in the **Guyon's canal** (handlebar palsy) or at the **cubital tunnel** in the elbow, causing these specific signs.
*Median nerve*
- Damage to the median nerve typically affects the **thumb**, **index**, **middle finger**, and radial half of the ring finger, causing **ape hand deformity** or **carpal tunnel syndrome**.
- It controls movements like **thumb opposition** and **flexion of the first three digits**, which are not primarily described as impaired here.
*Musculocutaneous nerve*
- This nerve primarily innervates the **biceps brachii**, **brachialis**, and **coracobrachialis muscles**, affecting **elbow flexion** and **forearm supination**.
- It provides sensory innervation to the **lateral forearm**, symptoms not consistent with this patient's presentation.
*Axillary nerve*
- Damage to the axillary nerve results in weakness of the **deltoid** and **teres minor muscles**, leading to impaired **shoulder abduction** and external rotation.
- Sensory loss would be over the **lateral aspect of the shoulder**, which is unrelated to the described hand symptoms.
*Radial nerve*
- Radial nerve damage typically results in **wrist drop** and impaired **extension of the fingers and thumb** due to innervation of the extensors.
- While there is difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits, the sensory loss pattern (4th and 5th digits) and specific **ulnar claw** appearance are more indicative of ulnar nerve involvement.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man presents to the ED complaining of back and left leg pain. He was lifting heavy furniture while helping his daughter move into college when all of sudden he felt a sharp pain at his back. The pain is described as severe, worse with movement, and shoots down his lateral thigh. The patient denies any bowel/urinary incontinence, saddle anesthesia, weight loss, or weakness. He denies any past medical history but endorses a family history of osteoporosis. He has been smoking 1 pack per day for the past 20 years. Physical examination demonstrated decreased sensation at the left knee, decreased patellar reflex, and a positive straight leg test. There is diffuse tenderness to palpation at the lower back but no vertebral step-offs were detected. What is the most likely etiology for this patient’s pain?
- A. Vertebral compression fracture
- B. Disc herniation at the L4/L5 vertebra
- C. Spinal metastasis from lung cancer
- D. Disc herniation at the L3/L4 vertebra (Correct Answer)
- E. Lumbar muscle sprain
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Disc herniation at the L3/L4 vertebra***
- The patient's symptoms of **acute back pain radiating down the lateral thigh** after lifting, combined with **decreased sensation at the left knee** and a **decreased patellar reflex**, are classic signs of L3/L4 nerve root compression.
- A **positive straight leg test** also supports nerve root irritation, and the absence of red flag symptoms like incontinence or saddle anesthesia makes a simple disc herniation more likely than other serious conditions.
*Vertebral compression fracture*
- While lifting heavy objects can cause compression fractures, these usually present with more **severe, localized pain** that is not typically radiating with specific dermatomal or reflex changes.
- Absence of **vertebral step-offs** or significant predisposing factors for a fracture (e.g., severe osteoporosis, trauma) makes this less likely given the specific neurological findings.
*Disc herniation at the L4/L5 vertebra*
- An L4/L5 disc herniation would typically cause symptoms related to the **L5 nerve root**, such as pain radiating down the **lateral leg into the foot**, **weakness in dorsiflexion of the ankle** or **big toe**, and potentially a **decreased medial hamstring reflex**.
- The patient's reported symptoms (lateral thigh pain, decreased knee sensation, decreased patellar reflex) are more consistent with **L4 nerve root** involvement.
*Spinal metastasis from lung cancer*
- Although the patient has a **smoking history** and could be at risk for lung cancer, this diagnosis typically presents with more **insidious onset** of unexplained back pain, often with **weight loss**, and sometimes with more profound neurological deficits or bone pain not relieved by rest.
- The acute onset after an inciting event and specific neurological findings of a single nerve root are less suggestive of metastasis.
*Lumbar muscle sprain*
- A muscle sprain would typically present with **localized back pain**, often worsened by movement, but would **not involve radicular pain** shooting down the leg, nor would it cause specific **neurological deficits** like decreased sensation or reflex changes.
- The positive straight leg test and neurological findings rule out a simple muscle sprain.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 24 weeks gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She reports dull aching pain and paresthesia over her left hand during the last few weeks. The pain radiates to her shoulder and is worse at night. Her hand feels numb upon waking up in the morning. She has a sister who has multiple sclerosis. Her current medications include iron supplements and a multivitamin. Vital signs are within normal limits. When the wrist is passively held in full flexion, aggravation of paresthesia is perceived immediately. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Demyelinating disease of peripheral nerves
- B. Ulnar nerve compression
- C. Demyelinating disease of CNS
- D. Median nerve compression (Correct Answer)
- E. Cervical radiculopathy
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Median nerve compression***
- The patient's symptoms of **dull aching pain**, **paresthesia** in the hand radiating to the shoulder, and **nocturnal worsening** relieved by activity are classic for **carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)**.
- The **Phalen's maneuver** (passive wrist flexion causing paresthesia) is a positive sign for CTS, indicating compression of the **median nerve** at the wrist, which is often exacerbated during pregnancy due to fluid retention and swelling.
*Demyelinating disease of peripheral nerves*
- While it can cause paresthesia, it typically presents with more diffuse and progressive sensory or motor deficits, and the specific pattern of hand symptoms and a positive Phalen's test are not characteristic.
- The symptoms are more localized and directly reproduced by a maneuver that specifically impinges the median nerve.
*Ulnar nerve compression*
- Compression of the ulnar nerve (e.g., at the **cubital tunnel**) would cause symptoms primarily in the **fourth and fifth digits**, which is not described here.
- A positive Phalen's maneuver specifically implicates the median nerve, not the ulnar nerve.
*Demyelinating disease of CNS*
- A demyelinating disease of the CNS, like **multiple sclerosis**, which runs in her family, would present with more widespread, fluctuating neurological deficits, often involving vision, balance, or motor weakness.
- The symptoms described are strictly localized to the hand and arm distribution, consistent with a peripheral nerve entrapment.
*Cervical radiculopathy*
- Cervical radiculopathy, caused by nerve root compression in the neck, would typically present with neck pain, and the pain and paresthesia would follow a **dermatomal pattern** corresponding to the affected nerve root.
- While it can radiate to the shoulder and arm, the positive Phalen's maneuver points specifically to a wrist-level median nerve compression, and the lack of neck pain makes it less likely.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 7: A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient was at a stop when he was rear-ended from behind by a vehicle traveling at 11 miles per hour. The patient complains of severe back pain but states he otherwise feels well. The patient is currently seeing a physical therapist who is giving him exercises to alleviate the back pain that is present every morning, relived by activity, and worse with inactivity. He is a student at the university and is struggling with his grades. His temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 117/78 mmHg, pulse is 116/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical exam demonstrates a decreased range of motion of the patient's spine and tenderness to palpation over the vertebrae. The rest of the exam is deferred due to pain. The patient is requesting a note to excuse him from final exams and work. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Spondylolisthesis
- B. Malingering
- C. Herniated nucleus pulposus
- D. Vertebral fracture
- E. Musculoskeletal strain (Correct Answer)
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Musculoskeletal strain***
- The patient has a **pre-existing chronic back pain condition** (morning stiffness relieved by activity) that is being managed with physical therapy, suggesting a baseline musculoskeletal issue.
- The **low-speed motor vehicle accident** (11 mph) is unlikely to cause significant structural injury and more likely represents an **acute-on-chronic exacerbation** of his underlying musculoskeletal condition.
- While the chronic pattern (morning stiffness, improved with activity) raises consideration for inflammatory spondyloarthropathy, among the options provided, musculoskeletal strain best captures the **acute exacerbation of chronic mechanical back pain** in the context of minor trauma.
- The patient's request for excuse from exams may represent legitimate need for rest or possible secondary gain, but does not change the primary musculoskeletal diagnosis.
*Spondylolisthesis*
- This involves **anterior slippage of one vertebra over another** and typically presents with mechanical back pain that worsens with **extension and activity** (not relieved by activity as in this patient).
- There is no mention of the characteristic **step-off deformity** on palpation or radicular symptoms that often accompany symptomatic spondylolisthesis.
- The patient's chronic pain pattern of improvement with activity argues against this diagnosis.
*Malingering*
- **Malingering** involves intentional fabrication or gross exaggeration of symptoms for external gain (avoiding exams/work).
- However, this patient has **documented chronic back pain** with ongoing physical therapy, suggesting real underlying pathology rather than pure fabrication.
- While secondary gain may be a factor, the presence of actual pre-existing symptoms and objective findings (decreased ROM, tenderness) makes pure malingering less likely.
*Herniated nucleus pulposus*
- A **herniated disc** typically presents with acute **radicular pain** radiating into the lower extremities, often with neurological deficits (weakness, numbness, reflex changes).
- This patient's presentation is primarily **axial back pain** without mention of leg pain, paresthesias, or neurological deficits, making HNP unlikely.
- The chronic nature and activity-related improvement pattern is atypical for acute disc herniation.
*Vertebral fracture*
- **Vertebral compression fractures** require either significant trauma or underlying bone pathology (osteoporosis, malignancy).
- The **low-speed impact** (11 mph rear-end collision) in a young, otherwise healthy 24-year-old male is insufficient mechanism for vertebral fracture.
- While there is tenderness over vertebrae, the patient's stable vital signs (aside from mild tachycardia likely from pain/anxiety) and absence of neurological compromise make acute fracture very unlikely.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 8: A 23-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with an acute exacerbation of her 3-month history of low back and right leg pain. She says she has had similar symptoms in the past, but this time the pain was so excruciating, it took her breath away. She describes the pain as severe, shock-like, and localized to her lower back and radiating straight down the back of her right thigh and to her calf, stopping at the ankle. Her pain is worse in the morning, and, sometimes, the pain wakes her up at night with severe buttock and posterior thigh pain but walking actually makes the pain subside somewhat. The patient reports no smoking history or alcohol or drug use. She has been working casually as a waitress and does find bending over tables a strain. She is afebrile, and her vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, her left straight leg raise test is severely limited and reproduces her buttock pain at 20° of hip flexion. Pain is worsened by the addition of ankle dorsiflexion. The sensation is intact. Her L4 and L5 reflexes are normal, but her S1 reflex is absent on the right side. A CT of the lumbar spine shows an L5–S1 disc protrusion with right S1 nerve root compression. Which of the following muscle-nerve complexes is involved in producing an S1 reflex?
- A. Adductors-obturator nerve
- B. Gastrocnemius/soleus-tibial nerve (Correct Answer)
- C. Sartorius-femoral nerve
- D. Tibialis posterior-tibial nerve
- E. Quadriceps femoris-femoral nerve
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Gastrocnemius/soleus-tibial nerve***
- The S1 reflex (also known as the **Achilles reflex**) tests the integrity of the **S1 nerve root**.
- This reflex arc involves the **gastrocnemius and soleus muscles**, which are innervated by the **tibial nerve** (derived primarily from S1).
*Adductors-obturator nerve*
- The **adductor muscles** of the thigh are primarily innervated by the **obturator nerve** (L2-L4).
- This complex is not involved in generating the **Achilles reflex**.
*Sartorius-femoral nerve*
- The **sartorius muscle** is innervated by the **femoral nerve** (L2-L4).
- This muscle and nerve are not part of the **S1 reflex arc**.
*Tibialis posterior-tibial nerve*
- The **tibialis posterior muscle** is innervated by the **tibial nerve** (L4-S3), but its primary role is in ankle inversion and plantarflexion, not the main component of the **Achilles reflex**.
- While the tibial nerve is involved in the S1 reflex, the **gastrocnemius and soleus** are the primary muscles for this reflex.
*Quadriceps femoris-femoral nerve*
- The **quadriceps femoris muscle** is responsible for the **patellar reflex** (knee jerk reflex), which tests the integrity of the **L3-L4 nerve roots**.
- It is innervated by the **femoral nerve** and is not involved in the **S1 reflex**.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 9: A 59-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with severe low back pain. She reports pain radiating down her left leg into her left foot. She also reports intermittent severe lower back spasms. The pain started after lifting multiple heavy boxes at her work as a grocery store clerk. She denies bowel or bladder dysfunction. Her past medical history is notable for osteoporosis and endometrial cancer. She underwent a hysterectomy 20 years earlier. She takes alendronate. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 135/85 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 22/min. Her BMI is 21 kg/m^2. On exam, she is unable to bend over due to pain. Her movements are slowed to prevent exacerbating her muscle spasms. A straight leg raise elicits severe radiating pain into her left lower extremity. The patient reports that the pain is worst along the posterior thigh and posterolateral leg into the fourth and fifth toes. Palpation along the lumbar vertebral spines demonstrates mild tenderness. Patellar reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. The Achilles reflex is decreased on the left. Which nerve root is most likely affected in this patient?
- A. L5
- B. S2
- C. L3
- D. L4
- E. S1 (Correct Answer)
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***S1***
- Pain radiating to the **posterior thigh**, **posterolateral leg**, and into the **fourth and fifth toes** is characteristic of **S1 dermatome involvement**.
- A **decreased Achilles reflex** (ankle jerk reflex) specifically points to compromise of the **S1 nerve root**.
*L5*
- **L5 radiculopathy** typically causes pain and sensory deficits in the **dorsum of the foot** and into the **first, second, and third toes**.
- Motor weakness often affects **foot dorsiflexion** and **toe extension**, not primarily the Achilles reflex.
*S2*
- **S2 radiculopathy** would primarily affect sensation along the **posterior thigh** and **calf**, with possible involvement of the **plantar aspect of the foot**.
- It does not typically cause a decrease in the **Achilles reflex**, which is predominantly S1.
*L3*
- **L3 radiculopathy** typically presents with pain and sensory changes along the **anterior thigh** and possibly the **medial knee**.
- It can affect the **patellar reflex**, which is intact in this patient, and does not cause pain in the posterior leg or foot.
*L4*
- **L4 radiculopathy** typically causes pain and sensory changes over the **anterior thigh**, **medial leg**, and potentially the **medial malleolus**.
- It often presents with weakness in **quadriceps muscle** and can cause a diminished **patellar reflex**, which is normal in this patient.
Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG Question 10: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of back pain for the past six months. The pain is worse with exercise and when reclining. He attends high school and is on the swim team. He also states that he lifts weights on a regular basis. He has not had any trauma to the back or any previous problems with his joints. He has no history of serious illness. His father has a disc herniation. Palpation of the spinous processes at the lumbosacral area shows that two adjacent vertebrae are displaced and are at different levels. Muscle strength is normal. Sensation to pinprick and light touch is intact throughout. When the patient is asked to walk, a waddling gait is noted. Passive raising of either the right or left leg causes pain radiating down the ipsilateral leg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Spondylolisthesis (Correct Answer)
- B. Overuse injury
- C. Ankylosing spondylitis
- D. Disc herniation
- E. Facet joint syndrome
Radiculopathy patterns by level Explanation: ***Spondylolisthesis***
- The patient presents with **back pain worse with exercise and reclining**, along with **palpable displacement of adjacent vertebrae** at different levels, which are classic signs of spondylolisthesis. The **waddling gait** and pain radiating down the leg upon passive leg raising (suggesting nerve root irritation) further support this diagnosis.
- Spondylolisthesis, particularly **isthmic type**, is common in adolescent athletes involved in sports like swimming and weightlifting due to repetitive hyperextension leading to stress fractures in the pars interarticularis.
*Overuse injury*
- While overuse injuries are common in athletes, they typically present with generalized pain or tenderness in the affected area without distinct **vertebral displacement** or neurological signs like radiating pain and a waddling gait.
- The specific signs of palpable vertebral displacement and nerve root irritation point to a more severe structural issue than a simple overuse soft tissue injury.
*Ankylosing spondylitis*
- **Ankylosing spondylitis** usually presents with **inflammatory back pain** that improves with exercise, not worsens, and often affects young adults, not typically a 14-year-old with these specific physical findings.
- It would not explain the **palpable vertebral displacement** or the sudden onset of neurological symptoms like radiating leg pain and waddling gait.
*Disc herniation*
- While disc herniation can cause **radiating leg pain** and back pain, it typically doesn't present with **palpable vertebral displacement** or a waddling gait in an adolescent without a history of significant trauma.
- The physical exam finding of displaced vertebrae is more indicative of a structural instability like spondylolisthesis rather than an isolated disc problem, even though a father has a history.
*Facet joint syndrome*
- Facet joint syndrome usually results in localized back pain that **worsens with extension and rotation** but typically does not cause **palpable vertebral displacement** or neurological deficits like radiating pain and a waddling gait.
- It is also more common in older adults due to degenerative changes, rather than a 14-year-old athlete.
More Radiculopathy patterns by level US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.