Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Thoracic cross-sections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old male patient presents with difficulty swallowing and hoarseness that has progressively worsened over the past month. During physical examination, the physician notices that the patient's left vocal cord is paralyzed. The paralysis is most likely due to compression of which of the following nerves?
- A. Left superior laryngeal nerve
- B. Left vagus nerve
- C. Right recurrent laryngeal nerve
- D. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve (Correct Answer)
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Left recurrent laryngeal nerve***
- The **left recurrent laryngeal nerve** innervates all intrinsic muscles of the left larynx, except the cricothyroid muscle [1].
- Damage or compression of this nerve leads to **left vocal cord paralysis** and associated symptoms like hoarseness and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
*Left superior laryngeal nerve*
- The **superior laryngeal nerve** innervates the cricothyroid muscle, which is responsible for tensing the vocal cords.
- Damage to this nerve primarily affects **pitch control** and would not typically cause complete vocal cord paralysis.
*Left vagus nerve*
- The **vagus nerve** gives rise to both the superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves [1].
- While damage to the main vagus nerve would cause vocal cord paralysis, the more specific finding of isolated vocal cord paralysis points to an issue with its branch, the recurrent laryngeal nerve [1].
*Right recurrent laryngeal nerve*
- The **right recurrent laryngeal nerve** controls the intrinsic muscles of the right larynx.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **right vocal cord paralysis**, not left vocal cord paralysis as described in the patient.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 2: A 36-year-old man presents to the physician with difficulty in breathing for 3 hours. There is no history of chest pain, cough or palpitation. He is a chronic smoker and underwent elective cholecystectomy one month back. There is no history of chronic or recurrent cough, wheezing or breathlessness. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F), pulse is 108/min, blood pressure is 124/80 mm Hg, and respirations are 25/min. His arterial oxygen saturation is 98% in room air as shown by pulse oximetry. After a detailed physical examination, the physician orders a plasma D-dimer level, which was elevated. A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the chest shows a filling defect in a segmental pulmonary artery on the left side. Which of the following signs is most likely to have been observed by the physician during the physical examination of this patient’s chest?
- A. Pleural friction rub
- B. Bilateral wheezing
- C. Systolic murmur at the left sternal border
- D. Localized rales (Correct Answer)
- E. S3 gallop
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Localized rales***
- The patient's presentation with **sudden onset dyspnea**, risk factors (recent surgery, smoking), elevated D-dimer, and a CT scan showing a filling defect in the pulmonary artery strongly points to a **pulmonary embolism (PE)**.
- While PE often presents with normal lung auscultation, localized rales or crackles can be heard if there is an associated **pulmonary infarction** or local inflammation.
*Pleural friction rub*
- A **pleural friction rub** indicates inflammation of the pleura, which can occur in PE if the infarct involves the pleural surface.
- However, it is a less common finding than localized rales and is more characteristic of conditions like pleurisy or pneumonia.
*Bilateral wheezing*
- **Bilateral wheezing** is typically associated with diffuse airway obstruction, as seen in asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- This patient has no history of chronic respiratory conditions and the presentation is acute dyspnea, making diffuse airway obstruction less likely.
*Systolic murmur at the left sternal border*
- A **systolic murmur at the left sternal border** can be indicative of tricuspid regurgitation, often seen in the setting of **pulmonary hypertension** and right heart strain associated with a massive PE.
- However, with a stable blood pressure and moderate heart rate, severe right heart strain leading to a murmur is less likely in this scenario of a segmental PE.
*S3 gallop*
- An **S3 gallop** is a low-pitched sound heard during early diastole, often indicating **volume overload** or **ventricular dysfunction**.
- In the context of PE, an S3 often suggests significant **right ventricular dysfunction** due to acute pressure overload; this is more common with large or massive PEs causing hemodynamic instability, which is not indicated here.
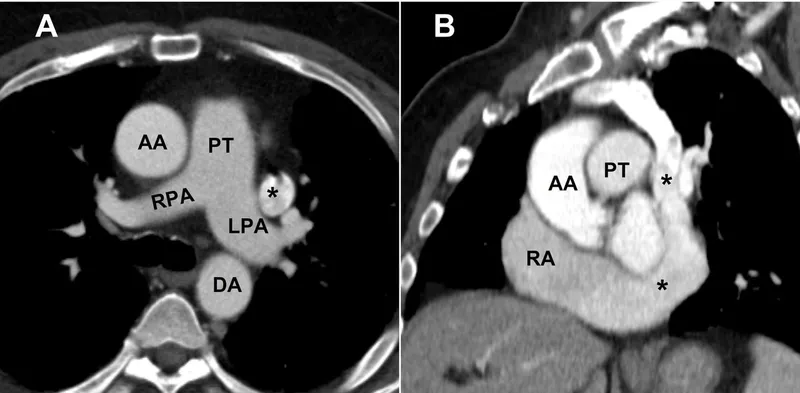
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 3: A 56-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 25 minutes after the sudden onset of severe pain in the middle of his chest. He describes the pain as tearing in quality; it radiates to his jaw. He has hypertension. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the 25 years. Current medications include enalapril. His blood pressure is 154/95 mm Hg in his right arm and 181/105 mm Hg in his left arm. A CT scan of the chest is shown. The structure indicated by the arrow is a derivative of which of the following?
- A. Right horn of sinus venosus
- B. Primitive atrium
- C. Right common cardinal vein
- D. Truncus arteriosus (Correct Answer)
- E. Bulbus cordis
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Truncus arteriosus***
- This clinical scenario describes an **aortic dissection**, suggested by the sudden onset of **tearing chest pain radiating to the jaw**, significant **blood pressure differential** between arms, and presenting in a patient with **hypertension and smoking history**.
- The image likely shows a dilated aorta or an aortic dissection. The **truncus arteriosus** is the embryonic precursor to the **ascending aorta** and the **pulmonary trunk**, making it the correct derivative for the affected structure.
*Right horn of sinus venosus*
- The **right horn of the sinus venosus** primarily contributes to the formation of the **smooth-walled part of the right atrium** (sinus venarum).
- It does not give rise to the aorta, which is the structure involved in the described pathology.
*Primitive atrium*
- The **primitive atrium** develops into the **trabeculated parts** of both the **right and left atria** (atrial appendages).
- It is not involved in the formation of the great arteries like the aorta.
*Right common cardinal vein*
- The **right common cardinal vein** contributes to the formation of the **superior vena cava**.
- It is not a developmental source for the aorta.
*Bulbus cordis*
- The **bulbus cordis** gives rise to the **conus arteriosus** (infundibulum) of the right ventricle, the **aortic vestibule** of the left ventricle, and part of the **right ventricle**.
- While it is a component of the outflow tract, the primary structure from which the ascending aorta develops is the truncus arteriosus.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 4: A 66-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of shortness of breath and confusion. His pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 109/73 mm Hg. He is oriented to person but not time or place. A graph of his breathing pattern and oxygen saturation is shown. Which of the following additional findings is most likely present in this patient?
- A. Rib fracture
- B. Fruity breath odor
- C. Ventricular gallop (Correct Answer)
- D. Miotic pupils
- E. Barrel chest
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Ventricular gallop***
- The patient's presentation with **shortness of breath**, **confusion**, and **oxygen desaturation** coupled with the breathing pattern shown (likely Cheyne-Stokes respiration from the image) strongly suggests **heart failure**. A **ventricular gallop (S3 heart sound)** is a classic finding in heart failure, indicating rapid ventricular filling into a stiff or dilated ventricle.
- The **confusional state** and **tachypnea (implied by oxygen desaturation)** are consistent with **hypoxia** and **reduced cardiac output** often seen in decompensated heart failure, where an S3 gallop is frequently heard.
*Rib fracture*
- While a rib fracture can cause shortness of breath due to pain and reduced chest expansion, it would not typically lead to **confusion** or a specific cyclical breathing pattern like Cheyne-Stokes, nor would it directly cause a ventricular gallop.
- The patient's vital signs and mental status point towards a more systemic issue rather than isolated chest trauma.
*Fruity breath odor*
- A **fruity breath odor** is a hallmark of **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**, caused by the exhalation of acetone. This condition would also present with confusion and tachypnea, but would typically involve hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis.
- There is no information to suggest diabetes, and the presentation of a specific breathing pattern in correlation with cardiac findings makes heart failure more likely.
*Miotic pupils*
- **Miotic pupils (pinpoint pupils)** are strongly associated with **opioid overdose** or organophosphate poisoning. These conditions would cause respiratory depression, not necessarily the specific breathing pattern, and would not explain the other findings in this specific context.
- The patient's pulse and blood pressure are also not typical of severe opioid overdose, which often involves bradycardia and hypotension.
*Barrel chest*
- A **barrel chest** is a physical finding typically associated with **chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)** due to chronic air trapping. While COPD can cause shortness of breath and confusion (in acute exacerbations), it does not directly lead to a ventricular gallop.
- Although the patient's age makes COPD possible, the acute presentation with a specific breathing pattern and the likelihood of heart failure make a barrel chest a less specific or primary finding in this context.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old smoker presents to physician after noticing that his face seems to be more swollen than usual. Upon further questioning, he reports increasing shortness of breath and cough over the past 6 months. On exam, his physician notices venous distention in his neck and distended veins in the upper chest and arms. Chest radiograph shows a right upper lobe mass. What is the embryologic origin of the vessel being compressed by this patient's tumor?
- A. Cardinal veins (Correct Answer)
- B. Primitive ventricle
- C. Left horn of sinus venosus
- D. Truncus arteriosus
- E. Bulbus cordis
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Cardinal veins***
- The symptoms of facial swelling, neck vein distention, and upper chest/arm vein distention, especially with a right upper lobe mass, are classic for **superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome**.
- The **SVC** is formed from the fusion of the anterior **cardinal veins**, which drain the upper body during embryonic development.
*Primitive ventricle*
- The **primitive ventricle** develops into parts of the left and right **ventricles** of the heart.
- It is not directly involved in the formation of major systemic veins like the SVC.
*Left horn of sinus venosus*
- The **left horn of the sinus venosus** mostly regresses and contributes to structures like the **coronary sinus** and the oblique vein of the left atrium.
- It does not form the SVC, which drains the upper body.
*Truncus arteriosus*
- The **truncus arteriosus** is an embryonic structure that separates to form the **aorta** and the **pulmonary artery**.
- It is an arterial structure, not a venous structure that would be compressed in SVC syndrome.
*Bulbus cordis*
- The **bulbus cordis** develops into the **conus arteriosus** (infundibulum) of the right ventricle and the **aortic vestibule** of the left ventricle.
- Like the truncus arteriosus, it is involved in arterial outflow tracts and not the formation of the SVC.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 6: A 38-year-old woman undergoes hemithyroidectomy for treatment of localized, well-differentiated papillary thyroid carcinoma. The lesion is removed with clear margins. However, during the surgery, a structure lying directly adjacent to the superior thyroid artery at the upper pole of the thyroid lobe is damaged. This patient is most likely to experience which of the following symptoms?
- A. Shortness of breath
- B. Weakness of shoulder shrug
- C. Voice pitch limitation (Correct Answer)
- D. Difficulty swallowing
- E. Ineffective cough
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Voice pitch limitation***
- Damage to the structure directly adjacent to the **superior thyroid artery** at the upper pole of the thyroid likely involves the **external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN)**.
- This nerve innervates the **cricothyroid muscle**, which is responsible for **tensing the vocal cords** and controlling **voice pitch**.
- Injury results in inability to change pitch, voice fatigue during prolonged speaking, and reduced vocal range.
*Shortness of breath*
- While damage to other nerves like the **recurrent laryngeal nerve** could cause vocal cord paralysis and potentially lead to airway compromise, this is less directly associated with the superior thyroid artery.
- Shortness of breath is not the specific consequence of EBSLN injury near the superior thyroid artery.
*Weakness of shoulder shrug*
- Weakness of shoulder shrug is associated with damage to the **spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)**, which innervates the **trapezius muscle**.
- This nerve is anatomically distinct from structures near the superior thyroid artery at the upper pole of the thyroid.
*Difficulty swallowing*
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) can result from damage to the **vagus nerve (cranial nerve X)** or its pharyngeal branches, but it is not the direct consequence of injury near the superior thyroid artery.
- Damage to the EBSLN primarily affects voice pitch and quality, not swallowing.
*Ineffective cough*
- An ineffective cough results from paralysis of the vocal cords (preventing glottic closure) or weakness of respiratory muscles, typically from **recurrent laryngeal nerve** damage or phrenic nerve injury.
- EBSLN damage primarily affects voice pitch and does not significantly impair cough effectiveness.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 7: A 50-year-old man presents with severe chest pain for a week. His pain increases with breathing and is localized to the right. He has tried over-the-counter medications at home, but they did not help. The patient has a 20-pack-year smoking history and currently smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and he drinks 3 to 4 cans of beer daily before dinner. His temperature is 39.1°C (102.3°F), blood pressure is 127/85 mm Hg, pulse is 109/min, and respirations are 20/min. Respiratory examination shows dullness to percussion from the 7th rib inferiorly at the right midaxillary line, decreased vocal tactile fremitus, and diminished breath sounds in the same area. Chest radiograph is shown in the image. The patient is prepared for thoracocentesis. Which of the following locations would be the most appropriate for insertion of a chest tube?
- A. Below the inferior border of the 7th rib in the midaxillary line
- B. Above the superior border of the 8th rib in the midaxillary line (Correct Answer)
- C. Above the superior border of the 5th rib in the midclavicular line
- D. Below the inferior border of the 5th rib in the midaxillary line
- E. Above the superior border of the 7th rib in the midclavicular line
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Above the superior border of the 8th rib in the midaxillary line***
- The patient presents with symptoms and signs suggestive of a **pleural effusion** (dullness to percussion, decreased fremitus, diminished breath sounds) and potentially an **empyema** given the fever and lung consolidation on the radiograph.
- Thoracocentesis should be performed in the **midaxillary line** between the 6th and 9th ribs to avoid injuring the **diaphragm and abdominal organs**, which can rise as high as the 5th intercostal space during expiration. To prevent damage to the neurovascular bundle that runs along the inferior border of the ribs, the needle should be inserted just **above the superior border** of the rib below the chosen intercostal space.
*Below the inferior border of the 7th rib in the midaxillary line*
- Inserting below the inferior border of the 7th rib increases the risk of injuring the **neurovascular bundle** that runs along the inferior rib margin.
- Such placement might also be too low, increasing the risk of penetrating the **diaphragm** or **abdominal organs**. This location would correspond to the 8th intercostal space, but the 'below inferior border' part is incorrect.
*Above the superior border of the 5th rib in the midclavicular line*
- The **midclavicular line** is typically used for needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax (2nd intercostal space) but is not the preferred site for thoracocentesis due to the risk of striking the lung parenchyma or internal mammary artery.
- Even if considering a pneumothorax, the 5th intercostal space in the midclavicular line is not the standard site, and an effusion is indicated here.
*Below the inferior border of the 5th rib in the midaxillary line*
- Inserting below the inferior border of the 5th rib, similar to option A, risks injury to the **neurovascular bundle**.
- While in the midaxillary line, the 5th rib might be too high for an effusion, and the technique of inserting below the inferior border is incorrect.
*Above the superior border of the 7th rib in the midclavicular line*
- The **midclavicular line** is generally avoided for thoracocentesis of effusions due to the risks mentioned previously and poor drainage if the effusion is posterior.
- The 7th intercostal space in the midclavicular line is also a non-standard and less safe location for this procedure.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife after falling down. About 90 minutes ago, they were standing in their kitchen making lunch and chatting when he suddenly complained that he could not see as well, felt weak, and was getting dizzy. He began to lean to 1 side, and he eventually fell to the ground. He did not hit his head. In the emergency department, he is swaying while seated, generally leaning to the right. The general physical exam is unremarkable. The neurologic exam is notable for horizontal nystagmus, 3/5 strength in the right arm, ataxia of the right arm, and absent pinprick sensation in the left arm and left leg. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely single location of this patient's central nervous system lesion?
- A. Primary motor cortex
- B. Thalamus
- C. Lateral medulla (Correct Answer)
- D. Primary somatosensory cortex
- E. Anterior spinal cord
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Lateral medulla***
- The combination of **ipsilateral ataxia** and **weakness** (right arm) along with **contralateral pain and temperature sensory loss** (left arm and leg) is classic for a **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**.
- **Horizontal nystagmus**, vertigo, and leaning to one side are also consistent with involvement of vestibular nuclei and cerebellar pathways in the lateral medulla.
*Primary motor cortex*
- A lesion here would cause **contralateral weakness or paralysis** but would not explain the ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, or contralateral pain and temperature loss.
- Sensory deficits would be minimal or absent, and would primarily affect discriminative touch.
*Thalamus*
- A thalamic lesion could cause **contralateral sensory loss** (affecting all modalities) and potentially some motor deficits or ataxia, but it typically does not cause **ipsilateral ataxia** or **nystagmus** in the pattern described.
- The specific combination of ipsilateral motor and contralateral sensory deficits points away from a pure thalamic lesion.
*Primary somatosensory cortex*
- A lesion in this area would primarily result in **contralateral deficits in discriminative touch, proprioception, and stereognosis**, not pain and temperature sensation.
- It would not explain the motor deficits, ataxia, or nystagmus seen in the patient.
*Anterior spinal cord*
- Damage to the anterior spinal cord (e.g., **anterior spinal artery syndrome**) would cause **bilateral motor weakness (paraplegia/quadriplegia)** and **bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It would not account for the nystagmus, vertigo, or the specific combination of ipsilateral and contralateral deficits observed in this patient, which are characteristic of brainstem involvement.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 9: A 23-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by a coworker for an injury sustained at work. He works in construction and accidentally shot himself in the chest with a nail gun. Physical examination shows a bleeding wound in the left hemithorax at the level of the 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line. Which of the following structures is most likely injured in this patient?
- A. Right atrium of the heart
- B. Inferior vena cava
- C. Left upper lobe of the lung (Correct Answer)
- D. Left atrium of the heart
- E. Superior vena cava
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***Left upper lobe of the lung***
- The **left upper lobe of the lung** extends to the 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line, making it the most probable structure to be traversed by a penetrating injury at this location.
- The **pleural cavity** and lung tissue are superficially located in this region, making them highly susceptible to injury from a nail gun.
*Right atrium of the heart*
- The **right atrium** is located predominantly on the right side of the sternum, more centrally, and slightly to the right of the midclavicular line.
- An injury at the **left 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line** would typically be too lateral and superior to directly injure the right atrium.
*Inferior vena cava*
- The **inferior vena cava (IVC)** enters the right atrium from below, primarily located within the abdomen and passing through the diaphragm at the level of T8.
- Its position is far too **inferior and posterior** relative to the 4th intercostal space to be directly injured by this wound.
*Left atrium of the heart*
- The **left atrium** is the most posterior chamber of the heart and is largely covered by the left ventricle.
- Although part of the heart is on the left, an injury at the **4th intercostal space, midclavicular line**, would likely impact the left ventricle or lung tissue before reaching the left atrium, which is located more posteriorly and medially.
*Superior vena cava*
- The **superior vena cava (SVC)** is located to the right of the midline, formed by the brachiocephalic veins behind the right first costal cartilage.
- Its position is too **medial and superior**, on the right side, to be directly injured by a nail penetrating the left 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line.
Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG Question 10: A 40-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by a paramedic team from the scene of a motor vehicle accident where she was the driver. The patient was restrained by a seat belt and was unconscious at the scene. On physical examination, the patient appears to have multiple injuries involving the trunk and extremities. There are no penetrating injuries to the chest. As part of her trauma workup, a CT scan of the chest is ordered. At what vertebral level of the thorax is this image from?
- A. T1
- B. T6
- C. T4
- D. T5
- E. T8 (Correct Answer)
Thoracic cross-sections Explanation: ***T8***
- The CT image shows the **inferior vena cava (IVC)** located anterior and to the right of the aorta, and the **esophagus** located posterior to the aorta and slightly to the left. The **azygos vein** is seen to the right of the vertebral body and posterior to the esophagus.
- The **mainstem bronchi** are no longer visible, indicating a level below the carina. The presence of the IVC, aorta, esophagus, and azygos vein with the absence of mainstem bronchi is characteristic of the **T8 vertebral level**.
*T1*
- At the T1 level, the structures would primarily be the **trachea** anterior to the esophagus, with the main great vessels (e.g., brachiocephalic veins and arteries) visible, not the IVC.
- The mainstem bronchi would not yet be visualized at this higher level.
*T6*
- At the T6 level, the **trachea would have already bifurcated into the mainstem bronchi**, which would be prominent structures visible on the CT scan.
- While the aorta and esophagus would be present, the specific arrangement relative to the mainstem bronchi would differentiate it from T8.
*T4*
- The T4 level is typically associated with the **carina**, where the trachea bifurcates into the mainstem bronchi.
- The great vessels would be prominent, but the IVC in its more inferior course would not be as distinctly visualized in this configuration compared to T8.
*T5*
- At the T5 level, the **mainstem bronchi** would still be clearly visible, having just diverged from the trachea.
- While vessels like the aorta are present, the key differentiating factor from T8 is the presence of the mainstem bronchi.
More Thoracic cross-sections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.