Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lower limb cross-sections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 1: Seven hours after undergoing left hip arthroplasty for chronic hip pain, a 67-year-old woman reports a prickling sensation in her left anteromedial thigh and lower leg. Neurologic examination shows left leg strength 3/5 on hip flexion and 2/5 on knee extension. Patellar reflex is decreased on the left. Sensation to pinprick and light touch are decreased on the anteromedial left thigh as well as medial lower leg. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Femoral nerve injury (Correct Answer)
- B. L5 radiculopathy
- C. Sural nerve injury
- D. S1 radiculopathy
- E. Fibular nerve injury
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Femoral nerve injury***
- The patient's symptoms—weakness in **hip flexion** (iliopsoas via femoral nerve) and **knee extension** (quadriceps via femoral nerve), decreased **patellar reflex** (femoral nerve), and sensory loss in the **anteromedial thigh** (femoral nerve) and **medial lower leg** (saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve)—are all consistent with femoral nerve dysfunction.
- **Hip arthroplasty procedures** can sometimes lead to iatrogenic femoral nerve damage due to retraction, compression, or direct injury during surgery, especially when positioning or using surgical instruments.
*L5 radiculopathy*
- L5 radiculopathy typically causes weakness in **foot dorsiflexion**, **eversion**, and **toe extension**, along with sensory loss over the **dorsum of the foot** and lateral lower leg, which does not match the patient's presentation.
- While it can cause hip abductor weakness, it would not explain the prominent **quadriceps weakness** and **decreased patellar reflex**.
*Sural nerve injury*
- The sural nerve provides sensation to the **posterolateral aspect of the lower leg** and lateral malleolus, and has no motor function to the hip or knee.
- Injury to this nerve would not account for the patient's **proximal weakness** or sensory loss in the anteromedial thigh.
*S1 radiculopathy*
- S1 radiculopathy typically leads to weakness in **plantarflexion**, **hip extension**, and an absent **Achilles reflex**, along with sensory loss over the lateral foot and sole.
- It would not explain the significant **quadriceps weakness**, **decreased patellar reflex**, or sensory changes in the anteromedial thigh.
*Fibular nerve injury*
- Fibular (peroneal) nerve injury primarily results in **foot drop** (weakness in dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot) and sensory loss over the **dorsum of the foot** and anterolateral lower leg.
- It does not affect hip flexion, knee extension, or the patellar reflex, nor does it cause sensory loss in the anteromedial thigh.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 2: A 34-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 3 hours after being bitten by a rattlesnake. He was hiking in the Arizona desert when he accidentally stepped on the snake and it bit his right leg. His pulse is 135/min and blood pressure is 104/81 mm Hg. Examination shows right lower leg swelling, ecchymosis, and blistering. Right ankle dorsiflexion elicits severe pain. A manometer inserted in the lateral compartment of the lower leg shows an intracompartmental pressure of 67 mm Hg. In addition to administration of the antivenom, the patient undergoes fasciotomy. Two weeks later, he reports difficulty in walking. Neurologic examination shows a loss of sensation over the lower part of the lateral side of the right leg and the dorsum of the right foot. Right foot eversion is 1/5. There is no weakness in dorsiflexion. Which of the following nerves is most likely injured in this patient?
- A. Sural nerve
- B. Tibial nerve
- C. Saphenous nerve
- D. Superficial peroneal nerve (Correct Answer)
- E. Deep peroneal nerve
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Superficial peroneal nerve***
- The **superficial peroneal nerve** (also known as the superficial fibular nerve) is responsible for **foot eversion** (peroneus longus and brevis muscles) and provides sensory innervation to the **dorsum of the foot**, except for the web space between the first and second toes.
- The patient's inability to evert the foot and sensory loss on the dorsum of the foot, combined with a history of **compartment syndrome** and fasciotomy in the lateral compartment, strongly indicates injury to the superficial peroneal nerve.
*Sural nerve*
- The **sural nerve** provides sensory innervation to the **posterolateral aspect of the lower leg** and the lateral aspect of the foot.
- It does not innervate muscles involved in foot eversion or dorsiflexion, so its injury would not lead to the motor deficits described.
*Tibial nerve*
- The **tibial nerve** innervates the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg, responsible for **plantarflexion** and inversion of the foot, and provides sensation to the sole of the foot.
- Its injury would lead to weakness in plantarflexion and sensory loss on the sole, not the symptoms described.
*Saphenous nerve*
- The **saphenous nerve** is a pure sensory nerve, supplying sensation to the **medial aspect of the lower leg and foot**.
- Its injury would result in sensory loss in this distribution but no motor deficits affecting foot eversion or dorsiflexion.
*Deep peroneal nerve*
- The **deep peroneal nerve** (also known as the deep fibular nerve) innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg, primarily responsible for **foot dorsiflexion** and toe extension, and provides sensation to the web space between the first and second toes.
- The patient has no weakness in dorsiflexion, ruling out significant injury to the deep peroneal nerve.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with pain along the bottom of his foot. The patient is a long-time runner but states that the pain has been getting worse recently. He states that when running and at rest he has a burning and aching pain along the bottom of his foot that sometimes turns to numbness. Taking time off from training does not improve his symptoms. The patient has a past medical history of surgical repair of his Achilles tendon, ACL, and medial meniscus. He is currently not taking any medications. The patient lives with his wife and they both practice a vegan lifestyle. On physical exam the patient states that he is currently not experiencing any pain in his foot but rather is experiencing numbness/tingling along the plantar surface of his foot. Strength is 5/5 and reflexes are 2+ in the lower extremities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- B. Common fibular nerve compression
- C. Tarsal tunnel syndrome (Correct Answer)
- D. Plantar fasciitis
- E. Herniated disc
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Tarsal tunnel syndrome***
- The patient presents with **burning/aching pain** and **numbness/tingling along the plantar surface of the foot**, symptoms highly indicative of **tarsal tunnel syndrome**, which involves compression of the **posterior tibial nerve**.
- His history of being a **long-time runner** and pain that doesn't improve with rest points to an overuse injury or nerve entrapment, fitting with tarsal tunnel syndrome.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- While a vegan lifestyle can predispose to **vitamin B12 deficiency**, which causes neuropathy, the symptoms of **burning pain** and **numbness localized to the plantar foot** are more specific to nerve entrapment.
- Neuropathy due to B12 deficiency typically presents as a more generalized **stocking-glove distribution**, rather than being confined to the sole of the foot.
*Common fibular nerve compression*
- Compression of the **common fibular nerve** (also known as the common peroneal nerve) typically affects the **dorsum of the foot** and the lateral aspect of the lower leg, leading to **foot drop** or weakness in dorsiflexion, which is not described.
- The patient's symptoms are specifically on the **plantar surface**, inconsistent with common fibular nerve compression.
*Plantar fasciitis*
- **Plantar fasciitis** is characterized by **heel pain** that is typically worse with the **first steps in the morning** or after periods of rest, which improves with activity.
- While it causes foot pain in runners, the prominent **numbness and tingling** described by the patient are not typical symptoms of plantar fasciitis.
*Herniated disc*
- A **herniated disc** causing radiating pain (sciatica) would involve symptoms that typically originate in the **lower back** or buttock and radiate down the leg.
- While it can cause numbness, the **localization to the plantar foot** without accompanying back pain or proximal leg symptoms makes a herniated disc less likely.
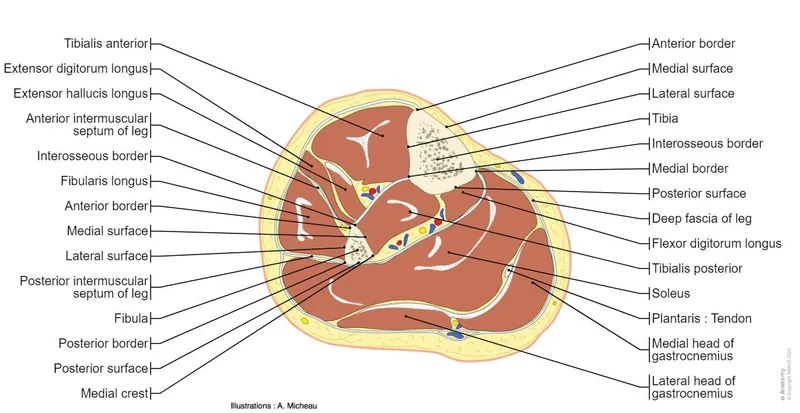
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 4: A 48-year-old male presents to his primary care provider with a two-week history of low back pain and left leg pain. He reports that his symptoms started while he was working at his job as a construction worker. He has since experienced intermittent achy pain over his lumbar spine. He has also noticed pain radiating into his left leg and weakness in left ankle dorsiflexion. On exam, he demonstrates the following findings on strength testing of the left leg: 5/5 in knee extension, 4/5 in ankle dorsiflexion, 4/5 in great toe extension, 5/5 in ankle plantarflexion, and 5/5 in great toe flexion. The patellar reflexes are 5/5 bilaterally. He is able to toe walk but has difficulty with heel walking. Weakness in which of the following compartments of the leg is most likely causing this patient’s foot drop?
- A. Lateral compartment
- B. Superficial posterior compartment
- C. Deep posterior compartment
- D. Anterior compartment (Correct Answer)
- E. Medial compartment
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Anterior compartment***
- Weakness in **ankle dorsiflexion** and **great toe extension**, coupled with difficulty **heel walking**, indicates a foot drop due to dysfunction of muscles in the anterior compartment, such as the **tibialis anterior**, **extensor hallucis longus**, and **extensor digitorum longus**.
- These muscles are primarily innervated by the **deep fibular nerve**, which is susceptible to compression from conditions like **lumbar radiculopathy** (L4-L5 nerve root involvement).
*Lateral compartment*
- Muscles in the lateral compartment (**fibularis longus** and **brevis**) are responsible for **eversion** of the foot.
- Weakness in this compartment would manifest as difficulty everting the foot, not primarily ankle dorsiflexion or great toe extension deficits.
*Superficial posterior compartment*
- This compartment contains muscles like the **gastrocnemius** and **soleus**, which are primarily responsible for **ankle plantarflexion**.
- The patient exhibits 5/5 strength in ankle plantarflexion and is able to toe walk, indicating these muscles are functioning well.
*Deep posterior compartment*
- Muscles in the deep posterior compartment (**tibialis posterior**, **flexor digitorum longus**, **flexor hallucis longus**) are involved in **inversion** and **toe flexion**.
- The patient has 5/5 strength in great toe flexion, suggesting intact function of these muscles, and his primary deficit is in dorsiflexion.
*Medial compartment*
- There is no distinct "medial compartment" of the leg in the anatomical sense comparable to the other listed compartments; rather, various muscles contribute to medial actions.
- The symptoms described specifically point to weakness in dorsiflexion and toe extension, localizing the problem to the anterior compartment.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 5: A 64-year-old man with osteoarthritis of the knee comes to the physician for evaluation of weakness in his foot. Physical examination shows a swelling in the popliteal fossa. There is weakness when attempting to plantarflex and invert his right foot. He is unable to curl his toes. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show decreased sensation over which of the following locations?
- A. First dorsal web space
- B. Sole of the foot (Correct Answer)
- C. Lateral border of the foot
- D. Medial plantar arch
- E. Second dorsal web space
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Sole of the foot***
- The patient's inability to **plantarflex the foot**, weakness with **inversion**, and inability to **curl the toes** indicate damage to the **tibial nerve**.
- A **popliteal fossa mass** (likely Baker's cyst) can compress the tibial nerve as it courses through this region.
- The **tibial nerve** supplies sensation to the **sole of the foot** via its medial and lateral plantar branches and innervates the muscles responsible for plantarflexion, foot inversion (tibialis posterior), and toe flexion.
*First dorsal web space*
- Sensation over the **first dorsal web space** is primarily supplied by the **deep fibular (peroneal) nerve**.
- Injury to this nerve would typically affect **dorsiflexion** and **toe extension**, not the plantarflexion and toe flexion deficits described.
*Lateral border of the foot*
- Sensation along the **lateral border of the foot** is predominantly supplied by the **sural nerve**.
- This nerve is primarily cutaneous and does not contribute to motor function related to plantarflexion or toe curling.
*Medial plantar arch*
- While the **medial plantar nerve** (a branch of the tibial nerve) supplies sensation to part of the plantar surface, the term "sole of the foot" more comprehensively describes the entire plantar sensory distribution of the tibial nerve.
- The motor deficits described indicate a proximal **tibial nerve** lesion affecting the entire nerve distribution.
*Second dorsal web space*
- Sensation to the **second dorsal web space** is primarily provided by the **superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve**.
- Motor deficits associated with fibular nerve injury would be dorsiflexion and eversion weakness, not the symptoms described.
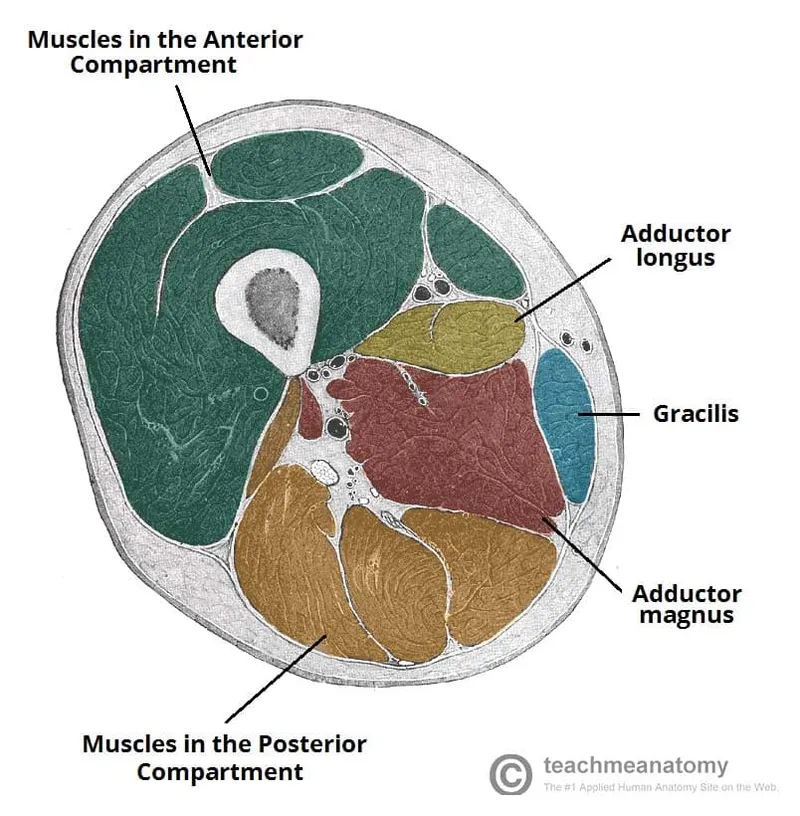
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 6: During a physical examination, a physician tests the strength of hip adduction against resistance. Which of the following nerves innervates the primary muscles responsible for this action?
- A. Sciatic nerve
- B. Superior gluteal nerve
- C. Femoral nerve
- D. Obturator nerve (Correct Answer)
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Obturator nerve***
- The **obturator nerve** primarily innervates the **adductor muscles** of the thigh, including the adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus (adductor part), gracilis, and pectineus (variable innervation).
- These muscles are responsible for **adducting the hip**, which is the action tested when a physician checks hip adduction strength against resistance.
*Sciatic nerve*
- The **sciatic nerve** innervates the **hamstring muscles** (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris) and all muscles below the knee.
- It does not significantly contribute to the innervation of the primary hip adductors.
*Superior gluteal nerve*
- The **superior gluteal nerve** mainly innervates the **gluteus medius**, **gluteus minimus**, and **tensor fasciae latae** muscles.
- These muscles are primarily involved in **hip abduction** and medial rotation, not adduction.
*Femoral nerve*
- The **femoral nerve** innervates the **quadriceps femoris muscles** (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius) and the sartorius.
- Its primary actions are **knee extension** and hip flexion, with no direct role in hip adduction.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 33-year-old woman comes to the physician because of pain and sometimes numbness in her right thigh for the past 2 months. She reports that her symptoms are worse when walking or standing and are better while sitting. Three months ago, she started going to a fitness class a couple times a week. She is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 88 kg (194 lb); BMI is 33.1 kg/m2. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination of the skin shows no abnormalities. Sensation to light touch is decreased over the lateral aspect of the right anterior thigh. Muscle strength is normal. Tapping the right inguinal ligament leads to increased numbness of the affected thigh. The straight leg test is negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
- A. Advise patient to wear looser pants (Correct Answer)
- B. Reduction of physical activity
- C. MRI of the lumbar spine
- D. X-ray of the hip
- E. Blood work for inflammatory markers
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Advise patient to wear looser pants***
- This patient presents with symptoms consistent with **meralgia paresthetica**, a condition caused by compression of the **lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN)**. Modifying clothing or belts that compress the inguinal ligament can relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Her increased weight, a recent increase in physical activity, and a positive Tinel's sign at the inguinal ligament (tapping leads to increased numbness) support this diagnosis.
*Reduction of physical activity*
- While excessive physical activity can contribute to meralgia paresthetica, simply reducing it without addressing the underlying compression might not fully resolve symptoms.
- The patient has recently increased physical activity, which could be a contributing factor, but it's not the primary or most direct intervention for nerve compression.
*MRI of the lumbar spine*
- An MRI of the lumbar spine would be considered if there were signs of **radiculopathy** or other spinal pathology, such as weakness, reflex changes, or a positive straight leg test, which are absent here.
- The symptoms are localized to the distribution of the LFCN, and the physical exam points away from a central spinal cause.
*X-ray of the hip*
- An X-ray of the hip would be indicated for suspected **hip joint pathology** or **bony abnormalities**, which are not suggested by the patient's symptoms (pain and numbness in the thigh, not hip joint pain).
- Meralgia paresthetica is a nerve entrapment syndrome, not a structural issue of the hip joint.
*Blood work for inflammatory markers*
- Inflammatory markers like **ESR** or **CRP** would be relevant if an **inflammatory arthritis**, infection, or systemic inflammatory condition was suspected, but the patient's symptoms are purely neurological and localized.
- There is no clinical evidence of inflammation, fever, or joint swelling to suggest an underlying inflammatory process.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 8: A 72-year-old male presents to a cardiac surgeon for evaluation of severe aortic stenosis. He has experienced worsening dyspnea with exertion over the past year. The patient also has a history of poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia. An echocardiogram revealed a thickened calcified aortic valve. The surgeon is worried that the patient will be a poor candidate for open heart surgery and decides to perform a less invasive transcatheter aortic valve replacement. In order to perform this procedure, the surgeon must first identify the femoral pulse just inferior to the inguinal ligament and insert a catheter into the vessel in order to gain access to the arterial system. Which of the following structures is immediately lateral to this structure?
- A. Lymphatic vessels
- B. Femoral vein
- C. Sartorius muscle
- D. Pectineus muscle
- E. Femoral nerve (Correct Answer)
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Femoral nerve***
- The **femoral nerve** lies lateral to the **femoral artery** within the **femoral triangle**.
- The order of structures from **lateral to medial** under the inguinal ligament is remembered by the mnemonic **NAVEL**: **N**erve, **A**rtery, **V**ein, **E**mpty space, **L**ymphatics.
*Lymphatic vessels*
- **Lymphatic vessels** and nodes are located most medially within the femoral triangle, medial to the femoral vein.
- This position is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Femoral vein*
- The **femoral vein** is located immediately medial to the **femoral artery**.
- It would not be found immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Sartorius muscle*
- The **sartorius muscle** forms the lateral boundary of the **femoral triangle** but is not immediately adjacent and lateral to the femoral artery within the triangle itself.
- The femoral nerve is enclosed within the iliopsoas fascial compartment, which runs deep to the sartorius.
*Pectineus muscle*
- The **pectineus muscle** forms part of the floor of the **femoral triangle**, but it is deep to the neurovascular structures.
- It is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife after falling down. About 90 minutes ago, they were standing in their kitchen making lunch and chatting when he suddenly complained that he could not see as well, felt weak, and was getting dizzy. He began to lean to 1 side, and he eventually fell to the ground. He did not hit his head. In the emergency department, he is swaying while seated, generally leaning to the right. The general physical exam is unremarkable. The neurologic exam is notable for horizontal nystagmus, 3/5 strength in the right arm, ataxia of the right arm, and absent pinprick sensation in the left arm and left leg. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely single location of this patient's central nervous system lesion?
- A. Primary motor cortex
- B. Thalamus
- C. Lateral medulla (Correct Answer)
- D. Primary somatosensory cortex
- E. Anterior spinal cord
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Lateral medulla***
- The combination of **ipsilateral ataxia** and **weakness** (right arm) along with **contralateral pain and temperature sensory loss** (left arm and leg) is classic for a **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**.
- **Horizontal nystagmus**, vertigo, and leaning to one side are also consistent with involvement of vestibular nuclei and cerebellar pathways in the lateral medulla.
*Primary motor cortex*
- A lesion here would cause **contralateral weakness or paralysis** but would not explain the ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, or contralateral pain and temperature loss.
- Sensory deficits would be minimal or absent, and would primarily affect discriminative touch.
*Thalamus*
- A thalamic lesion could cause **contralateral sensory loss** (affecting all modalities) and potentially some motor deficits or ataxia, but it typically does not cause **ipsilateral ataxia** or **nystagmus** in the pattern described.
- The specific combination of ipsilateral motor and contralateral sensory deficits points away from a pure thalamic lesion.
*Primary somatosensory cortex*
- A lesion in this area would primarily result in **contralateral deficits in discriminative touch, proprioception, and stereognosis**, not pain and temperature sensation.
- It would not explain the motor deficits, ataxia, or nystagmus seen in the patient.
*Anterior spinal cord*
- Damage to the anterior spinal cord (e.g., **anterior spinal artery syndrome**) would cause **bilateral motor weakness (paraplegia/quadriplegia)** and **bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It would not account for the nystagmus, vertigo, or the specific combination of ipsilateral and contralateral deficits observed in this patient, which are characteristic of brainstem involvement.
Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old boy is brought to his orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of leg pain and positioning. Specifically, over the past several months he has been complaining of thigh pain and has more difficulty sitting in his wheelchair. His medical history is significant for spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy since birth and has undergone a number of surgeries for contractures in his extremities. At this visit his legs are found to be scissored such that they cross each other at the knees and are difficult to separate. Surgery is performed and the boy is placed into a cast that keeps his legs abducted to prevent scissoring. Overactivity of the muscles innervated by which of the following nerves is most consistent with this patient's deformity?
- A. Nerve to the iliopsoas
- B. Sciatic nerve
- C. Femoral nerve
- D. Superior gluteal nerve
- E. Obturator nerve (Correct Answer)
Lower limb cross-sections Explanation: ***Obturator***
- The **obturator nerve** innervates the **adductor muscles** of the thigh (adductor longus, brevis, magnus, gracilis, and obturator externus).
- **Overactivity** of these muscles leads to thigh adduction, causing the characteristic **"scissoring" gait** seen in some patients with cerebral palsy.
*Nerve to the iliopsoas*
- The **iliopsoas muscle** is a primary **hip flexor**, important for activities like sitting and standing.
- While involvement of hip flexors can cause contractures, it would manifest as difficulty extending the hip, not a scissoring deformity.
*Sciatic nerve*
- The **sciatic nerve** innervates the **hamstring muscles** (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris) and most muscles of the leg and foot.
- Its overactivity or spasticity would primarily affect knee flexion and foot movements, not hip adduction or scissoring.
*Femoral nerve*
- The **femoral nerve** innervates the **quadriceps femoris muscles** (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, medialis, intermedius) and the sartorius.
- Overactivity would lead to strong knee extension and hip flexion, not the adducted and scissored leg position described.
*Superior gluteal nerve*
- The **superior gluteal nerve** innervates the **gluteus medius**, **gluteus minimus**, and **tensor fasciae latae** muscles, which are primarily hip abductors and internal rotators.
- Overactivity of these muscles would cause hip abduction, which is the opposite of the scissoring deformity.
More Lower limb cross-sections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.