Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Head and neck cross-sections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 1: A 36-year-old male is taken to the emergency room after jumping from a building. Bilateral fractures to the femur were stabilized at the scene by emergency medical technicians. The patient is lucid upon questioning and his vitals are stable. Pain only at his hips was elicited. Cervical exam was not performed. What is the best imaging study for this patient?
- A. AP and lateral radiographs of hips
- B. Lateral radiograph (x-ray) of hips
- C. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of hips, knees, lumbar, and cervical area
- D. Anterior-posterior (AP) and lateral radiographs of hips, knees, lumbar, and cervical area
- E. Computed tomography (CT) scan of cervical spine, hips, and lumbar area (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Computed tomography (CT) scan of cervical spine, hips, and lumbar area***
- In **high-energy trauma** (fall from height), a CT scan is the **gold standard** for evaluating the **spine and pelvis**, providing detailed cross-sectional images superior to plain radiographs.
- Since the **cervical exam was not performed**, cervical spine imaging is **mandatory** per ATLS (Advanced Trauma Life Support) protocols. High-energy falls carry significant risk of **cervical spine injury** even without obvious neurological symptoms.
- CT allows comprehensive assessment of **hip fractures, pelvic injuries, and the entire spine** (cervical, thoracic, lumbar), identifying both obvious and **subtle fractures** that may be missed on plain films.
- This approach provides the most **efficient and thorough evaluation** in the acute trauma setting, allowing for appropriate surgical planning and ruling out life-threatening spinal instability.
*AP and lateral radiographs of hips*
- Plain radiographs provide **limited detail** and may **miss subtle fractures**, particularly in complex areas like the pelvis and acetabulum.
- This option **fails to address cervical spine clearance**, which is essential in all high-energy trauma patients, especially when cervical exam has not been performed.
- Radiographs are insufficient for **comprehensive trauma evaluation** after a fall from height.
*Lateral radiograph (x-ray) of hips*
- A single lateral view is **grossly insufficient** for evaluating hip and pelvic fractures, providing only a **two-dimensional perspective** that can miss significant injuries.
- This option **completely neglects spinal evaluation**, which is dangerous in an uncleared trauma patient with a high-energy mechanism.
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of hips, knees, lumbar, and cervical area*
- While MRI excels at evaluating **soft tissues, ligaments, and bone marrow**, it is **not the initial imaging modality** for acute bony trauma due to longer scan times and lower sensitivity for acute fractures compared to CT.
- MRI is **time-consuming and impractical** in the emergency setting for initial fracture assessment, potentially delaying definitive treatment.
- CT is superior for evaluating **acute skeletal injuries** in the trauma bay.
*Anterior-posterior (AP) and lateral radiographs of hips, knees, lumbar, and cervical area*
- Multiple plain radiographs have **limited sensitivity** for complex or non-displaced fractures, particularly in the **spine and pelvis**, making them inadequate for high-energy trauma evaluation.
- Obtaining multiple radiographic views requires **numerous patient repositionings**, which risks further injury if **spinal instability** is present.
- Plain films provide significantly **less diagnostic information** than CT scanning for trauma assessment.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 2: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of a barking cough, a raspy voice, and noisy breathing for the last 3 days. Five days ago, she had a low-grade fever and runny nose. She attends daycare. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100°F) and respirations are 33/min. Physical examination shows supraclavicular retractions. There is a high-pitched sound present on inspiration. Examination of the throat shows erythema without exudates. Which of the following is the most likely location of the anatomic narrowing causing this patient's symptoms?
- A. Bronchioles
- B. Pharynx
- C. Subglottic larynx (Correct Answer)
- D. Distal trachea
- E. Epiglottis
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Subglottic larynx***
- The patient's symptoms of **barking cough**, **raspy voice**, **stridor** (high-pitched inspiratory sound), and **supraclavicular retractions** are classic for **croup** (laryngotracheobronchitis), which is caused by inflammation and narrowing of the subglottic region of the larynx.
- The preceding low-grade fever and runny nose are typical of a viral upper respiratory infection, which commonly precedes croup.
*Bronchioles*
- Narrowing in the bronchioles typically causes **wheezing** (a high-pitched whistling sound on expiration) and **respiratory distress**, often seen in conditions like **bronchiolitis** or **asthma**.
- A barking cough and raspy voice are not characteristic symptoms of bronchiolar obstruction.
*Pharynx*
- Inflammation and narrowing of the pharynx primarily cause **sore throat**, **difficulty swallowing** (dysphagia), and sometimes **muffled voice**.
- It would not typically lead to a barking cough, stridor, or severe inspiratory distress.
*Distal trachea*
- While tracheal narrowing can cause stridor, the classic **barking cough** and **hoarseness** (raspy voice) are more specifically localized to the laryngeal area.
- Obstruction in the distal trachea would be less likely to affect voice quality as significantly as subglottic narrowing.
*Epiglottis*
- **Epiglottitis** presents as a rapidly progressive, life-threatening condition with **high fever**, **dysphagia**, **drooling**, and a **muffled "hot potato" voice**.
- The patient would typically appear toxic and prefer to sit in the **tripod position**, which is not described in this case, and her symptoms are less acute.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with a midline swelling in his neck. He is unsure about when it appeared. He denies any difficulty with swallowing or hoarseness. His past medical history is insignificant. On physical examination, there is a 1 cm x 2 cm firm mildly tender nodule on the anterior midline aspect of the neck which moves with deglutition and elevates with protrusion of the tongue. Which of the following is the most likely embryologic origin of the nodule in this patient?
- A. Midline endoderm of the pharynx (Correct Answer)
- B. 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arch
- C. The branchial cleft
- D. 4th pharyngeal arch
- E. 4th pharyngeal pouch
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Midline endoderm of the pharynx***
- The symptoms described, particularly a midline neck swelling that **moves with deglutition** and **elevates with tongue protrusion**, are classic for a **thyroglossal duct cyst**.
- Thyroglossal duct cysts arise from remnants of the **thyroglossal duct**, an embryonic structure that forms from the **midline endoderm of the pharyngeal floor** and descends to form the thyroid gland.
*1st and 2nd pharyngeal arch*
- The 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches primarily contribute to the formation of structures in the **mandible**, **maxilla**, **middle ear**, and **hyoid bone**.
- Abnormalities in these arches typically lead to conditions like **Treacher Collins syndrome** or **Pierre Robin sequence**, not midline neck cysts with these specific movement characteristics.
*The branchial cleft*
- **Branchial cleft cysts** typically present as **lateral neck masses**, often anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and usually do not move with deglutition or tongue protrusion.
- They arise from incomplete obliteration of **pharyngeal clefts**, which are ectodermal structures.
*4th pharyngeal arch*
- The 4th pharyngeal arch contributes to the formation of the **cricothyroid muscle**, part of the **pharynx**, and the **laryngeal cartilages**.
- Anomalies of the 4th pharyngeal arch are rare and typically involve **vascular structures** or **recurrent laryngeal nerve** abnormalities, not midline neck cysts.
*4th pharyngeal pouch*
- The 4th pharyngeal pouch contributes to the development of the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (which gives rise to parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Malformations of this pouch are associated with parathyroid and thyroid conditions, not midline thyroglossal duct cysts.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 4: A 50-year-old man undergoes parathyroidectomy for treatment-resistant hyperparathyroidism. The procedure is complicated by brisk bleeding from the superior thyroid artery near the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. To stop the bleeding, the artery is ligated at its origin. Which of the following is most likely the origin of the artery that was injured in this patient?
- A. Thyrocervical trunk
- B. Ascending pharyngeal artery
- C. Internal carotid artery
- D. Subclavian artery
- E. External carotid artery (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***External carotid artery***
- The **superior thyroid artery** is the first branch to arise from the **external carotid artery** in the neck.
- Ligation of this artery at its origin is a common surgical maneuver to control bleeding during thyroid or parathyroid surgery.
*Thyrocervical trunk*
- The **thyrocervical trunk** is a branch of the **subclavian artery** and gives rise to the inferior thyroid artery, not the superior thyroid artery.
- Injury to the superior thyroid artery would not necessitate ligation of a vessel originating from the thyrocervical trunk.
*Ascending pharyngeal artery*
- The **ascending pharyngeal artery** is a small artery that branches from the **external carotid artery** but supplies the pharynx, not the thyroid gland.
- It is not typically implicated in bleeding during parathyroidectomy or in relation to the superior laryngeal nerve.
*Internal carotid artery*
- The **internal carotid artery** primarily supplies the brain and does not have branches in the neck that supply the thyroid or parathyroid glands.
- It arises from the common carotid artery but does not give off the superior thyroid artery.
*Subclavian artery*
- The **subclavian artery** gives rise to the **thyrocervical trunk**, which then supplies the inferior thyroid artery, but not directly the superior thyroid artery.
- The superior thyroid artery originates higher up from the external carotid artery.
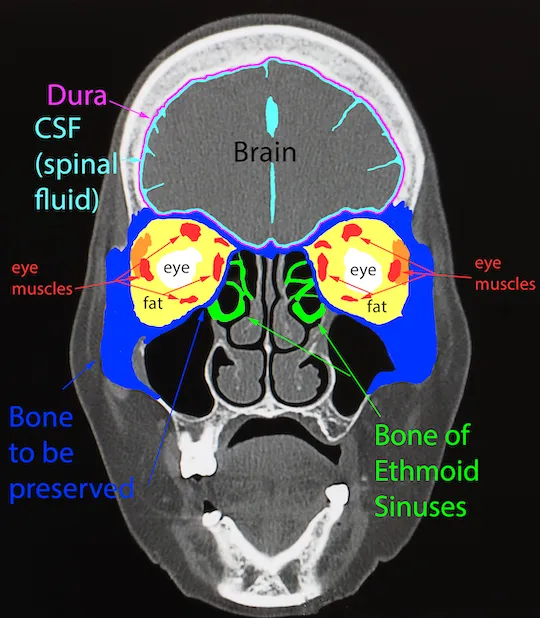
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 5: A 33-year-old man comes to the otolaryngologist for the evaluation of a 6-month history of difficulty breathing through his nose and clear nasal discharge. He has a history of seasonal atopic rhinosinusitis. Anterior rhinoscopy shows a nasal polyp obstructing the superior nasal meatus. A CT scan of the head is most likely to show opacification of which of the following structures?
- A. Nasolacrimal duct and eustachian tube
- B. Sphenoidal sinus and posterior ethmoidal sinuses (Correct Answer)
- C. Frontal sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus
- D. Maxillary sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus
- E. Pterygopalatine fossa and middle ethmoidal sinus
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Sphenoidal sinus and posterior ethmoidal sinuses***
- The **posterior ethmoidal sinuses** drain directly into the **superior nasal meatus**, making them the primary structures affected by obstruction at this location.
- The **sphenoid sinus** drains into the **sphenoethmoidal recess**, which is located immediately posterior and superior to the superior nasal meatus. Due to their anatomical proximity and shared drainage region, obstruction in the superior meatus can affect drainage and lead to **opacification** of both structures due to **mucus retention** and inflammation.
- This is the most appropriate answer among the given options for superior meatus obstruction.
*Nasolacrimal duct and eustachian tube*
- The **nasolacrimal duct** drains into the **inferior nasal meatus**, not the superior meatus.
- The **eustachian tube** opens into the **nasopharynx**, which has no direct anatomical connection to the superior nasal meatus.
- These structures would not be affected by superior meatus obstruction.
*Frontal sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus*
- The **frontal sinus** drains through the **frontonasal duct** into the **middle nasal meatus**.
- The **anterior ethmoid cells** also drain into the **middle nasal meatus** via the **infundibulum**.
- Obstruction in the **superior meatus** would not directly impact drainage of these sinuses.
*Maxillary sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus*
- The **maxillary sinus** drains through its **ostium** into the **middle nasal meatus**.
- The **anterior ethmoid cells** drain into the **middle nasal meatus** through the **infundibulum**.
- These structures are not affected by superior meatus obstruction.
*Pterygopalatine fossa and middle ethmoidal sinus*
- The **pterygopalatine fossa** is a deep anatomical space containing neurovascular structures, not a sinus that drains into the nasal cavity.
- The **middle ethmoidal sinuses** drain into the **middle nasal meatus**, not the superior meatus.
- This option is anatomically incorrect for superior meatus obstruction.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 6: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife after falling down. About 90 minutes ago, they were standing in their kitchen making lunch and chatting when he suddenly complained that he could not see as well, felt weak, and was getting dizzy. He began to lean to 1 side, and he eventually fell to the ground. He did not hit his head. In the emergency department, he is swaying while seated, generally leaning to the right. The general physical exam is unremarkable. The neurologic exam is notable for horizontal nystagmus, 3/5 strength in the right arm, ataxia of the right arm, and absent pinprick sensation in the left arm and left leg. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely single location of this patient's central nervous system lesion?
- A. Primary motor cortex
- B. Thalamus
- C. Lateral medulla (Correct Answer)
- D. Primary somatosensory cortex
- E. Anterior spinal cord
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Lateral medulla***
- The combination of **ipsilateral ataxia** and **weakness** (right arm) along with **contralateral pain and temperature sensory loss** (left arm and leg) is classic for a **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**.
- **Horizontal nystagmus**, vertigo, and leaning to one side are also consistent with involvement of vestibular nuclei and cerebellar pathways in the lateral medulla.
*Primary motor cortex*
- A lesion here would cause **contralateral weakness or paralysis** but would not explain the ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, or contralateral pain and temperature loss.
- Sensory deficits would be minimal or absent, and would primarily affect discriminative touch.
*Thalamus*
- A thalamic lesion could cause **contralateral sensory loss** (affecting all modalities) and potentially some motor deficits or ataxia, but it typically does not cause **ipsilateral ataxia** or **nystagmus** in the pattern described.
- The specific combination of ipsilateral motor and contralateral sensory deficits points away from a pure thalamic lesion.
*Primary somatosensory cortex*
- A lesion in this area would primarily result in **contralateral deficits in discriminative touch, proprioception, and stereognosis**, not pain and temperature sensation.
- It would not explain the motor deficits, ataxia, or nystagmus seen in the patient.
*Anterior spinal cord*
- Damage to the anterior spinal cord (e.g., **anterior spinal artery syndrome**) would cause **bilateral motor weakness (paraplegia/quadriplegia)** and **bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It would not account for the nystagmus, vertigo, or the specific combination of ipsilateral and contralateral deficits observed in this patient, which are characteristic of brainstem involvement.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 8: An otherwise healthy 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of episodic coughing whenever he cleans his left ear. There is no history of hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo. Stimulating his left ear canal with a cotton swab triggers a bout of coughing. The physician informs him that these symptoms are caused by hypersensitivity of a cranial nerve. A peripheral lesion of this nerve is most likely to manifest with which of the following findings on physical examination?
- A. Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- B. Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue
- C. Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow
- D. Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland
- E. Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy***
- The sensation in the external auditory canal that triggers a cough reflex is mediated by the **auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X)**, also known as Arnold's nerve.
- A peripheral lesion of the vagus nerve would most likely affect its motor functions, including the innervation of the **larynx**, leading to **ipsilateral vocal cord palsy** and hoarseness.
*Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss*
- Hearing loss is primarily associated with pathology of the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**, not the vagus nerve.
- The patient's presentation does not describe any auditory symptoms.
*Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue*
- Tongue deviation is a sign of compromise of the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which controls the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- This is not a function of the vagus nerve.
*Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow*
- The ability to raise the eyebrow is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which innervates the muscles of facial expression.
- Vagus nerve lesions do not typically present with facial weakness.
*Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland*
- Secretion from the sublingual gland is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)** via the submandibular ganglion.
- While the vagus nerve has autonomic functions, it does not directly control sublingual gland secretion.
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 9: A 40-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by a paramedic team from the scene of a motor vehicle accident where she was the driver. The patient was restrained by a seat belt and was unconscious at the scene. On physical examination, the patient appears to have multiple injuries involving the trunk and extremities. There are no penetrating injuries to the chest. As part of her trauma workup, a CT scan of the chest is ordered. At what vertebral level of the thorax is this image from?
- A. T1
- B. T6
- C. T4
- D. T5
- E. T8 (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***T8***
- The CT image shows the **inferior vena cava (IVC)** located anterior and to the right of the aorta, and the **esophagus** located posterior to the aorta and slightly to the left. The **azygos vein** is seen to the right of the vertebral body and posterior to the esophagus.
- The **mainstem bronchi** are no longer visible, indicating a level below the carina. The presence of the IVC, aorta, esophagus, and azygos vein with the absence of mainstem bronchi is characteristic of the **T8 vertebral level**.
*T1*
- At the T1 level, the structures would primarily be the **trachea** anterior to the esophagus, with the main great vessels (e.g., brachiocephalic veins and arteries) visible, not the IVC.
- The mainstem bronchi would not yet be visualized at this higher level.
*T6*
- At the T6 level, the **trachea would have already bifurcated into the mainstem bronchi**, which would be prominent structures visible on the CT scan.
- While the aorta and esophagus would be present, the specific arrangement relative to the mainstem bronchi would differentiate it from T8.
*T4*
- The T4 level is typically associated with the **carina**, where the trachea bifurcates into the mainstem bronchi.
- The great vessels would be prominent, but the IVC in its more inferior course would not be as distinctly visualized in this configuration compared to T8.
*T5*
- At the T5 level, the **mainstem bronchi** would still be clearly visible, having just diverged from the trachea.
- While vessels like the aorta are present, the key differentiating factor from T8 is the presence of the mainstem bronchi.
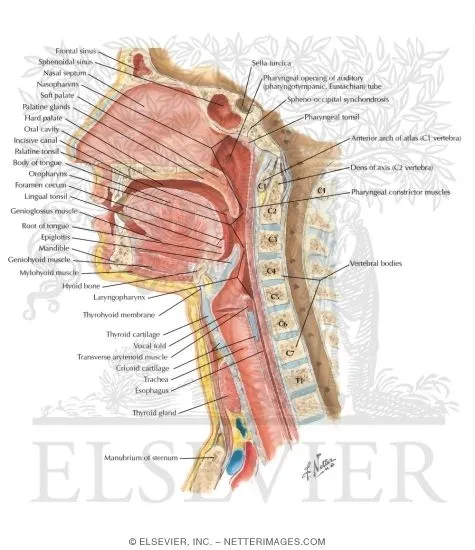
Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old mother brings in her 2-week-old baby boy to a pediatrician because he has been having difficulty feeding. The mother reveals that she had no prenatal care during her pregnancy and gave birth at home without complications. She says that her son seems to be having difficulty sucking, and she occasionally sees breast milk coming out of the infant’s nose. Physical exam reveals that this patient has a gap between his oral and nasal cavities behind the incisive foramen. He is therefore prescribed specialized bottles and his mom is taught positional techniques to ensure better feeding. Failure to fuse which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's disorder?
- A. Maxillary and medial nasal prominences
- B. Nasal septum with primary plates
- C. Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences
- D. Palatine shelves with primary plates
- E. Palatine shelves with nasal septum (Correct Answer)
Head and neck cross-sections Explanation: ***Palatine shelves with nasal septum***
- A **cleft palate** results from the **failure of fusion of the palatine shelves** with each other and/or with the **nasal septum**, creating an abnormal communication between the oral and nasal cavities.
- This anatomical defect explains the infant's **feeding difficulties** and the leakage of breast milk into the nose, as well as the observed **gap behind the incisive foramen**.
*Maxillary and medial nasal prominences*
- The failure of fusion between the maxillary and medial nasal prominences results in a **cleft lip**, which is an anterior defect and does not explain the posterior gap described.
- While cleft lip can coexist with cleft palate, the symptoms here specifically point to a palatal defect, not primarily a lip defect.
*Nasal septum with primary plates*
- The primary palate forms from the fusion of the medial nasal prominences, anterior to the incisive foramen.
- While crucial for normal development, the specific clinical presentation (gap *behind* the incisive foramen and feeding difficulties) is more characteristic of a secondary palate defect involving the palatine shelves.
*Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences*
- The fusion of these structures contributes to the formation of the **nasolacrimal groove** and parts of the cheek, not the palate.
- Deficiencies in this fusion would lead to defects in the lateral facial region, not an oro-nasal communication related to feeding.
*Palatine shelves with primary plates*
- The **primary palate** fuses with the anterior part of the secondary palate (formed by the palatine shelves) at the incisive foramen.
- However, the more common and clinically relevant defect leading to an open communication between the oral and nasal cavities, especially *behind* the incisive foramen, involves the failure of fusion of the **palatine shelves** with each other and the **nasal septum**.
More Head and neck cross-sections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.