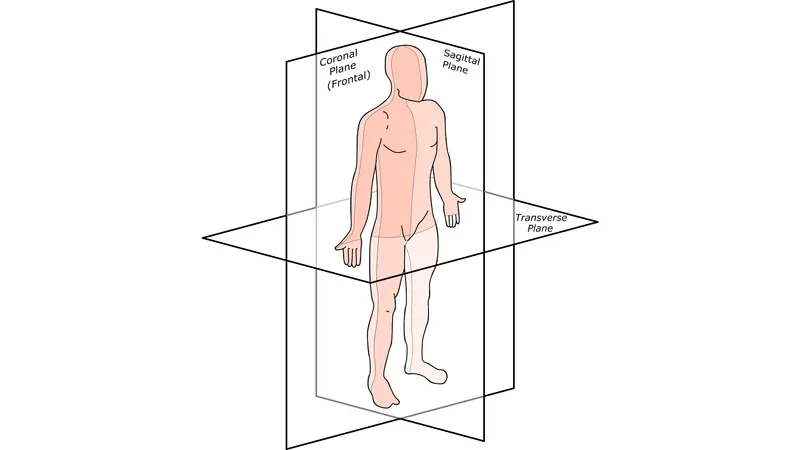
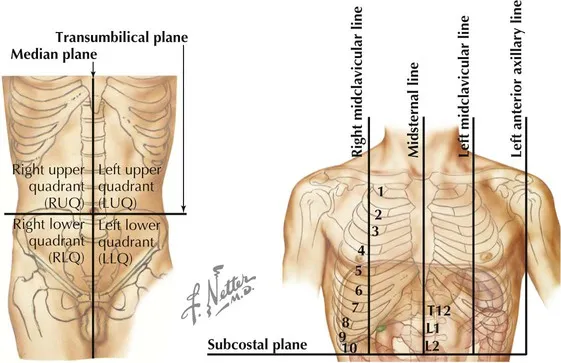
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Anatomical planes and reference lines. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 1: You are seeing a patient in clinic who presents with complaints of weakness. Her physical exam is notable for right sided hyperreflexia, as well as the reflex finding shown in the image below. Where is the most likely location of this patient's lesion?
- A. Postcentral gyrus
- B. Neuromuscular junction
- C. Lateral geniculate nucleus
- D. Internal capsule (Correct Answer)
- E. Subthalamic nucleus
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Internal capsule***
- The combination of **right-sided hyperreflexia** (an upper motor neuron sign) and a positive **Babinski sign** (as implied by a video demonstrating this reflex) points to an upper motor neuron lesion.
- The **internal capsule** contains descending motor pathways, and a lesion here would affect the contralateral side of the body, causing **weakness** and upper motor neuron signs.
*Postcentral gyrus*
- The **postcentral gyrus** is the primary somatosensory cortex and primarily deals with sensory processing, not motor output.
- A lesion here would typically cause **contralateral sensory deficits**, such as numbness or loss of proprioception, rather than motor weakness with hyperreflexia.
*Neuromuscular junction*
- Diseases of the **neuromuscular junction**, such as myasthenia gravis, cause **fatigable weakness** without hyperreflexia or other upper motor neuron signs.
- Reflexes are typically normal or decreased in these conditions.
*Lateral geniculate nucleus*
- The **lateral geniculate nucleus** is a thalamic relay center for visual information.
- Lesions here would result in **visual field deficits** (e.g., homonymous hemianopsia), not motor weakness or hyperreflexia.
*Subthalamic nucleus*
- The **subthalamic nucleus** is part of the basal ganglia and is involved in motor control, particularly in regulating movement initiation and stopping.
- Lesions here are classically associated with **hemiballismus**, which is characterized by wild, flinging movements, rather than weakness and hyperreflexia.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 2: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of acute left-sided chest pain and dyspnea following a motor vehicle accident. His pulse is 122/min and blood pressure is 85/45 mm Hg. Physical examination shows distended neck veins and tracheal displacement to the right side. The left chest is hyperresonant to percussion and there are decreased breath sounds. This patient would most benefit from needle insertion at which of the following anatomical sites?
- A. 5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line
- B. 8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line
- C. 2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line (Correct Answer)
- D. Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin
- E. 5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line***
- The patient's symptoms (chest pain, dyspnea, hypotension, distended neck veins, tracheal deviation, hyperresonance, and decreased breath sounds on the left) are classic signs of a **tension pneumothorax**.
- Immediate treatment for **tension pneumothorax** involves needle decompression at the **2nd intercostal space** in the midclavicular line to relieve pressure and restore hemodynamic stability.
*5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line*
- This location is typically used for **chest tube insertion** in a more controlled setting, not for emergent needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it's a safe location for pleural access, it is not the **first-line site** for immediate life-saving decompression.
*8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line*
- This site is too low and posterior for effective needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax, which requires rapid access to the **apex of the lung**.
- It is more commonly used for **thoracentesis** to drain fluid from the pleural cavity.
*Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin*
- This location is primarily used for **pericardiocentesis** to drain fluid from the pericardial sac in cases of cardiac tamponade.
- It is not appropriate for addressing a **pneumothorax**, which involves air in the pleural space.
*5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line*
- This site is a common alternative for **chest tube insertion** but is not the preferred or most immediate site for needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it offers pleural access, the **2nd intercostal space** anteriorly is chosen for expediency and safety in an emergency.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 3: A patient undergoes spinal surgery at the L4-L5 level. During the procedure, which of the following ligaments must be divided first to access the spinal canal?
- A. Nuchal ligament
- B. Anterior longitudinal ligament
- C. Supraspinous ligament
- D. Ligamentum flavum (Correct Answer)
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Ligamentum flavum***
- The **ligamentum flavum** connects the laminae of adjacent vertebrae and forms the posterior boundary of the spinal canal, making it the first ligament encountered anteriorly after removing the lamina.
- While performing a posterior approach **laminectomy**, the ligamentum flavum is typically divided or removed to gain access to the neural structures within the spinal canal.
*Nuchal ligament*
- The **nuchal ligament** is located in the cervical spine and provides attachment for muscles, extending from the external occipital protuberance to the spinous process of C7.
- It is not present at the **L4-L5 level** and therefore plays no role in lumbar spinal surgery.
*Anterior longitudinal ligament*
- The **anterior longitudinal ligament** runs along the anterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs.
- It would be encountered during an **anterior surgical approach** to the spine, not a posterior approach to access the spinal canal.
*Supraspinous ligament*
- The **supraspinous ligament** connects the tips of the spinous processes and is the most superficial ligament posteriorly.
- While it is incised during a posterior approach, it is **superficial to the lamina** and ligamentum flavum; therefore, the lamina and ligamentum flavum must be removed or divided first to access the canal.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 4: An 18-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after being stabbed in the chest during a fight. He has no other injuries. His pulse is 120/min, blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows a 4-cm deep, straight stab wound in the 4th intercostal space 2 cm medial to the right midclavicular line. The knife most likely passed through which of the following structures?
- A. Serratus anterior muscle, pleura, inferior vena cava
- B. External oblique muscle, superior epigastric artery, azygos vein
- C. Pectoralis minor muscle, dome of the diaphragm, right lobe of the liver
- D. Intercostal muscles, internal thoracic artery, right heart
- E. Pectoral fascia, transversus thoracis muscle, right lung (Correct Answer)
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Pectoral fascia, transversus thoracis muscle, right lung***
* The stab wound is in the **4th intercostal space**, 2 cm medial to the right midclavicular line, placing it over the anterior chest wall. This trajectory would first penetrate the **pectoral fascia**.
* Deeper structures in this region include the **transversus thoracis muscle** and, given the depth, the **right lung** as it extends superiorly behind the anterior chest wall.
* *Serratus anterior muscle, pleura, inferior vena cava*
* The **serratus anterior muscle** is more laterally positioned, typically covering the side of the rib cage.
* The **inferior vena cava** is located more medially and posteriorly within the mediastinum, deep to the diaphragm, making it an unlikely target for an anterior 4th intercostal stab.
* *External oblique muscle, superior epigastric artery, azygos vein*
* The **external oblique muscle** is part of the abdominal wall and would not be penetrated in the 4th intercostal space.
* The **superior epigastric artery** is lower, typically extending into the abdominal wall, and the **azygos vein** is in the posterior mediastinum, not in the path of this superficial anterior stab wound.
* *Pectoralis minor muscle, dome of the diaphragm, right lobe of the liver*
* The **pectoralis minor muscle** is located deep to the pectoralis major, which would be penetrated. However, a stab at the 4th intercostal space would be too high to directly involve the **dome of the diaphragm** or the **right lobe of the liver**, which are typically below the 5th intercostal space, especially in forced expiration.
* *Intercostal muscles, internal thoracic artery, right heart*
* The **intercostal muscles** would certainly be traversed.
* However, the **internal thoracic artery** runs paramedially (about 1-2 cm from the sternum), and getting to the **right heart** would require a more medial and deeper trajectory, potentially causing immediate tamponade or severe hemorrhage.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 5: A 50-year-old man presents with severe chest pain for a week. His pain increases with breathing and is localized to the right. He has tried over-the-counter medications at home, but they did not help. The patient has a 20-pack-year smoking history and currently smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and he drinks 3 to 4 cans of beer daily before dinner. His temperature is 39.1°C (102.3°F), blood pressure is 127/85 mm Hg, pulse is 109/min, and respirations are 20/min. Respiratory examination shows dullness to percussion from the 7th rib inferiorly at the right midaxillary line, decreased vocal tactile fremitus, and diminished breath sounds in the same area. Chest radiograph is shown in the image. The patient is prepared for thoracocentesis. Which of the following locations would be the most appropriate for insertion of a chest tube?
- A. Below the inferior border of the 7th rib in the midaxillary line
- B. Above the superior border of the 8th rib in the midaxillary line (Correct Answer)
- C. Above the superior border of the 5th rib in the midclavicular line
- D. Below the inferior border of the 5th rib in the midaxillary line
- E. Above the superior border of the 7th rib in the midclavicular line
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Above the superior border of the 8th rib in the midaxillary line***
- The patient presents with symptoms and signs suggestive of a **pleural effusion** (dullness to percussion, decreased fremitus, diminished breath sounds) and potentially an **empyema** given the fever and lung consolidation on the radiograph.
- Thoracocentesis should be performed in the **midaxillary line** between the 6th and 9th ribs to avoid injuring the **diaphragm and abdominal organs**, which can rise as high as the 5th intercostal space during expiration. To prevent damage to the neurovascular bundle that runs along the inferior border of the ribs, the needle should be inserted just **above the superior border** of the rib below the chosen intercostal space.
*Below the inferior border of the 7th rib in the midaxillary line*
- Inserting below the inferior border of the 7th rib increases the risk of injuring the **neurovascular bundle** that runs along the inferior rib margin.
- Such placement might also be too low, increasing the risk of penetrating the **diaphragm** or **abdominal organs**. This location would correspond to the 8th intercostal space, but the 'below inferior border' part is incorrect.
*Above the superior border of the 5th rib in the midclavicular line*
- The **midclavicular line** is typically used for needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax (2nd intercostal space) but is not the preferred site for thoracocentesis due to the risk of striking the lung parenchyma or internal mammary artery.
- Even if considering a pneumothorax, the 5th intercostal space in the midclavicular line is not the standard site, and an effusion is indicated here.
*Below the inferior border of the 5th rib in the midaxillary line*
- Inserting below the inferior border of the 5th rib, similar to option A, risks injury to the **neurovascular bundle**.
- While in the midaxillary line, the 5th rib might be too high for an effusion, and the technique of inserting below the inferior border is incorrect.
*Above the superior border of the 7th rib in the midclavicular line*
- The **midclavicular line** is generally avoided for thoracocentesis of effusions due to the risks mentioned previously and poor drainage if the effusion is posterior.
- The 7th intercostal space in the midclavicular line is also a non-standard and less safe location for this procedure.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife after falling down. About 90 minutes ago, they were standing in their kitchen making lunch and chatting when he suddenly complained that he could not see as well, felt weak, and was getting dizzy. He began to lean to 1 side, and he eventually fell to the ground. He did not hit his head. In the emergency department, he is swaying while seated, generally leaning to the right. The general physical exam is unremarkable. The neurologic exam is notable for horizontal nystagmus, 3/5 strength in the right arm, ataxia of the right arm, and absent pinprick sensation in the left arm and left leg. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely single location of this patient's central nervous system lesion?
- A. Primary motor cortex
- B. Thalamus
- C. Lateral medulla (Correct Answer)
- D. Primary somatosensory cortex
- E. Anterior spinal cord
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Lateral medulla***
- The combination of **ipsilateral ataxia** and **weakness** (right arm) along with **contralateral pain and temperature sensory loss** (left arm and leg) is classic for a **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**.
- **Horizontal nystagmus**, vertigo, and leaning to one side are also consistent with involvement of vestibular nuclei and cerebellar pathways in the lateral medulla.
*Primary motor cortex*
- A lesion here would cause **contralateral weakness or paralysis** but would not explain the ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, or contralateral pain and temperature loss.
- Sensory deficits would be minimal or absent, and would primarily affect discriminative touch.
*Thalamus*
- A thalamic lesion could cause **contralateral sensory loss** (affecting all modalities) and potentially some motor deficits or ataxia, but it typically does not cause **ipsilateral ataxia** or **nystagmus** in the pattern described.
- The specific combination of ipsilateral motor and contralateral sensory deficits points away from a pure thalamic lesion.
*Primary somatosensory cortex*
- A lesion in this area would primarily result in **contralateral deficits in discriminative touch, proprioception, and stereognosis**, not pain and temperature sensation.
- It would not explain the motor deficits, ataxia, or nystagmus seen in the patient.
*Anterior spinal cord*
- Damage to the anterior spinal cord (e.g., **anterior spinal artery syndrome**) would cause **bilateral motor weakness (paraplegia/quadriplegia)** and **bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It would not account for the nystagmus, vertigo, or the specific combination of ipsilateral and contralateral deficits observed in this patient, which are characteristic of brainstem involvement.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 7: A young researcher is responsible for graphing laboratory data involving pulmonary blood flow and ventilation pattern obtained from a healthy volunteer who was standing in an upright position. After plotting the following graph, the researcher realizes he forgot to label the curves and the x-axis (which represents the position in the lung). Which of the following is the appropriate label for each point on the graph?
- A. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung (Correct Answer)
- B. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- C. A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- D. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum
- E. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung***
- In an upright individual, both **ventilation** and **blood flow** are greater at the **base of the lung** than at the apex due to gravity.
- However, the increase in **perfusion** from apex to base (curve B) is proportionally much greater than the increase in **ventilation** (curve A), leading to a higher V/Q ratio at the apex and a lower V/Q ratio at the base.
*A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option correctly identifies curves A and B but incorrectly labels C as the **mid-portion of the lung** instead of the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung from base to apex or vice-versa, and the curve indicates the highest values at C.
*A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option incorrectly identifies curves A and B; they represent **ventilation** and **blood flow**, not dead space and shunt, which are concepts related to V/Q mismatch.
- **Dead space** refers to ventilated but unperfused areas, while a **shunt** is perfused but unventilated.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, as **blood flow** increases more steeply than **ventilation** towards the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not the **hilum**, which is a specific anatomical region.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, in addition to mislabeling C as the **apex of the lung**, where values are lowest, not highest.
- The X-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not focusing on the **hilum**.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 8: A 23-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by a coworker for an injury sustained at work. He works in construction and accidentally shot himself in the chest with a nail gun. Physical examination shows a bleeding wound in the left hemithorax at the level of the 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line. Which of the following structures is most likely injured in this patient?
- A. Right atrium of the heart
- B. Inferior vena cava
- C. Left upper lobe of the lung (Correct Answer)
- D. Left atrium of the heart
- E. Superior vena cava
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Left upper lobe of the lung***
- The **left upper lobe of the lung** extends to the 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line, making it the most probable structure to be traversed by a penetrating injury at this location.
- The **pleural cavity** and lung tissue are superficially located in this region, making them highly susceptible to injury from a nail gun.
*Right atrium of the heart*
- The **right atrium** is located predominantly on the right side of the sternum, more centrally, and slightly to the right of the midclavicular line.
- An injury at the **left 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line** would typically be too lateral and superior to directly injure the right atrium.
*Inferior vena cava*
- The **inferior vena cava (IVC)** enters the right atrium from below, primarily located within the abdomen and passing through the diaphragm at the level of T8.
- Its position is far too **inferior and posterior** relative to the 4th intercostal space to be directly injured by this wound.
*Left atrium of the heart*
- The **left atrium** is the most posterior chamber of the heart and is largely covered by the left ventricle.
- Although part of the heart is on the left, an injury at the **4th intercostal space, midclavicular line**, would likely impact the left ventricle or lung tissue before reaching the left atrium, which is located more posteriorly and medially.
*Superior vena cava*
- The **superior vena cava (SVC)** is located to the right of the midline, formed by the brachiocephalic veins behind the right first costal cartilage.
- Its position is too **medial and superior**, on the right side, to be directly injured by a nail penetrating the left 4th intercostal space at the midclavicular line.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 9: A 33-year-old man comes to the otolaryngologist for the evaluation of a 6-month history of difficulty breathing through his nose and clear nasal discharge. He has a history of seasonal atopic rhinosinusitis. Anterior rhinoscopy shows a nasal polyp obstructing the superior nasal meatus. A CT scan of the head is most likely to show opacification of which of the following structures?
- A. Nasolacrimal duct and eustachian tube
- B. Sphenoidal sinus and posterior ethmoidal sinuses (Correct Answer)
- C. Frontal sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus
- D. Maxillary sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus
- E. Pterygopalatine fossa and middle ethmoidal sinus
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Sphenoidal sinus and posterior ethmoidal sinuses***
- The **posterior ethmoidal sinuses** drain directly into the **superior nasal meatus**, making them the primary structures affected by obstruction at this location.
- The **sphenoid sinus** drains into the **sphenoethmoidal recess**, which is located immediately posterior and superior to the superior nasal meatus. Due to their anatomical proximity and shared drainage region, obstruction in the superior meatus can affect drainage and lead to **opacification** of both structures due to **mucus retention** and inflammation.
- This is the most appropriate answer among the given options for superior meatus obstruction.
*Nasolacrimal duct and eustachian tube*
- The **nasolacrimal duct** drains into the **inferior nasal meatus**, not the superior meatus.
- The **eustachian tube** opens into the **nasopharynx**, which has no direct anatomical connection to the superior nasal meatus.
- These structures would not be affected by superior meatus obstruction.
*Frontal sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus*
- The **frontal sinus** drains through the **frontonasal duct** into the **middle nasal meatus**.
- The **anterior ethmoid cells** also drain into the **middle nasal meatus** via the **infundibulum**.
- Obstruction in the **superior meatus** would not directly impact drainage of these sinuses.
*Maxillary sinus and anterior ethmoidal sinus*
- The **maxillary sinus** drains through its **ostium** into the **middle nasal meatus**.
- The **anterior ethmoid cells** drain into the **middle nasal meatus** through the **infundibulum**.
- These structures are not affected by superior meatus obstruction.
*Pterygopalatine fossa and middle ethmoidal sinus*
- The **pterygopalatine fossa** is a deep anatomical space containing neurovascular structures, not a sinus that drains into the nasal cavity.
- The **middle ethmoidal sinuses** drain into the **middle nasal meatus**, not the superior meatus.
- This option is anatomically incorrect for superior meatus obstruction.
Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG Question 10: A 71-year-old man undergoes CT angiography for suspected mesenteric ischemia. Axial sections at the L1 level show a dissection flap in the superior mesenteric artery with the true lumen severely narrowed. The false lumen extends into a vessel that crosses anterior to the left renal vein. Coronal reconstructions show this vessel arising from the anterolateral aspect of the aorta at L2. The patient has left flank pain and hematuria in addition to abdominal pain. Synthesize the cross-sectional and vascular anatomy to determine the additional vessel involved.
- A. Left gonadal artery arising from the aorta (Correct Answer)
- B. Left middle colic artery from the SMA
- C. Left renal artery from the aorta
- D. Left inferior phrenic artery
- E. Left lumbar artery
Anatomical planes and reference lines Explanation: ***Left gonadal artery arising from the aorta***
- The **left gonadal artery** originates from the **anterolateral aspect of the aorta** at the **L2 level** and is known to cross **anterior to the left renal vein** as it descends.
- Compromise or dissection involving this artery can cause **flank pain and hematuria** due to its proximity to the ureter and its vascular territory, correlating with the patient's symptoms.
*Left middle colic artery from the SMA*
- The **middle colic artery** arises from the **SMA** at the level of the lower border of the pancreas and supplies the **transverse colon**.
- While it is a branch of the SMA, its course does not classically cross **anterior to the left renal vein**, nor would its involvement typically cause **hematuria**.
*Left renal artery from the aorta*
- The **left renal artery** arises from the aorta at the **L1-L2 level** but typically passes **posterior to the left renal vein**.
- Although renal artery involvement causes hematuria and flank pain, the specific anatomical description of the vessel crossing **anterior to the renal vein** rules it out.
*Left inferior phrenic artery*
- The **inferior phrenic arteries** usually arise from the aorta just above the **celiac trunk** or from the celiac trunk itself at the **T12-L1 level**.
- These vessels supply the **diaphragm and suprarenal glands** and do not descend to cross the **left renal vein at the L2 level**.
*Left lumbar artery*
- **Lumbar arteries** arise from the **posterior aspect** of the abdominal aorta, usually in four pairs corresponding to the L1-L4 vertebrae.
- They travel **posteriorly** to supply the posterior abdominal wall and spinal cord, making the description of an **anterior crossing** of the renal vein anatomically incorrect.
More Anatomical planes and reference lines US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.