Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Decussation of pyramids. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 1: A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of sharp, stabbing pain in the lower back for 3 weeks. The pain radiates to the back of her right leg and is worse at night. She reports decreased sensation around her buttocks and inner thighs. During the last several days, she has had trouble urinating. Three years ago, she was diagnosed with breast cancer and was treated with lumpectomy and radiation. Her only medication is anastrozole. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg. Neurologic examination shows 4/5 strength in the left lower extremity and 2/5 strength in her right lower extremity. Knee and ankle reflexes are 1+ on the right. The resting anal sphincter tone is normal but the squeeze tone is reduced. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Anterior spinal cord syndrome
- B. Cauda equina syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Conus medullaris syndrome
- D. Central cord syndrome
- E. Brown-sequard syndrome
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Cauda equina syndrome***
- The patient's presentation with **severe low back pain**, **saddle anesthesia** (decreased sensation around buttocks and inner thighs), **bladder dysfunction** (trouble urinating), and **motor weakness** in the lower extremities is highly indicative of cauda equina syndrome. This can be caused by **spinal metastases** from her breast cancer.
- The **reduced squeeze tone** of the anal sphincter, despite normal resting tone, further supports the diagnosis, indicating dysfunction of the sacral nerve roots which are compressed in cauda equina syndrome.
*Anterior spinal cord syndrome*
- This syndrome typically presents with **motor paralysis**, loss of **pain** and **temperature** sensation below the lesion, but preservation of **proprioception** and **vibration sense**.
- It does not typically cause **saddle anesthesia** or **bladder dysfunction** to the extent seen in this patient.
*Conus medullaris syndrome*
- Conus medullaris syndrome involves the lower part of the spinal cord (T12-L2) and typically presents with **symmetric motor weakness**, **early onset bladder and bowel dysfunction**, and often **perianal numbness**.
- While there is bladder dysfunction, the described **asymmetric weakness** and prominent **radicular pain** radiating down one leg are more characteristic of cauda equina syndrome, which affects nerve roots rather than the spinal cord itself.
*Central cord syndrome*
- This syndrome usually results from hyperextension injuries and leads to **greater motor impairment in the upper extremities** than in the lower extremities.
- It is often associated with a **'shawl-like' distribution** of sensory loss and does not typically present with the same severe lower extremity weakness, saddle anesthesia, or bladder dysfunction as seen in this patient.
*Brown-Sequard syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **hemisection of the spinal cord**, resulting in **ipsilateral motor paralysis** and loss of **proprioception and vibration sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It also causes **contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** starting a few segments below the lesion, which does not match the patient's symptoms of bilateral sensory and motor deficits with saddle anesthesia.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 2: A 20-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after he sustained a stab wound to his back during an altercation. He reports weakness and numbness of the lower extremities. He has no history of serious illness. On arrival, he is alert and cooperative. His pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg. Examination shows a deep 4-cm laceration on his back next to the vertebral column at the level of the T10 vertebra. Neurologic examination shows right-sided motor weakness with diminished vibratory sense ipsilaterally, decreased sensation to light touch at the level of his laceration and below, and left-sided loss of hot, cold, and pin-prick sensation at the level of the umbilicus and below. Deep tendon reflexes of his right lower extremity are 4+ and symmetrical. Babinski sign is absent bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Brown-Sequard syndrome (Correct Answer)
- B. Anterior cord syndrome
- C. Posterior cord syndrome
- D. Cauda equina syndrome
- E. Central cord syndrome
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Brown-Sequard syndrome***
- This syndrome is characterized by **ipsilateral motor paresis** and **loss of proprioception/vibration sensation**, along with **contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation**.
- The patient's presentation of right-sided motor weakness and diminished vibratory sense ipsilaterally, coupled with left-sided loss of hot, cold, and pin-prick sensation, perfectly matches the classic signs of **Brown-Sequard syndrome** from a hemisection of the spinal cord (due to the stab wound).
*Anterior cord syndrome*
- This syndrome typically presents with **paraplegia or quadriplegia** and loss of pain and temperature sensation below the level of the lesion, with **preservation of proprioception and vibratory sensation**.
- The patient maintains **ipsilateral vibratory sensation** and has differential sensory loss, which is inconsistent with anterior cord syndrome where all distal sensation is broadly affected.
*Posterior cord syndrome*
- This syndrome is marked by a predominant loss of **proprioception and vibratory sensation** below the level of the lesion, with **preserved motor function** and pain/temperature sensation.
- The patient exhibits significant **motor weakness** and **contralateral loss of pain and temperature**, which are not typical features of posterior cord syndrome.
*Cauda equina syndrome*
- Cauda equina syndrome involves injury to the **nerve roots below the conus medullaris** and presents with **flaccid paralysis**, **saddle anesthesia**, and **bowel/bladder dysfunction**.
- The patient's presentation of spastic signs (4+ DTRs) and specific sensory deficits of a spinal cord lesion are inconsistent with the **lower motor neuron** signs of cauda equina syndrome.
*Central cord syndrome*
- This syndrome typically results in **greater motor impairment in the upper extremities than in the lower extremities**, along with a **variable sensory loss** below the level of the lesion, often involving a "cape-like" distribution of sensory loss.
- The patient's injury is at T10, and while there is motor weakness, the specific pattern of ipsilateral motor with contralateral pain/temperature loss is not characteristic of central cord syndrome, which usually affects the cervical region and has a different motor pattern.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 3: A 76-year-old woman with hypertension and coronary artery disease is brought to the emergency department after the sudden onset of right-sided weakness. Her pulse is 83/min and blood pressure is 156/90 mm Hg. Neurological examination shows right-sided facial drooping and complete paralysis of the right upper and lower extremities. Tongue position is normal and she is able to swallow liquids without difficulty. Knee and ankle deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the right. Sensation to vibration, position, and light touch is normal bilaterally. She is oriented to person, place, and time, and is able to speak normally. Occlusion of which of the following vessels is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
- A. Ipsilateral anterior cerebral artery
- B. Contralateral middle cerebral artery
- C. Anterior spinal artery
- D. Contralateral lenticulostriate artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Ipsilateral posterior inferior cerebellar artery
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Contralateral lenticulostriate artery***
- The patient presents with **pure motor hemiparesis** affecting the face, arm, and leg equally on the right side, with **no sensory deficits, aphasia, or cognitive impairment**.
- This clinical pattern is classic for a **lacunar stroke** affecting the **internal capsule**, which is supplied by the **lenticulostriate arteries** (branches of the middle cerebral artery).
- The internal capsule contains tightly packed corticospinal and corticobulbar fibers; a small infarct here causes complete contralateral motor deficits without cortical signs.
- The **absence of cortical findings** (normal speech, cognition, and sensation) distinguishes this from cortical MCA stroke.
*Contralateral middle cerebral artery*
- A **cortical MCA stroke** would typically present with **cortical signs** such as aphasia (if left hemisphere), neglect (if right hemisphere), sensory loss, and visual field defects.
- MCA strokes usually show **arm and face > leg** weakness (the leg area is supplied by ACA).
- This patient's **pure motor syndrome** without cortical signs points to a subcortical lesion, not cortical MCA occlusion.
*Ipsilateral anterior cerebral artery*
- First, the lateralization is incorrect - symptoms are right-sided, indicating left hemisphere pathology, so it would be **contralateral** ACA.
- ACA occlusion causes weakness predominantly in the **contralateral leg > arm**, with relative sparing of the face.
- This patient has equal involvement of face, arm, and leg, which is inconsistent with ACA territory.
*Anterior spinal artery*
- The **anterior spinal artery** supplies the anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord, including the corticospinal tracts and anterior horn cells.
- Occlusion causes **bilateral** motor weakness below the lesion level and bilateral loss of pain/temperature sensation.
- It does not cause **unilateral facial weakness** or the distribution of deficits seen in this patient.
*Ipsilateral posterior inferior cerebellar artery*
- Again, lateralization is incorrect - symptoms would be from **contralateral** PICA for motor findings, but PICA supplies the lateral medulla and inferior cerebellum.
- PICA occlusion causes **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**: ataxia, vertigo, dysphagia, dysarthria, Horner syndrome, and contralateral pain/temperature loss.
- The patient's **pure motor hemiparesis** without cerebellar or brainstem signs is incompatible with PICA occlusion.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 4: A 54-year-old man is referred to a tertiary care hospital with a history of 5 months of progressive difficulty in walking and left leg numbness. He first noticed mild gait unsteadiness and later developed gradual right leg weakness. His left leg developed progressive numbness and tingling. His blood pressure is 138/88 mm Hg, the heart rate is 72/min, and the temperature is 36.7°C (98.2°F). On physical examination, he is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. Cranial nerves are intact. Muscle strength is 5/5 in both upper extremities and left lower extremity, but 3/5 in the right leg with increased tone. The plantar reflex is extensor on the right. Pinprick sensation is decreased on the left side below the umbilicus. Vibration and joint position senses are decreased in the right foot and leg. All sensations are normal in the upper extremities. Finger-to-nose and heel-to-shin testing are normal. This patient’s lesion is most likely located in which of the following parts of the nervous system?
- A. Right hemi-spinal cord (Correct Answer)
- B. Right frontal lobe
- C. Left frontal lobe
- D. Left hemi-spinal cord
- E. Right pons
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Right hemi-spinal cord***
- The patient presents with **ipsilateral motor weakness** (right leg 3/5 with increased tone and extensor plantar reflex) and **ipsilateral dorsal column deficits** (decreased vibration and joint position senses in the right foot and leg) along with **contralateral spinothalamic loss** (decreased pinprick sensation on the left side below the umbilicus). This classic combination of symptoms is known as **Brown-Séquard syndrome**, which results from a lesion affecting one half of the spinal cord.
- The specific pattern of deficits—motor and proprioceptive loss on the same side as the lesion, and pain/temperature loss on the opposite side—localizes the lesion to the **right half of the spinal cord**.
*Right frontal lobe*
- A lesion in the right frontal lobe would typically cause **contralateral motor weakness** (left-sided) and potentially cognitive or behavioral changes, without the specific sensory dissociation seen in this patient.
- It would not explain the **ipsilateral proprioceptive loss** or the **contralateral pain/temperature loss** at different levels as observed in this case.
*Left frontal lobe*
- A lesion in the left frontal lobe would primarily result in **contralateral motor weakness** (right-sided), similar to the right leg weakness observed, but it would not explain the other sensory deficits, particularly the **contralateral pain/temperature loss** (right-sided in this scenario) and the **ipsilateral proprioceptive loss**.
- **Speech disturbances** (aphasia) are also common with left frontal lobe lesions, depending on the exact location, which are not mentioned here.
*Left hemi-spinal cord*
- A lesion in the left hemi-spinal cord would cause **ipsilateral motor weakness** (left leg weakness) and **ipsilateral dorsal column deficits** (decreased vibration and joint position senses in the left foot and leg), along with **contralateral spinothalamic loss** (decreased pinprick sensation on the right side).
- This pattern is the opposite of the patient's symptoms, which show right-sided weakness and proprioceptive loss, and left-sided pain/temperature loss.
*Right pons*
- A lesion in the pons would typically present with a **combination of cranial nerve deficits** (e.g., facial sensory or motor abnormalities, gaze palsies) **and long tract signs**, often affecting both sides of the body due to the compact nature of the brainstem.
- While it could cause long tract signs, the specific pattern of **dissociated ipsilateral and contralateral sensory/motor deficits** observed below the umbilical level is highly characteristic of a spinal cord lesion and less so of a pontine lesion.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 5: A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being stabbed with a knife during an altercation. Physical examination shows a 4-cm stab wound on the right lateral border of the T1 spinous process. An MRI of the spinal cord shows damage to the area of the right lateral corticospinal tract at the level of T1. Further evaluation will most likely show which of the following findings?
- A. Absence of right-sided motor function below T1 (Correct Answer)
- B. Absence of left-sided proprioception below T1
- C. Presence of left-sided Babinski sign
- D. Absence of left-sided fine touch sensation below T1
- E. Absence of right-sided temperature sensation below T1
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Absence of right-sided motor function below T1***
- The **right lateral corticospinal tract** controls **voluntary motor function** on the **ipsilateral side** of the body.
- Damage to this tract at T1 would therefore lead to a loss of motor function on the right side below the level of the injury.
*Absence of left-sided proprioception below T1*
- **Proprioception** is carried by the **dorsal columns**, which ascend **ipsilaterally** before decussating in the brainstem.
- Damage to the right lateral corticospinal tract would not affect left-sided proprioception.
*Presence of left-sided Babinski sign*
- A **Babinski sign** (upgoing plantar reflex) indicates an **upper motor neuron lesion**.
- Since the corticospinal tract decussates in the **medulla** (before reaching the spinal cord), a lesion in the **right lateral corticospinal tract at T1** affects motor function on the **right side** of the body.
- Therefore, if a Babinski sign were present, it would be on the **right side**, not the left.
*Absence of left-sided fine touch sensation below T1*
- **Fine touch** sensation is transmitted by the **dorsal columns**, which ascend **ipsilaterally** and decussate in the brainstem.
- Damage to the right lateral corticospinal tract would not affect fine touch sensation on the left side.
*Absence of right-sided temperature sensation below T1*
- **Temperature sensation** is carried by the **spinothalamic tracts**, which decussate at the level of entry into the spinal cord.
- Therefore, a lesion of the right lateral corticospinal tract would not affect temperature sensation on the right side; ipsilateral temperature loss would be due to damage to the right spinothalamic tract, which is located more anterolaterally in the spinal cord.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because she thinks he has had a stroke. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current medications include enalapril and metformin. He has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes per day for the past 35 years. His blood pressure is 162/95 mm Hg. A CT scan of the brain shows a lacunar stroke involving the left subthalamic nucleus. The patient most likely presented with which of the following findings on physical examination?
- A. Cogwheel rigidity
- B. Dystonia
- C. Hemispatial agnosia
- D. Vertical gaze palsy
- E. Hemiballismus (Correct Answer)
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Hemiballismus***
- A lacunar stroke in the **subthalamic nucleus (STN)** typically causes **hemiballismus**, which is characterized by wild, involuntary, large-amplitude flinging movements on one side of the body.
- The STN is part of the **basal ganglia circuit** and its damage leads to disinhibition of the thalamus, resulting in hyperkinetic movements.
*Cogwheel rigidity*
- This is a feature of **Parkinson's disease**, resulting from damage to the **substantia nigra** affecting dopamine production, not typically a direct result of a lacunar stroke in the subthalamic nucleus.
- It is characterized by a jerky resistance to passive movement in a limb.
*Dystonia*
- Characterized by sustained or repetitive muscle contractions resulting in **twisting and repetitive movements** or abnormal fixed postures.
- While basal ganglia dysfunction can cause dystonia, it's a broader term, and **hemiballismus** is a more specific and classic presentation of STN lesions.
*Hemispatial agnosia*
- Refers to a deficit in attention to one side of space, most commonly associated with lesions in the **non-dominant (right) parietal lobe**.
- This is distinct from the motor symptoms expected from a subthalamic nucleus lesion.
*Vertical gaze palsy*
- Commonly associated with lesions in the **midbrain**, particularly the **dorsal midbrain syndrome (Parinaud syndrome)**.
- This is not a typical presentation of a lacunar stroke specifically involving the subthalamic nucleus.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 7: A 21-year-old man was involved in a motor vehicle accident and died. At autopsy, the patient demonstrated abnormally increased mobility at the neck. A section of cervical spinal cord at C6 was removed and processed into slides. Which of the following gross anatomic features is most likely true of this spinal cord level?
- A. Cuneate and gracilis fasciculi are present (Correct Answer)
- B. Least amount of white matter
- C. Prominent lateral horns
- D. Absence of gray matter enlargement
- E. Involvement with parasympathetic nervous system
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: **Cuneate and gracilis fasciculi are present**
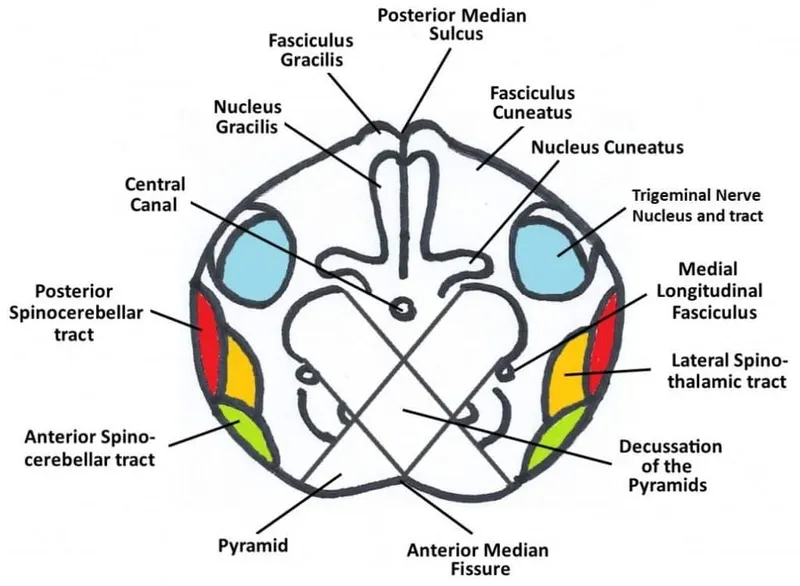
- At the **C6 level** of the spinal cord, both the **fasciculus gracilis** (carrying information from the lower body) and the **fasciculus cuneatus** (carrying information from the upper body) are present in the dorsal column.
- The fasciculus cuneatus typically appears at **T6 and above**, making it visible at C6.
*Least amount of white matter*
- The cervical spinal cord, particularly at C6, contains a **significant amount of white matter** because it carries all ascending and descending tracts to and from the brain, including those for the upper and lower limbs.
- The **sacral segments** typically have the least amount of white matter due to fewer tracts remaining.
*Prominent lateral horns*
- **Lateral horns** are characteristic of the **thoracic and upper lumbar (T1-L2/L3)** spinal cord segments, where they house preganglionic sympathetic neurons.
- They are generally **absent or poorly developed** in the cervical spinal cord.
*Absence of gray matter enlargement*
- The **cervical enlargement** of the spinal cord, particularly pronounced from C4 to T1, contains an increased amount of gray matter to accommodate the innervation of the **upper limbs**.
- Therefore, the C6 level would show **significant gray matter enlargement**.
*Involvement with parasympathetic nervous system*
- The **parasympathetic nervous system** exits the spinal cord at the **sacral levels (S2-S4)** and as cranial nerves, not primarily from the cervical spinal cord through distinct horns.
- The cervical spinal cord is primarily associated with **somatic motor and sensory pathways** for the neck, shoulders, and upper limbs, and receives some sympathetic input, but is not where parasympathetic outflow predominantly originates.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 8: A 61-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his son after collapsing to the ground while at home. His son immediately performed cardiopulmonary resuscitation and later the patient underwent successful defibrillation after being evaluated by the emergency medical technician. The patient has a medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type II diabetes mellitus. He has smoked one-half pack of cigarettes for approximately 30 years. The patient was admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit, and after a few days developed acute onset right upper extremity weakness. His temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 145/91 mmHg, pulse is 102/min and irregularly irregular, and respirations are 16/min. On physical examination, the patient is alert and orientated to person, place, and time. His language is fluent and he is able to name, repeat, and read. His strength is 5/5 throughout except in the right hand, wrist, and arm, which is 2/5. Based on this patient's clinical presentation, the affected neuronal fibers decussate at which level of the central nervous system?
- A. Caudal medulla (Correct Answer)
- B. Pons
- C. Spinal cord
- D. Primary motor cortex
- E. Thalamus
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Caudal medulla***
- The patient's **acute right upper extremity weakness** following a cardiac event suggests a **stroke** affecting the left motor pathways.
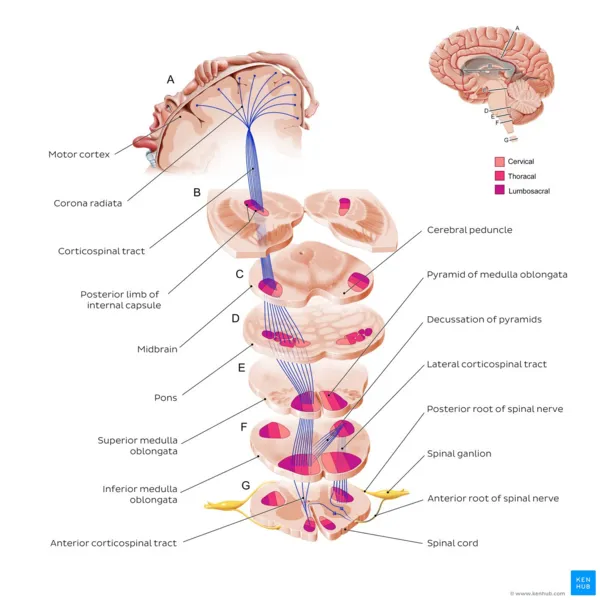
- The **pyramidal decussation**, where the vast majority of the **corticospinal tracts** cross to the contralateral side, occurs in the **caudal medulla**.
*Pons*
- While the corticospinal tracts pass through the pons, they generally do not decussate at this level.
- Lesions in the pons often present with **ipsilateral cranial nerve** deficits and **contralateral body weakness**.
*Spinal cord*
- Only a small percentage (about 10-15%) of the corticospinal fibers decussate in the spinal cord, and these form the **anterior corticospinal tract**, mainly supplying axial muscles.
- Significant contralateral upper extremity weakness implies a lesion higher up, before the spinal cord.
*Primary motor cortex*
- Lesions in the primary motor cortex would cause contralateral weakness, but the decussation itself occurs in the brainstem, not the cortex.
- The motor cortex is where the motor commands originate, not where they cross over.
*Thalamus*
- The thalamus is a major **sensory relay station** and also plays a role in motor control, but it is not the site of decussation for the corticospinal tracts.
- Thalamic lesions typically cause **sensory deficits** (e.g., contralateral hemianesthesia) and sometimes ataxia or dyskinesias.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 9: A 63-year-old man presents to the clinic concerned about numbness and weakness in his bilateral shoulders and arms for the past 8 weeks. The symptoms started when he fell from scaffolding at work and landed on his back. Initial workup was benign and he returned to normal duty. However, his symptoms have progressively worsened since the fall. He denies fever, back pain, preceding vomiting, and diarrhea. He has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, ischemic heart disease, and a 48-pack-year cigarette smoking history. He takes atorvastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, labetalol, and metformin. His blood pressure is 132/82 mm Hg, the pulse is 72/min, and the respiratory rate is 15/min. All cranial nerves are intact. Muscle strength is reduced in the upper limbs (4/5 bilaterally) but normal in the lower limbs. Perception of sharp stimuli and temperature is reduced on his shoulders and upper arms. The vibratory sense is preserved. Sensory examination is normal in the lower limbs. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Anterior cord syndrome
- B. Central cord syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Guillain-Barre syndrome
- D. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- E. Pontine infarction
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Central cord syndrome***
- This syndrome typically results from a **hyperextension injury** in patients with pre-existing cervical spinal stenosis, leading to damage to the central gray matter and surrounding tracts.
- It classically presents with greater **motor weakness in the upper extremities** than in the lower extremities, and a **"cape-like" distribution of sensory loss** (impaired pain and temperature sensation) over the shoulders and arms due to spinothalamic tract involvement, as seen in this patient.
*Anterior cord syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **paraplegia/quadriplegia**, dissociated sensory loss (loss of **pain and temperature sensation**), and bowel/bladder dysfunction below the level of the lesion.
- It spares **proprioception and vibratory sensation** since the posterior columns remain intact, which is not fully consistent with the patient's presentation of primarily sensory symptoms in the upper limbs with normal strength.
*Guillain-Barre syndrome*
- This is an **acute demyelinating polyneuropathy** that typically presents with **progressive, ascending weakness** and often **areflexia**, usually following an infection.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily sensory, descending, and lack significant weakness or preceding infection, making this diagnosis less likely.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- This deficiency can cause **subacute combined degeneration** of the spinal cord, affecting the **posterior columns** (vibratory and proprioception loss) and **corticospinal tracts** (weakness, spasticity).
- The patient primarily has loss of pain and temperature sensation with preserved vibratory sense and normal strength, which is inconsistent with B12 deficiency.
*Pontine infarction*
- A pontine infarction would present with a constellation of cranial nerve deficits, motor weakness (hemiparesis or quadriplegia), and cerebellar signs due to its location in the brainstem.
- The patient has intact cranial nerves, normal muscle strength, and specific sensory deficits limited to the shoulders and arms, which does not align with a brainstem stroke.
Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of burning pain in his neck and arms for a year. He has also had paresthesias in his hands during this period. He has had increasing weakness in both hands during the past 3 months. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension. He was involved in a motor vehicle collision 3 years ago. Current medications include metformin, sitagliptin, enalapril, atorvastatin, and aspirin. He has had 7 sexual partners in his lifetime; he uses condoms inconsistently. He is oriented to time, place, and person. Vital signs are within normal limits. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Examination of the upper extremities shows decreased muscle strength, absent reflexes, and decreased hand grip with fasciculations bilaterally. Sensation to temperature and pain is absent over the chest and bilateral upper arms. Vibration and joint position sensations are present in the upper limbs. Cranial nerve examination shows no focal findings. Examination of the lower extremities show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Brown-Séquard syndrome
- B. Tabes dorsalis
- C. Multiple sclerosis
- D. Syringomyelia (Correct Answer)
- E. Cervical disk prolapse
Decussation of pyramids Explanation: ***Syringomyelia***
- This condition is characterized by a central canal cavitation (syrinx) in the spinal cord, leading to damage to the **spinothalamic tracts** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) and anterior horn cells (weakness, fasciculations, absent reflexes). The **'cape-like' distribution** of sensory loss over the chest and arms, along with hand weakness, is classic.
- The sensation loss to temperature and pain over the chest and bilateral upper arms with preserved vibration and joint position sensation in upper limbs is a **dissociated sensory loss**, a hallmark of syringomyelia, as the dorsal columns (responsible for vibration and proprioception) are typically spared.
*Brown-Séquard syndrome*
- This syndrome results from **hemitransaction of the spinal cord**, causing ipsilateral loss of motor function and proprioception/vibration sensation, and contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation below the lesion.
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral sensory loss** and **bilateral weakness** do not fit this unilateral lesion pattern.
*Tabes dorsalis*
- This is a late manifestation of **syphilis**, primarily affecting the posterior columns of the spinal cord (dorsal columns), leading to loss of **proprioception and vibration sensation**, along with ataxia and shooting pains.
- The patient presents with loss of pain and temperature sensation, not primarily proprioception and vibration, and has **motor weakness with fasciculations**, which are not typical for tabes dorsalis.
*Multiple sclerosis*
- MS is characterized by **demyelination in the central nervous system**, presenting with diverse neurological symptoms that often wax and wane, affecting multiple areas of the brain and spinal cord.
- While it can cause sensory and motor deficits, the **dissociated sensory loss** (pain/temperature vs. vibration/proprioception) in a "cape-like" distribution with prominent fasciculations points away from MS.
*Cervical disk prolapse*
- A cervical disk prolapse typically causes **radicular pain and neurological deficits** (motor weakness, sensory loss, reflex changes) in a dermatomal or myotomal distribution corresponding to the compressed nerve root.
- While it can cause arm pain and weakness, the **bilateral, "cape-like" dissociated sensory loss** over the chest and arms is not characteristic of a single or multiple cervical nerve root compressions.
More Decussation of pyramids US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.