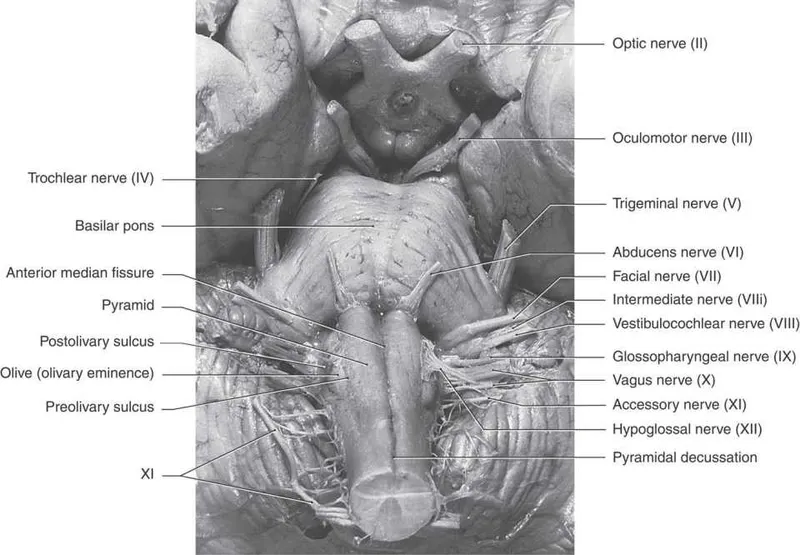
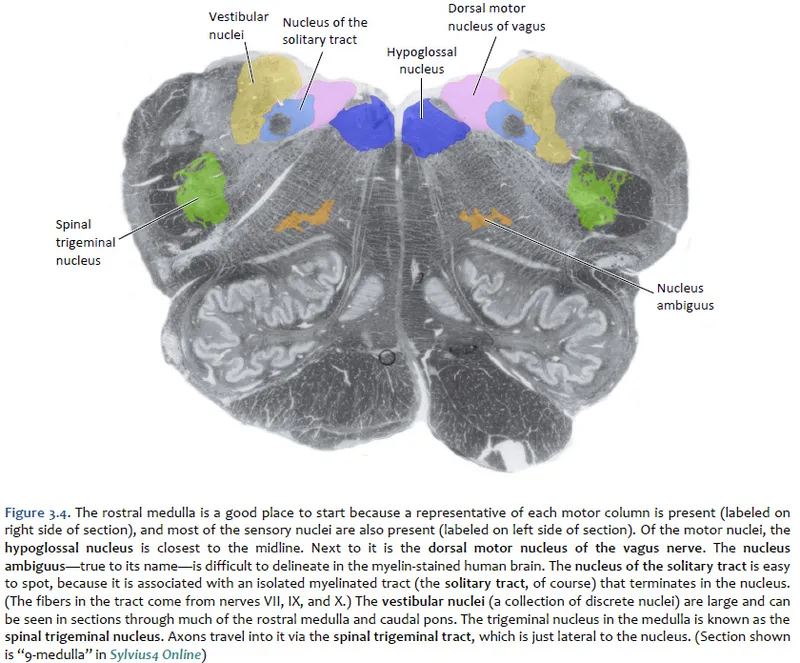
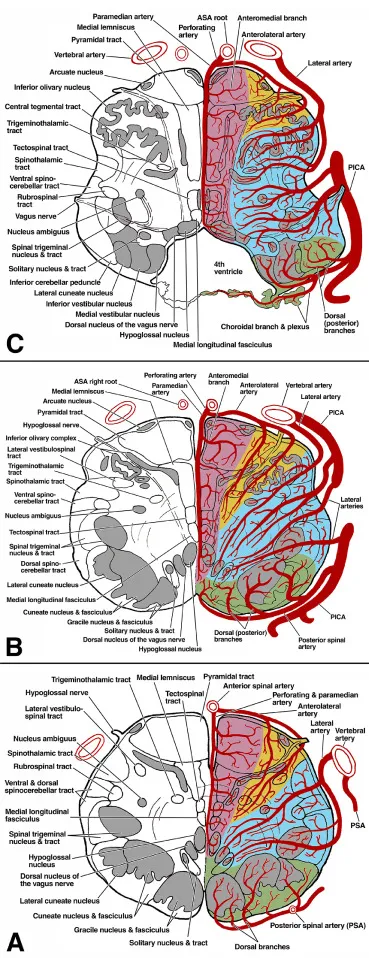
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Medulla oblongata nuclei. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 1: An otherwise healthy 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of episodic coughing whenever he cleans his left ear. There is no history of hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo. Stimulating his left ear canal with a cotton swab triggers a bout of coughing. The physician informs him that these symptoms are caused by hypersensitivity of a cranial nerve. A peripheral lesion of this nerve is most likely to manifest with which of the following findings on physical examination?
- A. Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- B. Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue
- C. Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow
- D. Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland
- E. Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy (Correct Answer)
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy***
- The sensation in the external auditory canal that triggers a cough reflex is mediated by the **auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X)**, also known as Arnold's nerve.
- A peripheral lesion of the vagus nerve would most likely affect its motor functions, including the innervation of the **larynx**, leading to **ipsilateral vocal cord palsy** and hoarseness.
*Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss*
- Hearing loss is primarily associated with pathology of the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**, not the vagus nerve.
- The patient's presentation does not describe any auditory symptoms.
*Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue*
- Tongue deviation is a sign of compromise of the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which controls the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- This is not a function of the vagus nerve.
*Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow*
- The ability to raise the eyebrow is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which innervates the muscles of facial expression.
- Vagus nerve lesions do not typically present with facial weakness.
*Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland*
- Secretion from the sublingual gland is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)** via the submandibular ganglion.
- While the vagus nerve has autonomic functions, it does not directly control sublingual gland secretion.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 2: A 25-year-old woman presents to the physician with a complaint of several episodes of headaches in the past 4 weeks that are affecting her school performance. These episodes are getting progressively worse, and over-the-counter medications do not seem to help. She also mentions having to raise her head each time to look at the board while taking notes; she cannot simply glance up with just her eyes. She has no significant past medical or family history and was otherwise well prior to this visit. Physical examination shows an upward gaze palsy and convergence-retraction nystagmus. What structure is most likely to be affected in this patient?
- A. Aqueduct of Sylvius
- B. Inferior colliculi
- C. 3rd ventricle
- D. Tegmentum
- E. Corpora quadrigemina (Correct Answer)
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Corpora quadrigemina***
- The patient presents with classic **Parinaud syndrome** (dorsal midbrain syndrome), characterized by **upward gaze palsy** and **convergence-retraction nystagmus**.
- These specific oculomotor signs result from direct damage to the **superior colliculi** and **pretectal area**, which are anatomical components of the **corpora quadrigemina** in the tectal region of the midbrain.
- The superior colliculi control vertical gaze, and the pretectal area coordinates pupillary reflexes and convergence movements. Compression or infiltration of this region (commonly by pineal tumors) produces the characteristic eye movement abnormalities.
- Progressive headaches indicate increased intracranial pressure, often from associated **aqueduct obstruction** causing hydrocephalus, which in turn compresses the tectal structures.
*Aqueduct of Sylvius*
- While obstruction of the aqueduct of Sylvius commonly **causes** Parinaud syndrome by leading to hydrocephalus and mass effect, the aqueduct itself is a CSF pathway and does not directly produce the eye movement abnormalities.
- The question asks which structure is "**affected**" - the affected structure producing these specific symptoms is the tectal region (corpora quadrigemina), not the obstructed aqueduct.
- This is an important distinction: the aqueduct is obstructed, but the corpora quadrigemina is compressed/affected.
*Inferior colliculi*
- The inferior colliculi are part of the corpora quadrigemina but serve the **auditory pathway**, not visual or oculomotor functions.
- Isolated lesions here would cause hearing deficits, not upward gaze palsy or convergence-retraction nystagmus.
*3rd ventricle*
- Lesions obstructing the third ventricle can cause hydrocephalus and headaches but do not directly affect the midbrain tectum unless they extend posteriorly.
- Third ventricular masses more commonly produce **endocrine disturbances** (hypothalamic-pituitary axis dysfunction) rather than the specific dorsal midbrain syndrome seen here.
*Tegmentum*
- The tegmentum is the ventral portion of the midbrain containing the **red nucleus**, **substantia nigra**, and **cranial nerve nuclei (III, IV)**.
- Tegmental lesions produce different oculomotor deficits (e.g., internuclear ophthalmoplegia, third nerve palsy) and movement disorders, not the dorsal midbrain syndrome pattern of Parinaud.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 3: A neurology resident sees a stroke patient on the wards. This 57-year-old man presented to the emergency department after sudden paralysis of his right side. He was started on tissue plasminogen activator within 4 hours, as his wife noticed the symptoms and immediately called 911. When the resident asks the patient how he is doing, he replies by saying that his apartment is on Main St. He does not seem to appropriately answer the questions being asked, but rather speaks off topic. He is able to repeat the word "fan." His consciousness is intact, and his muscle tone and reflexes are normal. Upon striking the lateral part of his sole, his big toe extends upward and the other toes fan out. Which of the following is the area most likely affected in his condition?
- A. Caudate nucleus
- B. Broca’s area
- C. Arcuate fasciculus
- D. Temporal lobe (Correct Answer)
- E. Cuneus gyrus
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Temporal lobe***
- The patient exhibits features of **Wernicke's aphasia**, characterized by **fluent but nonsensical speech** ("apartment is on Main St." when asked how he is), poor comprehension, and the ability to repeat words. **Wernicke's area**, responsible for language comprehension, is located in the **posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus**.
- **Sudden paralysis of the right side** indicates involvement of the left cerebral hemisphere (**contralateral motor cortex** lesion), while speech disturbances point to the dominant hemisphere, which is typically the **left temporal lobe**.
*Caudate nucleus*
- Lesions of the **caudate nucleus** are primarily associated with **movement disorders** (e.g., chorea) and **behavioral changes**, not typically with fluent aphasia as described.
- While it plays a role in cognitive functions, its direct involvement in the specific language deficits presented is less likely.
*Broca’s area*
- Damage to **Broca's area**, located in the **frontal lobe**, causes **Broca's aphasia**, characterized by **non-fluent, halting speech** with good comprehension and poor repetition.
- The patient's speech is **fluent**, though off-topic, which contrasts with the typical presentation of Broca's aphasia.
*Arcuate fasciculus*
- The **arcuate fasciculus** connects Broca's and Wernicke's areas, and damage to it typically causes **conduction aphasia**, characterized by **impaired repetition** despite fluent speech and good comprehension.
- While the patient has impaired comprehension, his ability to repeat "fan" makes conduction aphasia less likely than Wernicke's aphasia, where repetition can vary but comprehension is profoundly affected.
*Cuneus gyrus*
- The **cuneus gyrus** is located in the **occipital lobe** and is primarily involved in **visual processing**.
- Damage to this area would lead to **visual field deficits** (e.g., hemianopia) rather than the language and comprehension problems described.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 4: A 72-year-old woman is brought in to the emergency department after her husband noticed that she appeared to be choking on her dinner. He performed a Heimlich maneuver but was concerned that she may have aspirated something. The patient reports a lack of pain and temperature on the right half of her face, as well as the same lack of sensation on the left side of her body. She also states that she has been feeling "unsteady" on her feet. On physical exam you note a slight ptosis on the right side. She is sent for an emergent head CT. Where is the most likely location of the neurological lesion?
- A. Pons
- B. Internal capsule
- C. Cervical spinal cord
- D. Medulla (Correct Answer)
- E. Midbrain
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Medulla***
- This presentation describes **Wallenberg syndrome** (lateral medullary syndrome), characterized by **ipsilateral facial sensory loss**, **contralateral body sensory loss**, and **ataxia** due to involvement of the spinothalamic tracts, trigeminal nucleus, and cerebellar pathways.
- **Dysphagia** (choking) and **Horner's syndrome** (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis) are also classic signs, specifically the ptosis seen here, pointing to an infarct in the **lateral medulla**.
*Pons*
- Lesions in the pons typically present with varying degrees of **cranial nerve deficits** (e.g., trigeminal, abducens, facial) and **motor or sensory deficits** affecting both sides of the body due to the decussation of tracts.
- The specific combination of **crossed sensory loss** and other symptoms seen here is not characteristic of isolated pontine lesions.
*Internal capsule*
- A lesion in the internal capsule would primarily cause **contralateral motor weakness (hemiparesis)** and **sensory loss** affecting both the face and body on the same side, without the ipsilateral facial involvement.
- It would not explain the **ataxia** or specific cranial nerve signs like ptosis.
*Cervical spinal cord*
- Spinal cord lesions result in **sensory and motor deficits below the level of the lesion**, affecting both sides of the body symmetrically, or ipsilaterally depending on the tract involved.
- They do not cause **facial sensory disturbances**, **dysphagia**, or **ataxia** in the manner described.
*Midbrain*
- Midbrain lesions typically involve the **oculomotor nerve** (CN III), causing eye movement abnormalities, and can result in **contralateral hemiparesis**.
- They do not produce the **crossed sensory deficits** (ipsilateral face, contralateral body) or **ataxia** characteristic of this case.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 5: A 47-year-old man presents to you with gradual loss of voice and difficulty swallowing for the past couple of months. The difficulty of swallowing is for both solid and liquid foods. His past medical history is insignificant except for occasional mild headaches. Physical exam also reveals loss of taste sensation on the posterior third of his tongue and palate, weakness in shrugging his shoulders, an absent gag reflex, and deviation of the uvula away from the midline. MRI scanning was suggested which revealed a meningioma that was compressing some cranial nerves leaving the skull. Which of the following openings in the skull transmit the affected cranial nerves?
- A. Jugular foramen (Correct Answer)
- B. Foramen rotundum
- C. Foramen spinosum
- D. Foramen ovale
- E. Foramen lacerum
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Jugular foramen***
- The symptoms described—loss of voice, difficulty swallowing, loss of taste on the posterior third of the tongue, absent gag reflex, and uvula deviation—point to impairment of **cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory)**, which all exit the skull via the **jugular foramen**.
- The **vagus nerve** (CN X) is responsible for voice and swallowing (via innervation of the pharynx and larynx), the **glossopharyngeal nerve** (CN IX) for taste from the posterior third of the tongue and the gag reflex, and the **accessory nerve** (CN XI) for shoulder shrugging (trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles).
- Note: Loss of taste on the palate may involve CN VII (facial nerve) fibers, but the dominant clinical picture with absent gag reflex, uvula deviation, dysphagia, and dysphonia clearly indicates jugular foramen pathology.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Damage to V2 would primarily cause sensory deficits in the midface and upper teeth, which are not described in this patient.
*Foramen spinosum*
- The **foramen spinosum** transmits the **middle meningeal artery** and the **meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (V3)**.
- Injury here would not explain the constellation of symptoms related to voice, swallowing, taste, or shoulder movement.
*Foramen ovale*
- The **foramen ovale** transmits the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, the **accessory meningeal artery**, and occasionally the superficial petrosal nerve.
- Damage to V3 would result in sensory loss to the lower face and motor deficits in the muscles of mastication, which are not reported.
*Foramen lacerum*
- The **foramen lacerum** is filled with cartilage in vivo and does not typically transmit major neurovascular structures directly through its aperture.
- The **internal carotid artery** passes superior to it, and some small nerves may traverse its vicinity, but not the specific cranial nerves indicated by the patient's symptoms.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 6: A 56-year-old man with a significant past medical history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia is brought to the emergency department by his wife. The wife states the symptoms started 1 hour ago when she noticed that he was having difficulty swallowing his breakfast and that his voice was hoarse. The patient had a recent admission for a transient ischemic attack but was not compliant with his discharge instructions and medication. Examination of the eye shows left-sided partial ptosis and miosis along with diplopia and nystagmus. During the examination, it is noted that the right side of the face and body has markedly more sweating than the left side. An MRI of the brain reveals an ischemic infarct at the level of the left lateral medulla. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Postganglionic sympathetic lesion
- B. Injury to the cervical sympathetic ganglia
- C. 3rd-order neuron lesion
- D. Denervation of the descending sympathetic tract (Correct Answer)
- E. Preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Denervation of the descending sympathetic tract***
- The patient's symptoms, including **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **facial anhidrosis** on the left, **miosis**, **ptosis**, **diplopia**, and **nystagmus**, are classic for **Wallenberg syndrome** (lateral medullary syndrome).
- This syndrome is caused by an infarct in the **lateral medulla**, which damages the **descending sympathetic tracts (1st-order neurons)**, leading to **Horner's syndrome** (miosis, ptosis, anhidrosis) on the ipsilateral side and contralateral hyperhidrosis due to lack of sympathetic tone to the affected side, along with other neurological deficits due to involvement of vital brainstem nuclei.
*Postganglionic sympathetic lesion*
- A postganglionic lesion (also called a **3rd-order neuron lesion**) would typically affect structures supplied by the superior cervical ganglion, such as the eye and face.
- However, it would not explain the other brainstem symptoms like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **diplopia**, or **nystagmus**, which point to a central lesion in the medulla.
*Injury to the cervical sympathetic ganglia*
- An injury here would cause **Horner's syndrome** affecting the eye and face on the ipsilateral side.
- It would not account for the brainstem deficits like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, or **nystagmus**, nor the specific finding of an **ischemic infarct in the lateral medulla**.
*3rd-order neuron lesion*
- A 3rd-order neuron lesion is synonymous with a **postganglionic sympathetic lesion** and would cause **Horner's syndrome**.
- This would not explain the additional cranial nerve and brainstem signs found in this patient, which are characteristic of a **lateral medullary infarct** affecting central (1st-order) sympathetic pathways.
*Preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn*
- A preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn (T1-T2 spinal cord, **2nd-order neurons**) would cause **Horner's syndrome**.
- However, it would not explain the upper brainstem symptoms like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **diplopia**, or **nystagmus**, which result from damage to cranial nerve nuclei and tracts within the medulla, not the spinal cord.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife after falling down. About 90 minutes ago, they were standing in their kitchen making lunch and chatting when he suddenly complained that he could not see as well, felt weak, and was getting dizzy. He began to lean to 1 side, and he eventually fell to the ground. He did not hit his head. In the emergency department, he is swaying while seated, generally leaning to the right. The general physical exam is unremarkable. The neurologic exam is notable for horizontal nystagmus, 3/5 strength in the right arm, ataxia of the right arm, and absent pinprick sensation in the left arm and left leg. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely single location of this patient's central nervous system lesion?
- A. Primary motor cortex
- B. Thalamus
- C. Lateral medulla (Correct Answer)
- D. Primary somatosensory cortex
- E. Anterior spinal cord
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Lateral medulla***
- The combination of **ipsilateral ataxia** and **weakness** (right arm) along with **contralateral pain and temperature sensory loss** (left arm and leg) is classic for a **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**.
- **Horizontal nystagmus**, vertigo, and leaning to one side are also consistent with involvement of vestibular nuclei and cerebellar pathways in the lateral medulla.
*Primary motor cortex*
- A lesion here would cause **contralateral weakness or paralysis** but would not explain the ipsilateral ataxia, nystagmus, or contralateral pain and temperature loss.
- Sensory deficits would be minimal or absent, and would primarily affect discriminative touch.
*Thalamus*
- A thalamic lesion could cause **contralateral sensory loss** (affecting all modalities) and potentially some motor deficits or ataxia, but it typically does not cause **ipsilateral ataxia** or **nystagmus** in the pattern described.
- The specific combination of ipsilateral motor and contralateral sensory deficits points away from a pure thalamic lesion.
*Primary somatosensory cortex*
- A lesion in this area would primarily result in **contralateral deficits in discriminative touch, proprioception, and stereognosis**, not pain and temperature sensation.
- It would not explain the motor deficits, ataxia, or nystagmus seen in the patient.
*Anterior spinal cord*
- Damage to the anterior spinal cord (e.g., **anterior spinal artery syndrome**) would cause **bilateral motor weakness (paraplegia/quadriplegia)** and **bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** below the level of the lesion.
- It would not account for the nystagmus, vertigo, or the specific combination of ipsilateral and contralateral deficits observed in this patient, which are characteristic of brainstem involvement.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 9: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG Question 10: A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He does not open his eyes on command or respond to verbal cues. A CT scan of the head shows a hyperdense fluid collection in the right medial temporal lobe with medial displacement of the uncus and parahippocampal gyrus of the temporal lobe. Which of the following cranial nerves is most likely to be injured as a result of this patient's lesion?
- A. Vagus
- B. Facial
- C. Oculomotor (Correct Answer)
- D. Abducens
- E. Trigeminal
Medulla oblongata nuclei Explanation: ***Oculomotor***
- The description of **medial displacement of the uncus and parahippocampal gyrus** (uncus herniation) compresses the **oculomotor nerve (CN III)** as it passes between the posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries.
- Compression of the oculomotor nerve leads to a **dilated pupil** (due to parasympathetic fiber involvement) and **down-and-out deviation of the eye** (due to paralysis of extraocular muscles it innervates).
*Vagus*
- The vagus nerve (CN X) is deep within the skull and brainstem, far from the temporal lobe, and is not directly affected by uncal herniation.
- Injury to the vagus nerve typically presents with dysphagia, hoarseness, or cardiac arrhythmias, symptoms not indicated here.
*Facial*
- The facial nerve (CN VII) exits the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction and is located more superiorly and laterally than the structures involved in uncal herniation.
- Damage to the facial nerve causes facial muscle weakness or paralysis, which is not the primary concern with uncal herniation.
*Abducens*
- The abducens nerve (CN VI) is a long, slender nerve that can be affected by **generalized increases in intracranial pressure**, but is less commonly directly compressed by an uncal herniation itself.
- Injury to the abducens nerve causes **lateral rectus muscle paralysis**, leading to medial deviation of the eye, whereas uncal herniation typically affects the oculomotor nerve.
*Trigeminal*
- The trigeminal nerve (CN V) exits the pons and is located superior to the tentorial notch and medial temporal lobe, making it unlikely to be directly compressed by uncal herniation.
- Injury to the trigeminal nerve causes sensory loss in the face or weakness of the muscles of mastication, which are not consistent with the described lesion.
More Medulla oblongata nuclei US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.