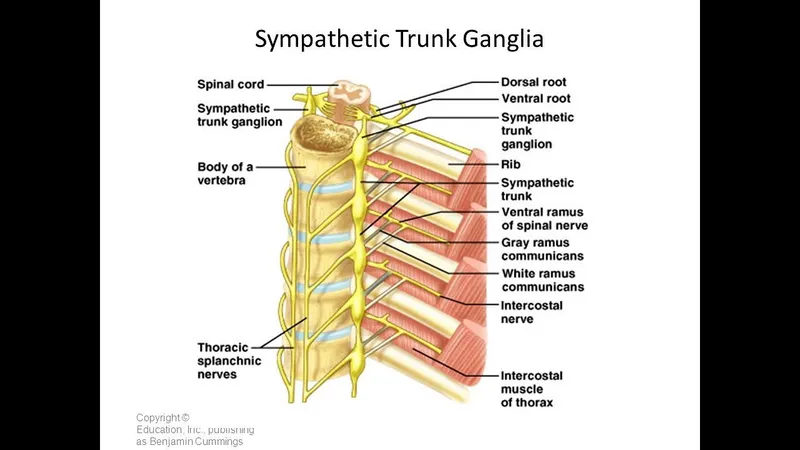
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sympathetic ganglia and rami. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 1: A 68-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of a bulge in his scrotum that has enlarged over the past several months. He is found to have a right-sided inguinal hernia and undergoes elective hernia repair. At his first follow-up visit, he complains of a tingling sensation on his scrotum. Which of the following nerve roots communicates with the injured tissues?
- A. S1-S3
- B. L1-L2 (Correct Answer)
- C. S2-S4
- D. L4-L5
- E. L2-L3
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***L1-L2***
- The **ilioinguinal nerve** and **genitofemoral nerve**, which are commonly injured during inguinal hernia repair, arise from the **L1 and L2 spinal nerves**.
- These nerves provide sensory innervation to the **scrotum**, **inguinal region**, and **medial thigh**, explaining the patient's tingling sensation.
*S1-S3*
- These nerve roots typically contribute to the **sciatic nerve** and innervate the posterior thigh, leg, and foot, and are not directly involved in scrotal sensation relevant to an inguinal hernia repair.
- They also contribute to the **pudendal nerve**, which primarily supplies the perineum and external genitalia, but injury to this nerve is less common in routine inguinal hernia repair.
*S2-S4*
- These nerve roots primarily form the **pudendal nerve**, which innervates the **perineum** and external genitalia (including some scrotal sensation), but injury to these specific nerves is not a typical complication of routine inguinal hernia repair.
- They also contribute to the **pelvic splanchnic nerves**, controlling bladder and bowel function, which are unrelated to the described sensory deficit.
*L4-L5*
- These nerve roots primarily contribute to nerves supplying the **lower limb**, such as the **femoral nerve** and **sciatic nerve**, and do not directly innervate the scrotum.
- Injury to these roots would typically result in motor or sensory deficits of the **thigh and leg**, not isolated scrotal tingling.
*L2-L3*
- While L2 contributes to nerves supplying the inguinal region and scrotum (genitofemoral nerve), the **ilioinguinal nerve** originates from L1.
- The **lateral femoral cutaneous nerve**, which originates from L2-L3, innervates the **lateral thigh**, and its injury would cause tingling there, not in the scrotum.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 2: A 74-year-old gentleman presents to his family practitioner with the complaint of an inability to open his left eye since this morning. He also complains of intermittent pain and numbness in his left arm that has been present for the last few days. He denies ocular pain, difficulty swallowing, fatigability, or diplopia. His symptoms remain constant without fluctuation. He has a history of diabetes mellitus type 2, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Further history reveals that he has lost 5.4 kg (12 lb) of weight in the past 4 months. He is a chronic smoker with a 72 pack-year smoking history. His blood pressure is 142/76 mm Hg, the heart rate is 76/min, the respiratory rate is 12/min, the temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F), and BMI is the 18.2 kg/m2. The patient is awake, alert, and oriented to person, place, and time. He has partial drooping of the left eyelid while the right eyelid appears normal. The left pupil is 1 mm and the right pupil is 3 mm in diameter. Extraocular muscle movements are normal. What additional clinical feature would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Facial asymmetry
- B. Urinary retention
- C. Ipsilateral loss of touch sensations on the face
- D. Tongue deviation to the left side
- E. Loss of hemifacial sweating (Correct Answer)
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Loss of hemifacial sweating***
- The patient's presentation with **ptosis**, **miosis**, and an absence of other cranial nerve deficits strongly suggests **Horner's syndrome**. This syndrome is characterized by the classic triad of **ptosis**, **miosis**, and **anhidrosis** (loss of sweating).
- The history of **weight loss**, **smoking**, and intermittent left arm pain and numbness raises concern for a **Pancoast tumor** in the lung apex, which can compress the sympathetic chain and cause Horner's syndrome.
*Facial asymmetry*
- **Facial asymmetry** typically results from lesions affecting the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), such as in Bell's palsy or stroke.
- While ptosis can cause some asymmetry in eye appearance, it does not typically lead to generalized facial asymmetry in the way a CN VII lesion would, as other facial muscles are unaffected.
*Urinary retention*
- **Urinary retention** is not a typical symptom of Horner's syndrome, which primarily affects the sympathetic innervation to the eye and face.
- It could be associated with conditions affecting the bladder's innervation, such as spinal cord lesions or prostate enlargement, which are not directly indicated here.
*Ipsilateral loss of touch sensations on the face*
- **Loss of touch sensations on the face** would indicate involvement of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) or its sensory pathways.
- Horner's syndrome specifically affects the sympathetic nervous system and does not directly cause sensory deficits on the face.
*Tongue deviation to the left side*
- **Tongue deviation** to one side is a sign of hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII) palsy, which would affect the ipsilateral tongue muscles.
- This symptom is unrelated to Horner's syndrome, which involves oculosympathetic pathways.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 3: A 56-year-old man with a significant past medical history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia is brought to the emergency department by his wife. The wife states the symptoms started 1 hour ago when she noticed that he was having difficulty swallowing his breakfast and that his voice was hoarse. The patient had a recent admission for a transient ischemic attack but was not compliant with his discharge instructions and medication. Examination of the eye shows left-sided partial ptosis and miosis along with diplopia and nystagmus. During the examination, it is noted that the right side of the face and body has markedly more sweating than the left side. An MRI of the brain reveals an ischemic infarct at the level of the left lateral medulla. Which of the following most likely accounts for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Postganglionic sympathetic lesion
- B. Injury to the cervical sympathetic ganglia
- C. 3rd-order neuron lesion
- D. Denervation of the descending sympathetic tract (Correct Answer)
- E. Preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Denervation of the descending sympathetic tract***
- The patient's symptoms, including **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **facial anhidrosis** on the left, **miosis**, **ptosis**, **diplopia**, and **nystagmus**, are classic for **Wallenberg syndrome** (lateral medullary syndrome).
- This syndrome is caused by an infarct in the **lateral medulla**, which damages the **descending sympathetic tracts (1st-order neurons)**, leading to **Horner's syndrome** (miosis, ptosis, anhidrosis) on the ipsilateral side and contralateral hyperhidrosis due to lack of sympathetic tone to the affected side, along with other neurological deficits due to involvement of vital brainstem nuclei.
*Postganglionic sympathetic lesion*
- A postganglionic lesion (also called a **3rd-order neuron lesion**) would typically affect structures supplied by the superior cervical ganglion, such as the eye and face.
- However, it would not explain the other brainstem symptoms like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **diplopia**, or **nystagmus**, which point to a central lesion in the medulla.
*Injury to the cervical sympathetic ganglia*
- An injury here would cause **Horner's syndrome** affecting the eye and face on the ipsilateral side.
- It would not account for the brainstem deficits like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, or **nystagmus**, nor the specific finding of an **ischemic infarct in the lateral medulla**.
*3rd-order neuron lesion*
- A 3rd-order neuron lesion is synonymous with a **postganglionic sympathetic lesion** and would cause **Horner's syndrome**.
- This would not explain the additional cranial nerve and brainstem signs found in this patient, which are characteristic of a **lateral medullary infarct** affecting central (1st-order) sympathetic pathways.
*Preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn*
- A preganglionic lesion at the lateral gray horn (T1-T2 spinal cord, **2nd-order neurons**) would cause **Horner's syndrome**.
- However, it would not explain the upper brainstem symptoms like **dysphagia**, **hoarseness**, **diplopia**, or **nystagmus**, which result from damage to cranial nerve nuclei and tracts within the medulla, not the spinal cord.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 4: A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of involuntary leakage of urine for the past 4 months, which she has experienced when bicycling to work and when laughing. She has not had any dysuria or urinary urgency. She has 4 children that were all delivered vaginally. She is otherwise healthy and takes no medications. The muscles most likely affected by this patient's condition receive efferent innervation from which of the following structures?
- A. S3–S4 nerve roots (Correct Answer)
- B. Obturator nerve
- C. Superior hypogastric plexus
- D. Superior gluteal nerve
- E. S1-S2 nerve roots
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***S3–S4 nerve roots***
- The patient's symptoms of **involuntary urine leakage** during physical activity (**stress incontinence**) and a history of multiple vaginal deliveries strongly suggest **pelvic floor muscle weakness**.
- The **levator ani muscles**, which are crucial for maintaining urinary continence, receive their primary innervation from the **pudendal nerve**, which originates from the **S2-S4 spinal nerves** (though contributions from S3-S4 are often highlighted for pelvic floor efferent innervation).
*Obturator nerve*
- The **obturator nerve** primarily innervates the **adductor muscles of the thigh** (e.g., adductor longus, magnus, brevis, gracilis), as well as the obturator externus muscle.
- It does not significantly contribute to the innervation of the **pelvic floor muscles** responsible for urinary continence.
*Superior hypogastric plexus*
- The **superior hypogastric plexus** is part of the **autonomic nervous system** and primarily carries **sympathetic innervation** to the pelvic organs.
- While it plays a role in bladder function (e.g., bladder relaxation and internal urethral sphincter contraction), it does not provide **somatic efferent innervation** to the skeletal muscles of the pelvic floor.
*Superior gluteal nerve*
- The **superior gluteal nerve** innervates the **gluteus medius**, **gluteus minimus**, and **tensor fasciae latae muscles**.
- These muscles are involved in **hip abduction** and **medial rotation** and are not directly involved in maintaining urinary continence through the pelvic floor.
*S1-S2 nerve roots*
- While the **S1-S2 nerve roots** contribute to the innervation of various lower limb muscles and sensory pathways, their primary efferent contributions related to pelvic floor continence are not as direct as S3-S4.
- The **pudendal nerve**, critical for pelvic floor muscle function, originates predominantly from **S2-S4**, with S3-S4 being particularly important for the motor components.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 5: During a physical examination, a physician tests the strength of hip adduction against resistance. Which of the following nerves innervates the primary muscles responsible for this action?
- A. Sciatic nerve
- B. Superior gluteal nerve
- C. Femoral nerve
- D. Obturator nerve (Correct Answer)
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Obturator nerve***
- The **obturator nerve** primarily innervates the **adductor muscles** of the thigh, including the adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus (adductor part), gracilis, and pectineus (variable innervation).
- These muscles are responsible for **adducting the hip**, which is the action tested when a physician checks hip adduction strength against resistance.
*Sciatic nerve*
- The **sciatic nerve** innervates the **hamstring muscles** (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris) and all muscles below the knee.
- It does not significantly contribute to the innervation of the primary hip adductors.
*Superior gluteal nerve*
- The **superior gluteal nerve** mainly innervates the **gluteus medius**, **gluteus minimus**, and **tensor fasciae latae** muscles.
- These muscles are primarily involved in **hip abduction** and medial rotation, not adduction.
*Femoral nerve*
- The **femoral nerve** innervates the **quadriceps femoris muscles** (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius) and the sartorius.
- Its primary actions are **knee extension** and hip flexion, with no direct role in hip adduction.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 6: A 26-year-old woman presents to the obstetrics ward to deliver her baby. The obstetrician establishes a pudendal nerve block via intravaginal injection of lidocaine near the tip of the ischial spine. From which of the following nerve roots does the pudendal nerve originate?
- A. L4-L5
- B. S2-S4 (Correct Answer)
- C. L3-L4
- D. L5-S2
- E. L5-S1
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***S2-S4***
- The **pudendal nerve** originates from the **sacral plexus**, specifically from the ventral rami of spinal nerves **S2, S3, and S4**.
- Its origin from these segments is crucial for its function in innervating structures of the **perineum**, **external genitalia**, and the **anal and urethral sphincters**, making it highly relevant for procedures like **pudendal nerve blocks** during childbirth.
*L4-L5*
- Nerve roots **L4-L5** contribute significantly to the **lumbar plexus** and subsequently to nerves like the **femoral nerve** and portions of the **sciatic nerve**.
- These roots are primarily involved in innervating the **lower limbs** (e.g., quadriceps, tibialis anterior) and are not the primary origin of the pudendal nerve.
*L3-L4*
- The **L3-L4** nerve roots are also part of the **lumbar plexus**, chiefly contributing to the **femoral nerve**.
- They are essential for motor innervation of the **anterior thigh muscles** and sensation in this area, distinct from the pudendal nerve's role in the perineum.
*L5-S2*
- While **S2** is part of the pudendal nerve's origin, the inclusion of **L5** and **S1** primarily characterizes the origin of the **sciatic nerve** (which is formed by L4-S3) and its branches, such as the common fibular and tibial nerves.
- These roots are primarily concerned with the **posterior thigh** and **leg innervation**, not the perineum, which differentiates it from the pudendal nerve.
*L5-S1*
- The nerve roots **L5-S1** are key components of the **lumbosacral plexus** and contribute significantly to the **sciatic nerve**, particularly its innervation of the **hamstrings** and certain lower leg muscles.
- This origin does not align with the known roots of the **pudendal nerve** which stems from S2-S4.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 7: A 48-year-old man with retroperitoneal sarcoma requires extensive resection including portions of the sympathetic chain from T10-L2 and the celiac/superior mesenteric ganglia. Preoperative evaluation is needed to predict postoperative autonomic consequences. The multidisciplinary team must evaluate which combination of deficits is most likely based on the precise anatomical structures being resected and the potential for compensation.
- A. Pan-sympathetic failure including cardiovascular collapse due to loss of all preganglionic outflow
- B. Minimal deficits due to complete bilateral compensation from contralateral sympathetic chain
- C. Complete loss of lower extremity sweating and thermoregulation with normal GI and genitourinary function due to enteric nervous system compensation
- D. Severe orthostatic hypotension, GI dysmotility, and ejaculatory dysfunction with preserved upper body sympathetic function (Correct Answer)
- E. Isolated loss of visceral pain sensation with completely preserved motor and secretory autonomic functions
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Severe orthostatic hypotension, GI dysmotility, and ejaculatory dysfunction with preserved upper body sympathetic function***
- Resection of the **celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia** and the **sympathetic chain (T10-L2)** drastically reduces total peripheral resistance and venous return regulation, leading to **severe orthostatic hypotension**.
- Disrupting the **lumbar sympathetic chain (L1-L2)** interrupts the pathways for **emission**, while ganglionic resection causes **GI dysmotility** via loss of inhibitory sympathetic input.
*Complete loss of lower extremity sweating and thermoregulation with normal GI and genitourinary function due to enteric nervous system compensation*
- While **anhidrosis** occurs, the **enteric nervous system** cannot fully compensate for the loss of extrinsic sympathetic modulation, leading to significant GI dysfunction.
- Genitourinary function is significantly impacted as the **sympathetic input** required for the contraction of the internal urethral sphincter and seminal vesicles is removed.
*Isolated loss of visceral pain sensation with completely preserved motor and secretory autonomic functions*
- Although **visceral afferents** are interrupted, the resection of **preganglionic and postganglionic motor fibers** guarantees motor and secretory deficits.
- Sympathetic fibers are essential for the **vasoconstriction** and inhibitory signaling to the gut, which cannot remain "completely preserved" after such extensive resection.
*Pan-sympathetic failure including cardiovascular collapse due to loss of all preganglionic outflow*
- **Pan-sympathetic failure** is avoided because segments above **T10** (supplying the head, neck, and upper extremities) and the **adrenal medulla** (if T10-L2 is the primary resection) provide partial function.
- Cardiovascular collapse is unlikely because the **cardiac sympathetic nerves (T1-T4)** remain intact, maintaining heart rate and contractility.
*Minimal deficits due to complete bilateral compensation from contralateral sympathetic chain*
- Sympathetic innervation of the viscera is **bilateral**, but the **celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia** are midline structures; their resection leaves no contralateral alternative.
- Extensive **bilateral resection** of the chain segments at this level ensures profound deficits that cannot be compensated for by remaining neural pathways.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 8: A 62-year-old man with atrial fibrillation undergoes catheter ablation of the pulmonary vein ostia. Post-procedure, he develops gastroparesis, but his cardiologist notes preserved heart rate variability and normal baroreceptor responses. Surgical anatomy review suggests the ablation may have damaged autonomic structures. Evaluate the most likely anatomical explanation for isolated gastric dysmotility with preserved cardiovascular autonomic function.
- A. Injury to the celiac ganglion via retrograde thermal conduction
- B. Direct damage to the enteric nervous system myenteric plexus
- C. Thermal injury to epicardial vagal branches specifically innervating the stomach via the gastric plexus (Correct Answer)
- D. Damage to the stellate ganglion causing isolated sympathetic denervation of the stomach
- E. Disruption of the entire vagal trunk causing pan-autonomic dysfunction
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Thermal injury to epicardial vagal branches specifically innervating the stomach via the gastric plexus***
- The **vagus nerves** descend behind the heart and form the **esophageal plexus** near the **posterior wall of the left atrium**, making them vulnerable to energy during **pulmonary vein ablation**.
- Damage at this level can disrupt parasympathetic supply to the stomach, causing **gastroparesis**, while sparing the cardiac branches that already branched off superiorly, thereby preserving **heart rate variability**.
*Damage to the stellate ganglion causing isolated sympathetic denervation of the stomach*
- The **stellate ganglion** is located at the **C7-T1** level and supplies sympathetic fibers to the head, neck, and upper limbs; it is anatomically distant from the left atrium ablation site.
- Injury to this ganglion would present with **Horner Syndrome**, not isolated gastric dysmotility.
*Disruption of the entire vagal trunk causing pan-autonomic dysfunction*
- Complete **vagal trunk** damage would result in systemic symptoms, including significant changes in **heart rate variability** and loss of **baroreceptor reflex** sensitivity.
- The preservation of cardiovascular autonomic function indicates that the injury was localized and **distal to the cardiac branches**.
*Injury to the celiac ganglion via retrograde thermal conduction*
- The **celiac ganglion** is located in the **upper abdomen** around the root of the celiac trunk, making it an unlikely target for direct or retrograde thermal injury from the heart.
- This ganglion primarily handles **sympathetic output**; its injury would not typically cause the delayed gastric emptying characteristic of **vagal (parasympathetic) denervation**.
*Direct damage to the enteric nervous system myenteric plexus*
- The **myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus** is located within the muscular layers of the **stomach wall**.
- Catheter ablation occurs in the **thoracic cavity** at the pulmonary veins; it cannot directly reach or damage the intrinsic nerves located within the abdominal viscus.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 9: A 35-year-old woman with familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome) presents with absent corneal reflexes, impaired lacrimation, and absent fungiform papillae on the tongue, but preserved parotid gland function. Genetic testing confirms IKBKAP gene mutation affecting neural crest cell migration. Evaluate which embryological principle explains this specific pattern of autonomic and sensory deficits while certain parasympathetic functions remain intact.
- A. Preferential loss of sympathetic neurons with compensatory parasympathetic hyperfunction
- B. Uniform degeneration of both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems proportionally
- C. Selective degeneration of all parasympathetic ganglia with preserved sympathetic function
- D. Failed migration of neural crest cells destined for cranial sensory and parasympathetic ganglia, with preserved placode-derived neurons (Correct Answer)
- E. Isolated defect in myelination of all autonomic preganglionic fibers
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Failed migration of neural crest cells destined for cranial sensory and parasympathetic ganglia, with preserved placode-derived neurons***
- **Riley-Day syndrome** (IKBKAP mutation) results in the failed development of **neural crest-derived** structures, specifically sensory and autonomic neurons, which explains the **absent corneal reflex** and **fungiform papillae**.
- Certain craniofacial neurons and glandular functions may be spared if they arise from **ectodermal placodes** rather than the neural crest, explaining the complex pattern of deficits.
*Selective degeneration of all parasympathetic ganglia with preserved sympathetic function*
- This syndrome actually involves significant **sympathetic denervation**, leading to signs like postural hypotension and **instability of blood pressure**.
- The deficits are not limited to the parasympathetic system; they involve a widespread loss of **small-fiber sensory** and sympathetic neurons.
*Isolated defect in myelination of all autonomic preganglionic fibers*
- The primary pathology in familial dysautonomia is **neuronal cell death** and failed migration, not primarily a **demyelinating** process.
- Prefibrillar or preganglionic fiber loss occurs, but the most characteristic finding is the **reduced number** of neurons in the **dorsal root** and autonomic ganglia.
*Preferential loss of sympathetic neurons with compensatory parasympathetic hyperfunction*
- While sympathetic loss is prominent, there is no **parasympathetic hyperfunction**; instead, there is impaired **lacrimation** and other parasympathetic deficits.
- Defective **sweating** and gastrointestinal dysmotility reflect a combined failure of both autonomic limbs rather than a compensatory mechanism.
*Uniform degeneration of both sympathetic and parasympathetic systems proportionally*
- The degeneration is not uniform; different populations of **neural crest-derived cells** show varying levels of sensitivity to the **IKBKAP protein** deficiency.
- Features like the **preservation of parotid gland function** (CN IX innervation) highlight that specific autonomic pathways are more resilient than others like the lacrimal pathway.
Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG Question 10: A 50-year-old man undergoes bilateral truncal vagotomy for refractory peptic ulcer disease. Postoperatively, he develops gastroparesis, but surprisingly maintains normal pancreatic enzyme secretion and normal bile flow during meals. Analysis of his preserved functions suggests alternate autonomic pathways are compensating. Which anatomical principle best explains the preservation of these exocrine functions despite vagotomy?
- A. The pancreas and biliary system receive redundant parasympathetic innervation from pelvic splanchnic nerves
- B. Sympathetic innervation alone is sufficient to maintain basal pancreatic and biliary secretion
- C. Enteric nervous system provides autonomous control independent of vagal input
- D. Parasympathetic innervation to pancreas and gallbladder travels via splanchnic nerves below the vagotomy level
- E. Hormonal regulation via secretin and CCK can maintain function independent of neural control (Correct Answer)
Sympathetic ganglia and rami Explanation: ***Hormonal regulation via secretin and CCK can maintain function independent of neural control***
- The intestinal phase of digestion is primarily mediated by **Secretin** and **Cholecystokinin (CCK)**, which stimulate pancreatic secretion and gallbladder contraction regardless of vagal status.
- These hormonal pathways act as a safeguard, ensuring that **pancreatic enzymes** and **bile flow** continue to meet digestive demands even after a **truncal vagotomy**.
*The pancreas and biliary system receive redundant parasympathetic innervation from pelvic splanchnic nerves*
- **Pelvic splanchnic nerves** (S2-S4) provide parasympathetic innervation only to the **hindgut** (distal third of the transverse colon to the rectum).
- They do not extend superiorly enough to provide autonomic control to the **pancreas** or **biliary system**, which are derivatives of the foregut.
*Sympathetic innervation alone is sufficient to maintain basal pancreatic and biliary secretion*
- **Sympathetic fibers** originating from the **celiac ganglion** generally inhibit gastrointestinal secretions and promote vasoconstriction.
- They cannot substitute for the excitatory **pro-secretory** effects of the parasympathetic system (vagus nerve).
*Enteric nervous system provides autonomous control independent of vagal input*
- While the **enteric nervous system (ENS)** can coordinate local peristalsis and mucosal secretion, it lacks the broad integrative capacity to fully stimulate large-scale **exocrine glands** like the pancreas without extrinsic input.
- The ENS works in tandem with the vagus, but it cannot completely replicate the **vago-vagal reflex** necessary for the cephalic and gastric phases of secretion.
*Parasympathetic innervation to pancreas and gallbladder travels via splanchnic nerves below the vagotomy level*
- **Splanchnic nerves** typically refer to the **greater, lesser, and least splanchnic nerves**, which carry **sympathetic** preganglionic fibers, not parasympathetic ones.
- There are no known significant anatomical pathways where **parasympathetic fibers** bypass the truncal vagus to reach the hepatobiliary tree via inferior spinal levels.
More Sympathetic ganglia and rami US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.